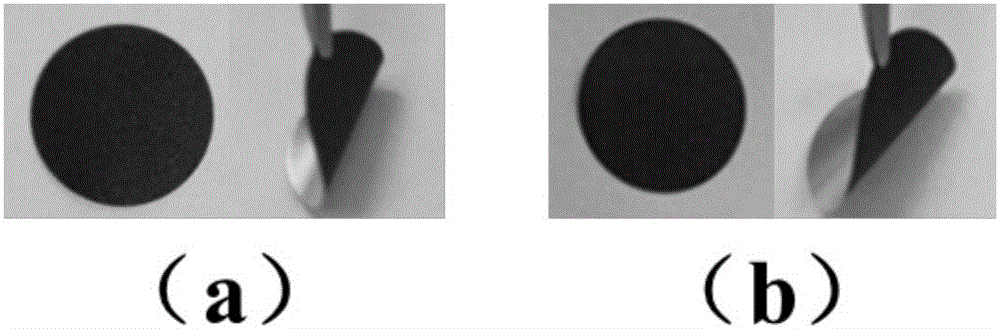
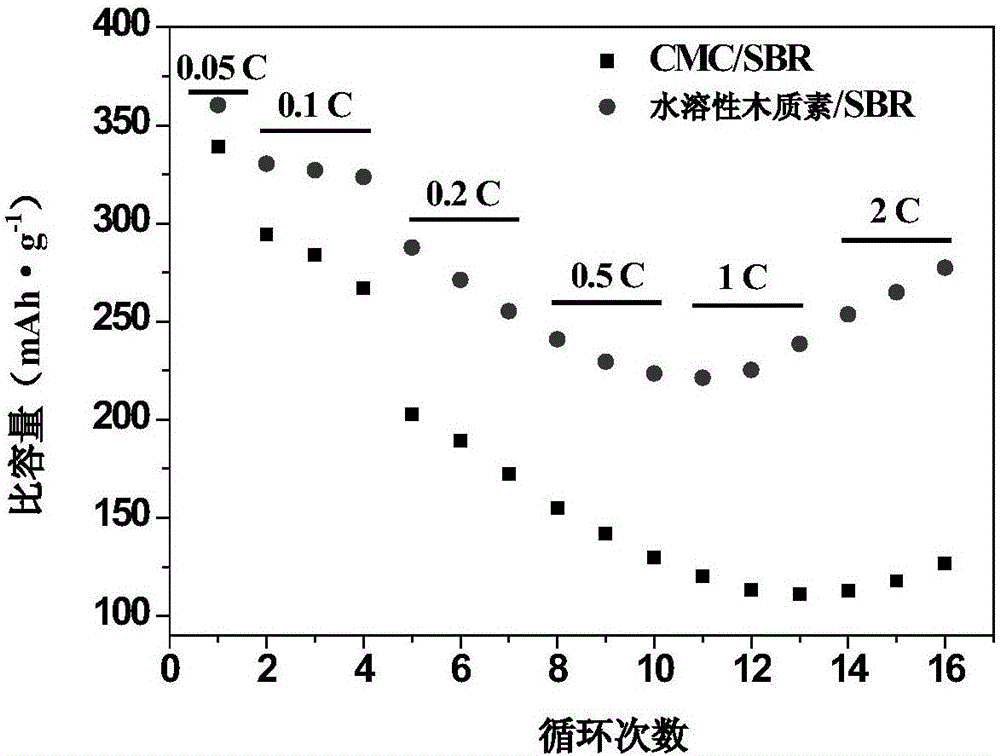
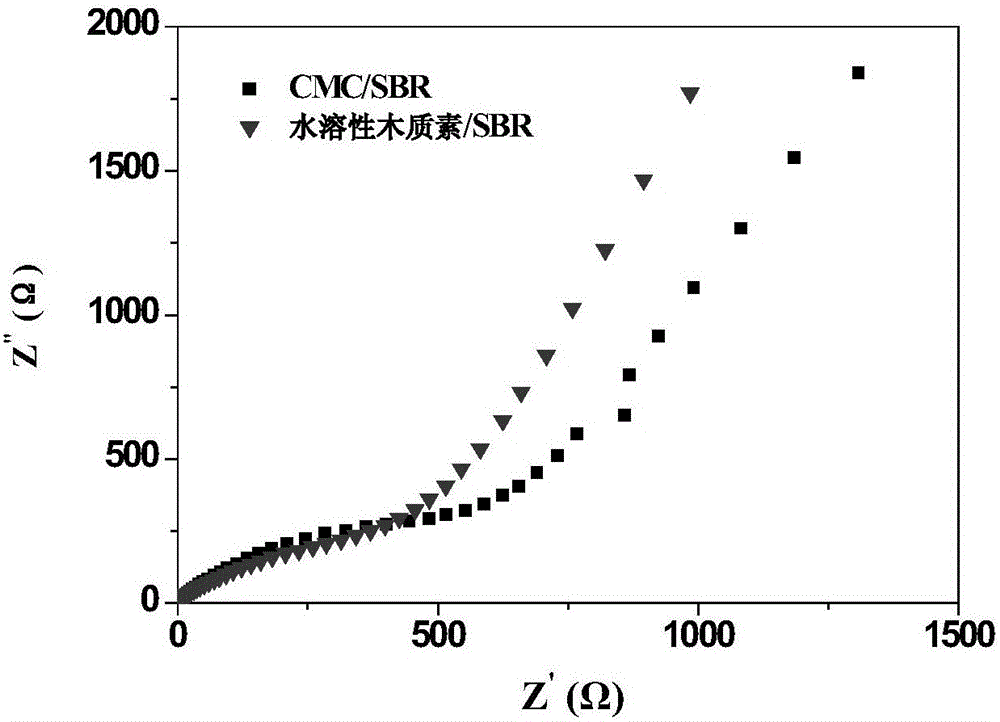
Lignin-based aqueous adhesive applied to negative electrode of lithium ion battery, electrode plate based on adhesive and lithium ion battery
A lithium-ion battery, water-based binder technology, applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, circuits, etc., to achieve the effects of improving coating uniformity, improving high-rate performance, and reducing resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] 1. Preparation of test electrodes:
[0043]The mass ratio of graphite, conductive carbon black (Super P) and lignin-based water-based binder is 85:6:9. The mass ratio of water-soluble lignin (sodium lignosulfonate) to SBR in the lignin-based water-based binder is 2:1. Add the water-soluble lignin in the lignin-based water-based binder to an appropriate amount of deionized water, and stir to fully dissolve it; add the conductive carbon black to the water-soluble lignin aqueous solution obtained in the previous step, and stir until it is uniformly dispersed; the graphite Add it to the mixture obtained in the previous step, and stir until uniformly dispersed; add the SBR in the lignin-based water-based binder to the mixture obtained in the previous step, and stir until uniformly dispersed to obtain an electrode slurry (solid content: 60%); The obtained electrode slurry is evenly coated on the Cu foil, dried in vacuum at 100° C., and rolled to obtain the graphite negative ...
Embodiment 2
[0055] 1. Preparation of test electrodes:
