Routing frequency slot allocation method based on evolutionary multiple objectives in elastic optical network
A technology of elastic optical network and distribution method, which is applied in the field of network communication, can solve problems such as complex implementation, inability to achieve a good compromise between resource usage and blocking rate, complex RSA problem solving, etc., to achieve uniform distribution, excellent performance, and cumbersome operation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
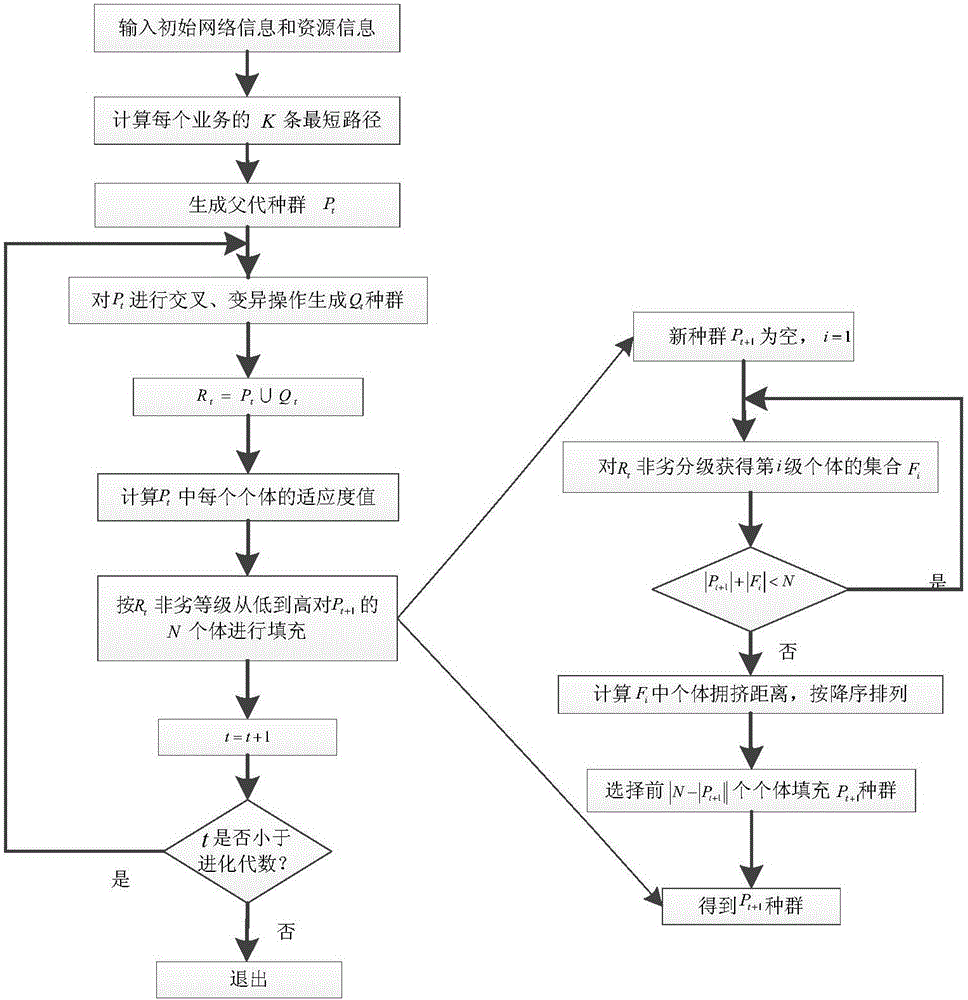
[0042] Aiming at the problem that it is difficult to obtain a good compromise between resource consumption and service discarding in the communication field, resulting in low frequency spectrum utilization, the present invention proposes a routing frequency slot allocation method based on evolutionary multi-objective in an elastic optical network, see figure 1 , the specific steps include:
[0043] (1) Input network topology information and initial resource configuration information, that is, input initial network information and resource information, and specifically need to input network structure information such as the location of each network topology node, the connection relationship between them, and the physical length of each link, Input information such as static service flow and number of static services, total number of frequency slots, population size, routing and spectrum allocation method chromosome crossover probability, mutation probability, and iteration times...
