Fine particle production method
A manufacturing method and technology for microparticles, which are applied in chemical instruments and methods, medical preparations containing active ingredients, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve the problem of difficulty in producing microparticles stably, room for improvement of residues, difficulty in producing uniform and homogeneous microparticles, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~3
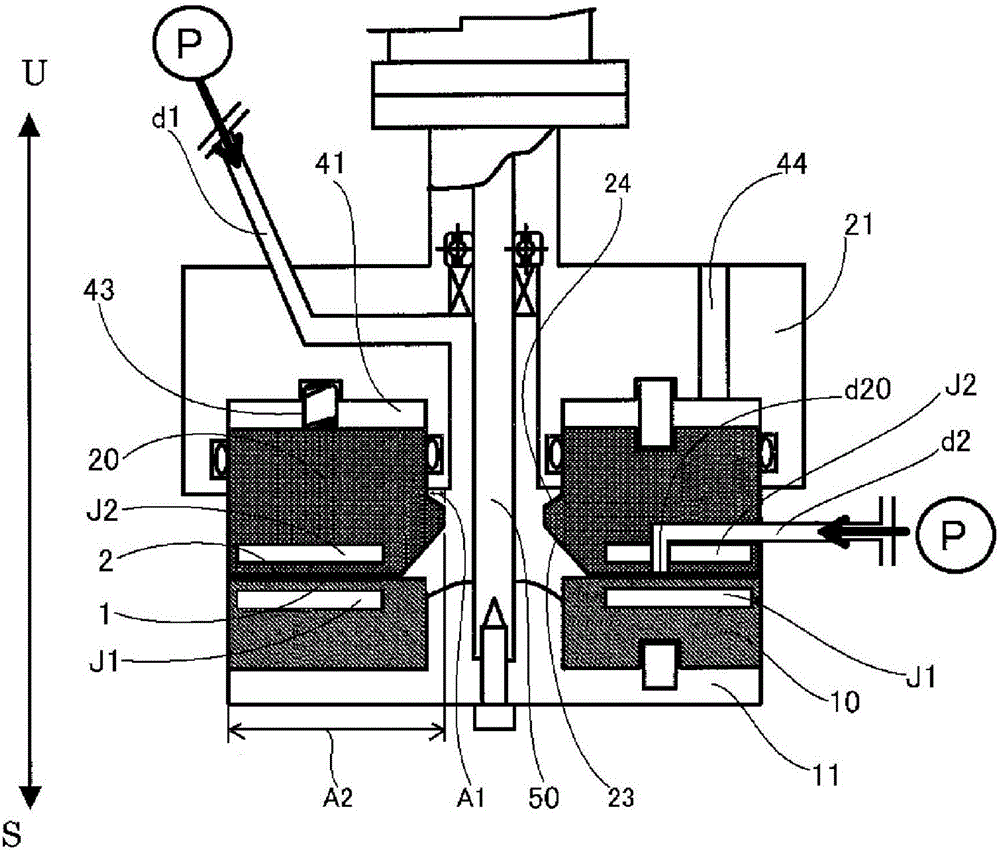
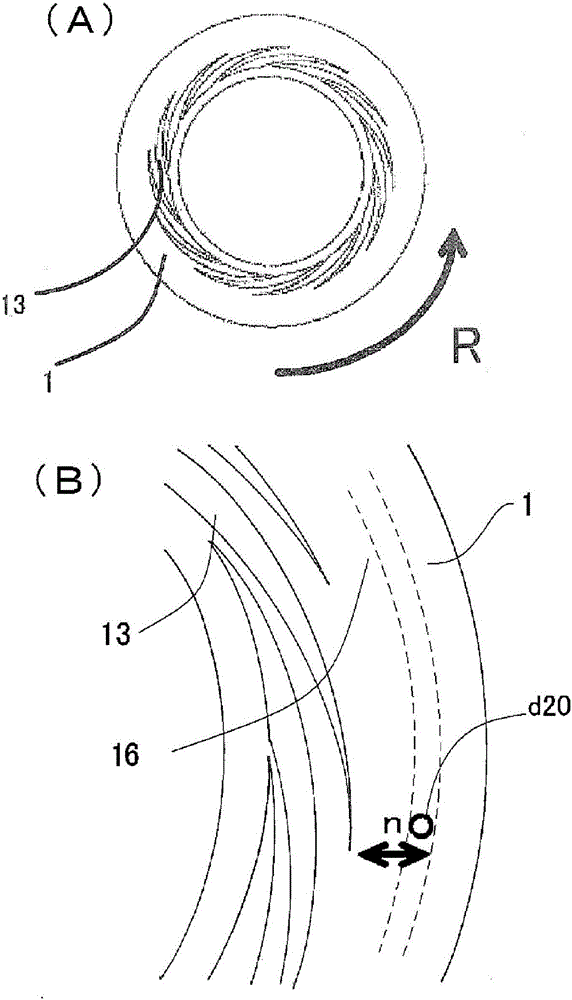
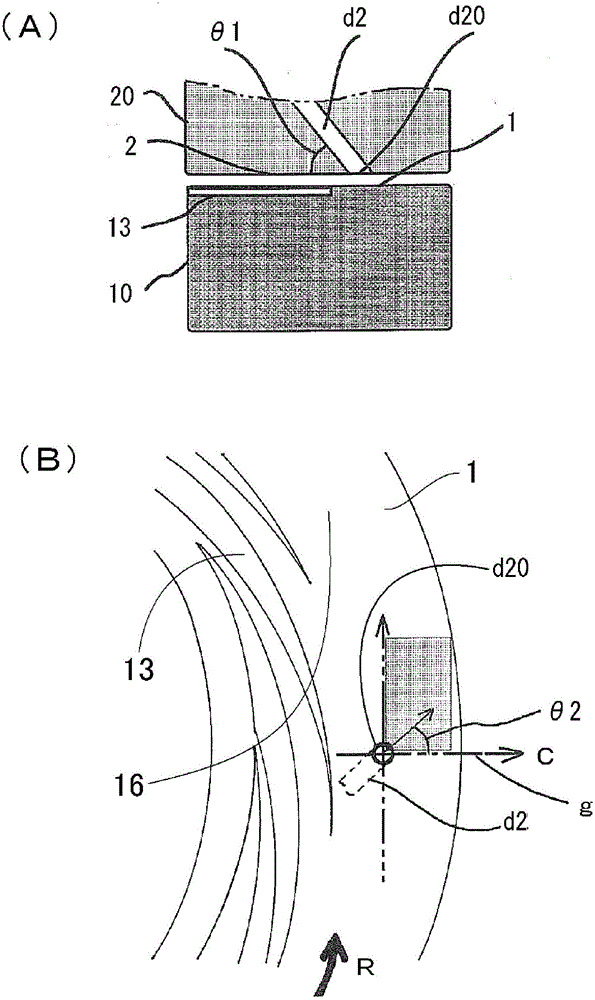
[0255] use figure 1 In the fluid processing device shown in , the pigment solution and the precipitation solvent as the particle raw material solution are arranged oppositely, have accessible and / or separate processing surfaces, and at least one of them rotates relative to the other. Mix in the thin film fluid formed between 1 and 2, and precipitate the pigment particles in the thin film fluid. In the preparation of the pigment solution, a stirrer with a rotating stirring blade is used, and at least one of the three conditions (stirring time, stirring blade circumferential speed, and temperature of the particle raw material solution) of the predetermined stirring energy is changed, Increase or decrease stirring energy. In Examples 1 to 3, the stirring energy was increased or decreased by changing the temperature (preparation temperature) of the pigment solution.
[0256] First, use Figure 4 and Figure 5 The pigment solution was prepared using a stirrer (Clearmix (manufac...
Embodiment 4~16
[0266] Except having changed the preparation conditions of the pigment solution into any of Tables 3-5, it carried out similarly to the case of Examples 1-3, and obtained the dry powder of PR122 microparticles|fine-particles. The results are shown in Tables 3-5. In Examples 4 to 16, the stirring energy was increased or decreased by changing the stirring time (preparation time) of the pigment solution as the second fluid.