[0056] The difference between this example and Example 1 is that the test electrode also uses a lignin-based water-based binder as a binder, but uses activated carbon as an active material. The mass ratio of activated carbon, conductive carbon black (Super P) and lignin-based water-based binder is 75:15:10. The mass ratio of water-soluble lignin (a binary mixture of calcium lignosulfonate and sulfonated alkali lignin) to SBR in the lignin-based water-based binder is 3:1. Add the water-soluble lignin in the lignin-based water-based binder to an appropriate amount of deionized water, and stir to fully dissolve it; add conductive carbon black to the lignin aqueous solution obtained in the previous step, and stir until it is evenly dispersed; add activated carbon to the In the mixture obtained in the previous step, stir until uniformly dispersed; add the SBR in the lignin-based water-based binder to the mixture obtained in the previous ...
Embodiment 3
[0062] 1. Preparation of test electrodes:
[0063] The difference between this example and Example 1 is that the test electrode also uses a lignin-based water-based binder as a binder, but uses mesocarbon microspheres as an active material. The mass ratio of mesophase carbon microspheres, conductive carbon black (Super P) and lignin-based water-based binder is 80:10:10. The mass ratio of water-soluble lignin (a ternary mixture of sodium lignosulfonate, sulfonated enzymatic lignin and carboxylated alkali lignin) to SBR in the lignin-based water-based binder was 1:3. Add the water-soluble lignin in the lignin-based water-based binder to an appropriate amount of deionization, and stir to fully dissolve it; add conductive carbon black to the lignin aqueous solution obtained in the previous step, and stir until it is evenly dispersed; the mesophase carbon Add the microspheres to the mixture obtained in the previous step, and stir until uniformly dispersed; add the SBR in the ligni...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com