A kind of inorganic cementitious material resistant to water and sulfate erosion and preparation method thereof
An inorganic gelling material and gelling material technology, applied in the field of building materials, can solve problems such as poor product performance, high fly ash quality requirements, and less fly ash consumption, so as to improve gelling properties and increase production efficiency and equipment efficiency, the effect of increasing content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] The batch contains the following ingredients in parts by mass:
[0026] 80 parts of fly ash
[0027] Quicklime calculated as CaO 20 parts
[0028] Sodium hydroxide 0.5 parts
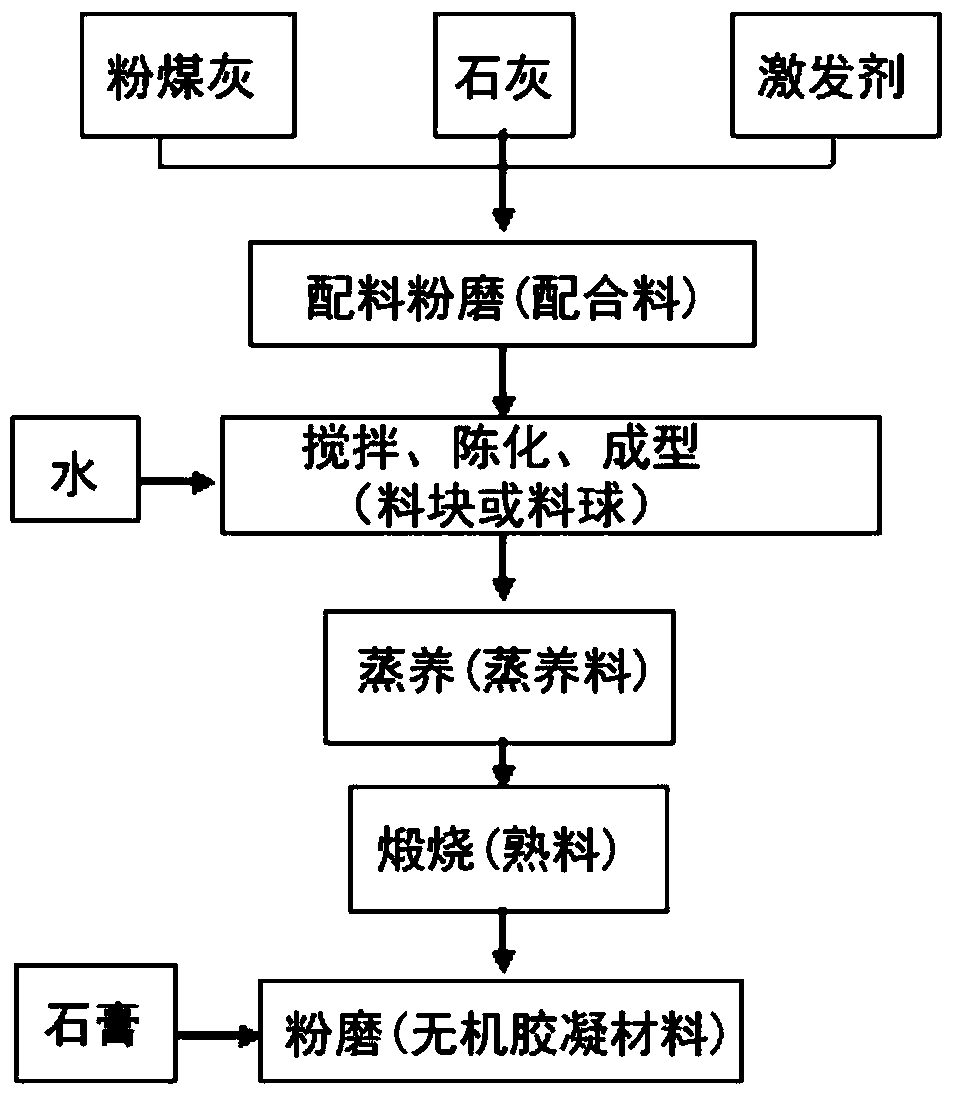
[0029] Weigh fly ash, quicklime, and sodium hydroxide according to the above mass ratio, and grind them together until the fineness is 45 μm and the sieve residue is 5.2% of the batching material; pour the batching material into the mixer, add 45 parts of water, stir for 3 minutes, and age After melting for 2 hours, use a ball forming disc to form pellets with a diameter of 8 to 16 mm; steam the pellets in a steam curing box at 90°C for 10 hours to obtain steamed feed, calcinate the steamed feed in a small kiln at 750°C for 120 minutes, and then blow it to cool. Clinker: take 90 parts of clinker and 10 parts of anhydrous gypsum to grind together until the specific surface area is 350m 2 / kg to prepare an inorganic gelling material.
Embodiment 2
[0031] The batch contains the following ingredients in parts by mass:
[0032] 75 parts of fly ash
[0033] Quicklime calculated as CaO 25 parts
[0034] Sodium carbonate 1.4 parts
[0035] Weigh fly ash, quicklime, and sodium carbonate according to the above mass ratio, and grind them together until the fineness is 45 μm and the sieve residue is 9.8%; pour the batch into a mixer, add 48 parts of water, stir for 3 minutes, and age After 3 hours, extrude into a material block of 240mm×115mm×53mm, steam the material block in a steam curing box at 90°C for 16 hours to obtain the steamed nutrient, calcinate the steamed nutrient in a small kiln at 750°C for 90 minutes, and then cool it naturally in the air to get cooked material; use a crusher to crush the clinker into particles smaller than 16mm, take 93 parts of clinker and 7 parts of hemihydrate gypsum to grind together until the specific surface area is 425m 2 / kg to prepare an inorganic gelling material.
Embodiment 3
[0037] The batch contains the following ingredients in parts by mass:
[0038] 70 parts of fly ash
[0039] Quicklime calculated as CaO 30 parts
[0040] Sodium hydroxide 1.0 parts
[0041] Weigh fly ash, quicklime, and sodium hydroxide according to the above mass ratio, and grind them together until the fineness is 45 μm and the sieve residue is 5.8% of the batching material; pour the batching material into the mixer, add 50 parts of water, stir for 2 minutes, and age After melting for 2.5 hours, use a ball forming disc to form pellets with a diameter of 8-16mm; steam the pellets in a steam curing box at 95°C for 8 hours to obtain steamed feed, and then calcine the steamed feed in a small kiln at 800°C for 60 minutes and then blow it to cool Obtain clinker; take 93 parts of clinker and 7 parts of dihydrate gypsum to grind together until the specific surface area is 495m 2 / kg to prepare an inorganic gelling material.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com