[0267] [table 3]
[0268]
[0269] [Table 4]
[0270]
[0271] [table 5]
[0272]
[0273] The changes in the crystallinity / average particle diameter and β-type crystal ratio / average particle diameter of PR122 fine particles with respect to the preparation time of the second fluid in Examples 4 to 7 are shown in Figure 7 , the changes in the crystallinity / average particle diameter and β-type crystal ratio / average particle diameter of PR122 particles with respect to the preparation time of the second fluid in Examples 8 to 11 are shown in Figur...
Embodiment 17~22
[0277] The preparation conditions of the pigment solution were changed to those in Table 6 or 7, and it was carried out in the same manner as in Examples 1 to 3 to obtain a dry powder of PR122 fine particles. The results are shown in Tables 6-7. In Examples 17 to 22, the stirring energy was increased or decreased by changing the circumferential speed of the stirring blades at the time of preparing the pigment solution as the second fluid.
[0278] [Table 6]
[0279]
[0280] [Table 7]
[0281]
[0282] In Examples 17 to 22, changes in the crystallinity / average particle diameter of the PR122 microparticles with respect to the peripheral speed of the stirring blade during the preparation of the second fluid are shown in Figure 12 , the changes in the β-type crystal ratio / average particle diameter of the PR122 microparticles with respect to the peripheral speed of the stirring blade during the preparation of the second fluid in Examples 17 to 22 are shown in Figure 13 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com