Preparation method of 131I-labeled metaiodobenzylguanidine
A technology of m-iodobenzylguanidine and benzylguanidine, which is applied in the field of preparation of m-iodobenzylguanidine, can solve the problems of high transport requirements of radioactive substances, impossibility of clinical application, harsh reaction, etc., and achieve good clinical diagnosis and treatment effect and high radiochemical purity , the effect of mild and simple conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
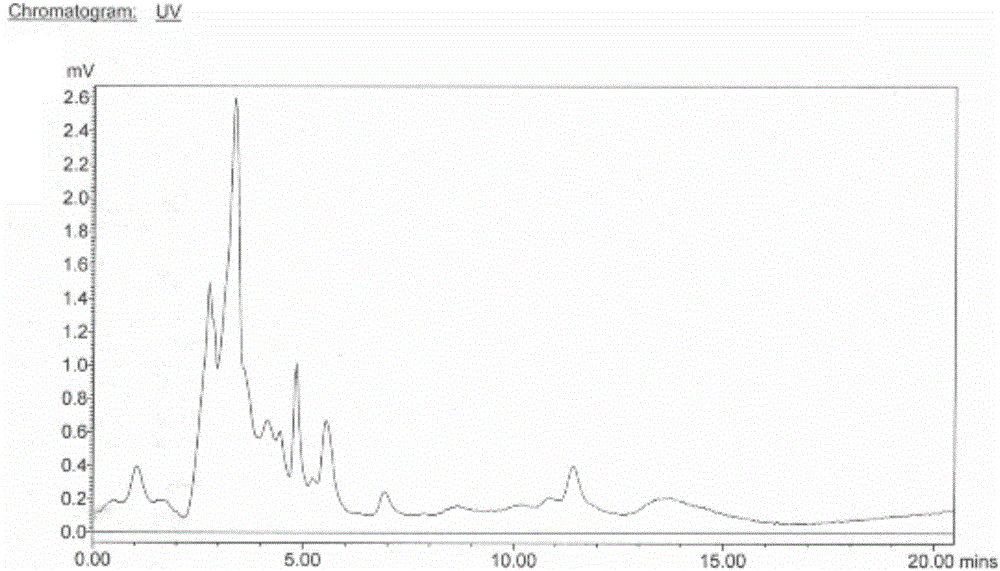
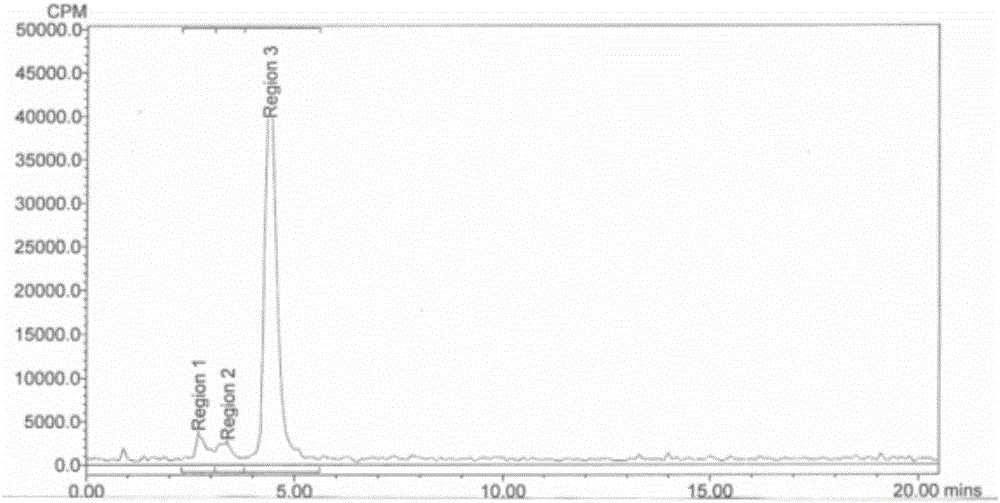
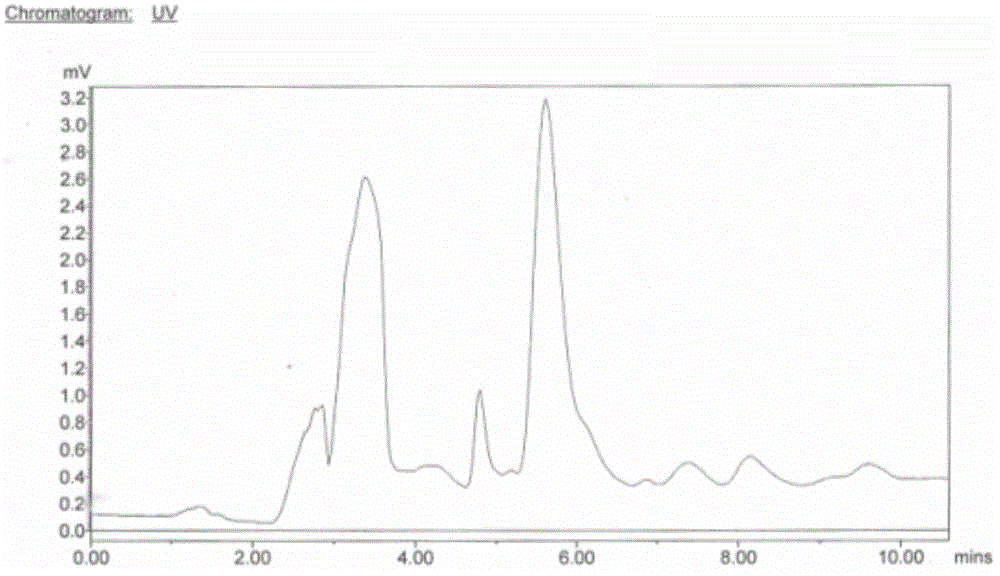
[0038] Embodiment 1: Add N,N'-di(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-3-(tributyltin base)-benzylguanidine 70 μ g successively in 10 ml control vial, 500 μ l of acetic acid, 16.5 μ l of 30% hydrogen peroxide solution, Na 131 I solution 13.5mCi (0.1ml), physiological saline 1ml, react at room temperature for 20 minutes. Add 100 μl of trifluoroacetic acid and heat to 100° C. for 20 minutes. After the reaction was completed, let it stand still, cooled to room temperature, added 1 g of 717 anion exchange resin, and stirred gently for 2 minutes. Aspirate the supernatant and filter it through a 0.22 μm microporous membrane to obtain the marker 131 I-m-iodobenzylguanidine.