Embodiment 2
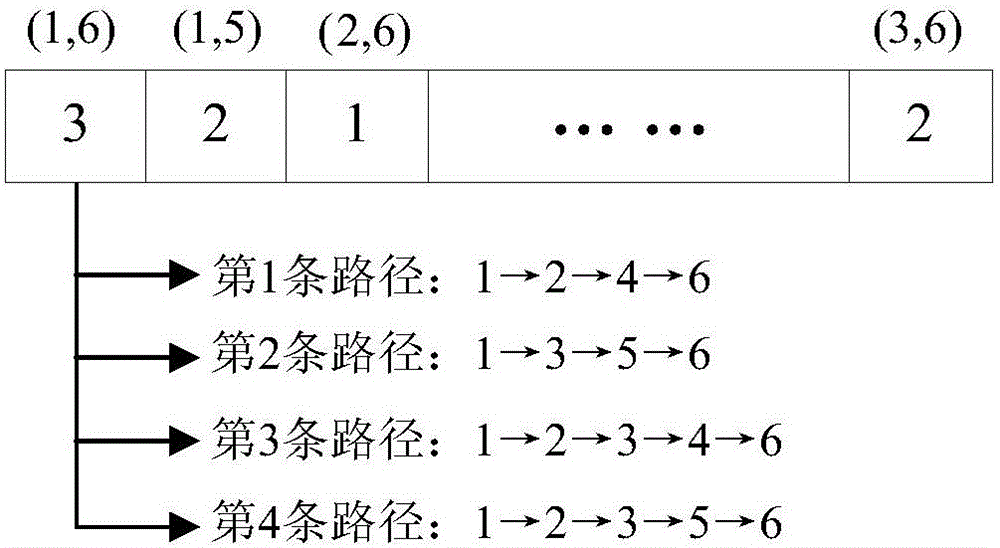
[0065] The routing frequency slot allocation method based on evolutionary multi-objective in the elastic optical network is the same as that in Embodiment 1, step (3) uses the routing and spectrum allocation chromosome coding method for coding to generate chromosomes, and each chromosome represents an allocation scheme of network resources. The specific steps of the encoding method include:
[0066] 3a): Using the chromosome coding method based on the selected K paths, each chromosome represents a routing scheme for all services;
[0067] 3b): The number of genes in the chromosome is equal to the total number of service requests, each gene bit corresponds to a service, the gene value represents one of the K shortest paths of the service, and all initial gene values of the chromosome are randomly generated. According to the resource information of the initial configuration, a corresponding number of chromosomes is generated, and the set of chromosomes constitutes the parent...
Embodiment 3
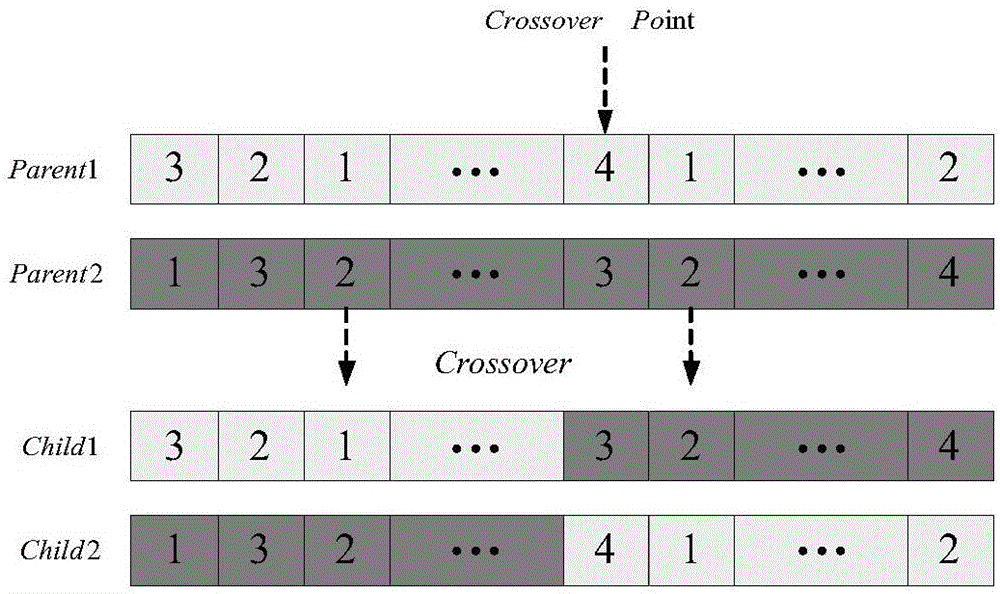
[0071] The routing frequency slot allocation method based on evolutionary multi-objective in the elastic optical network is the same as that of embodiment 1-2, and the specific steps of the crossover method described in step 4a) include:
[0072] 4a1): if image 3 As shown, a single-point crossover is used to randomly select two parent chromosomes from the mating pool to generate a random number P random ∈(0,1), if P random Less than the preset crossover probability P crossover , randomly select a gene bit as the intersection point, and perform a crossover operation on two individuals, that is, the former part of the two chromosomes remains unchanged, and the latter part of the two chromosomes is exchanged; if P random Greater than or equal to the crossover probability, the two individuals remain unchanged, and finally put the crossover chromosomes into the offspring population;
[0073] 4a2): When the evolutionary generation reaches half of the evolutionary generation set ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com