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment 2: Add N,N'-di(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-3-(tributyltin base)-benzylguanidine 70 μ g successively in 10 ml control vial, 500 μ l of acetic acid, 16.5 μ l of 30% hydrogen peroxide solution, Na 131 I solution 13.5mCi (0.1ml), physiological saline 1ml, react at room temperature for 20 minutes. Add 100 μl of trifluoroacetic acid and heat to 100° C. for 20 minutes. After the reaction, let it stand still, cool to room temperature, draw out the reaction solution with a syringe, inject it into a self-made small disposable 717 anion exchange resin packed column, and then elute with 1ml of normal saline. Combine the solutions and filter them with a needle filter with a 0.22 μm filter membrane to obtain the marker 131 I-m-iodobenzylguanidine.
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3: 70 μg of N,N'-bis(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-3-(tributyltin-yl)-benzylguanidine, 25 μg of N-chlorosuccinimide, and dihydrogen phosphate were sequentially added to a 10ml control vial Potassium 3.4mg, Sodium Hydroxide 0.3mg, Na 131 I solution 13.5mCi (0.1ml), physiological saline 1.5ml, react at room temperature for 20 minutes. Add 40 μg of sodium metabisulfite, and heat to 100° C. for 20 minutes to react. After the reaction was completed, let it stand still, cooled to room temperature, added 1 g of 717 anion exchange resin, and stirred gently for 2 minutes. Aspirate the supernatant and filter it through a 0.22 μm microporous membrane to obtain the marker 131 I-m-iodobenzylguanidine.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com