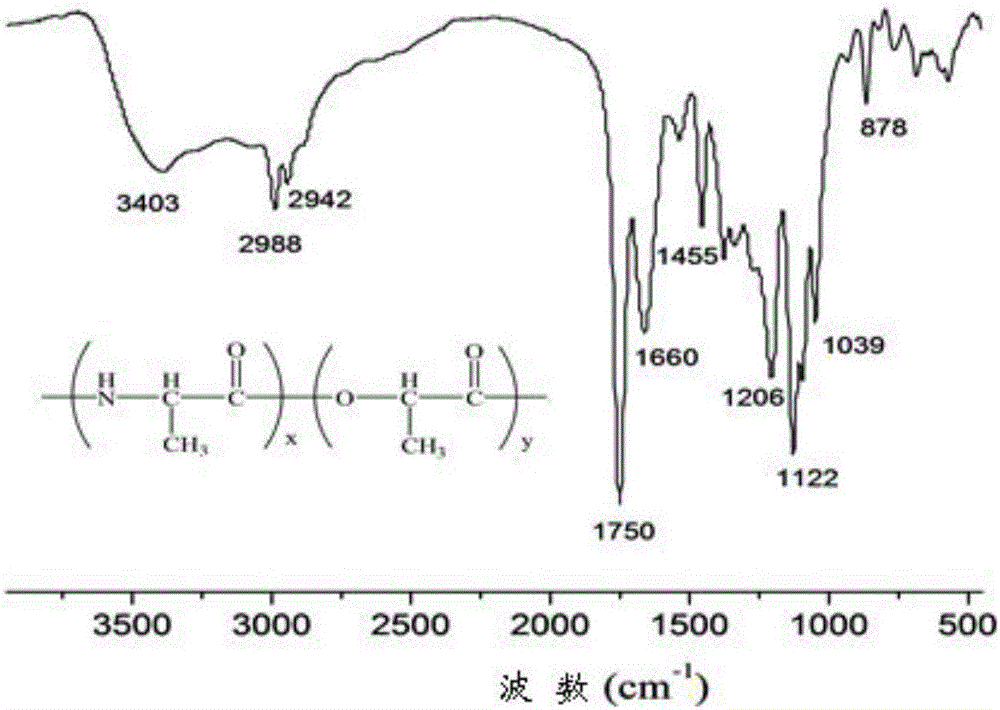
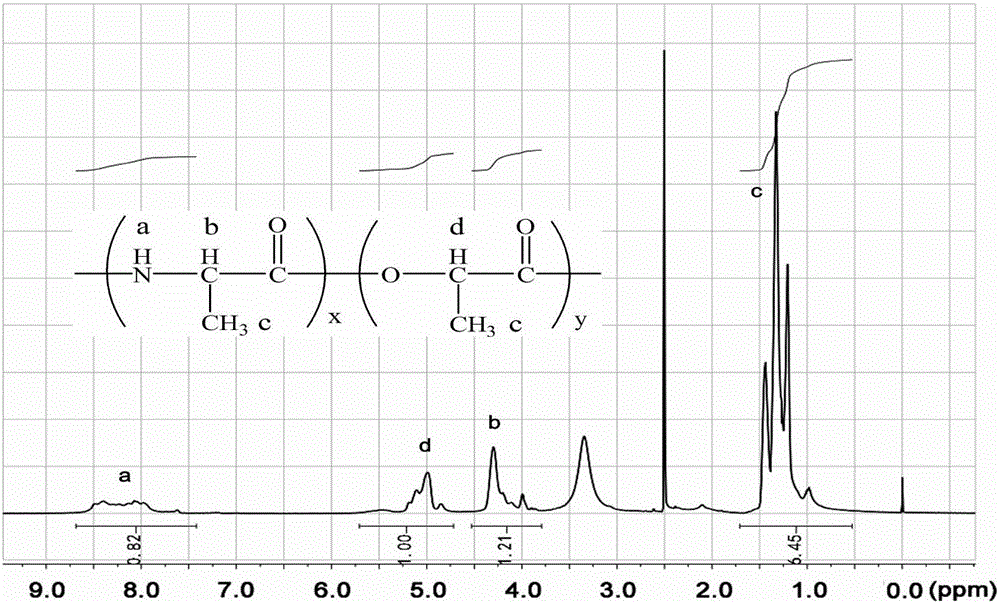
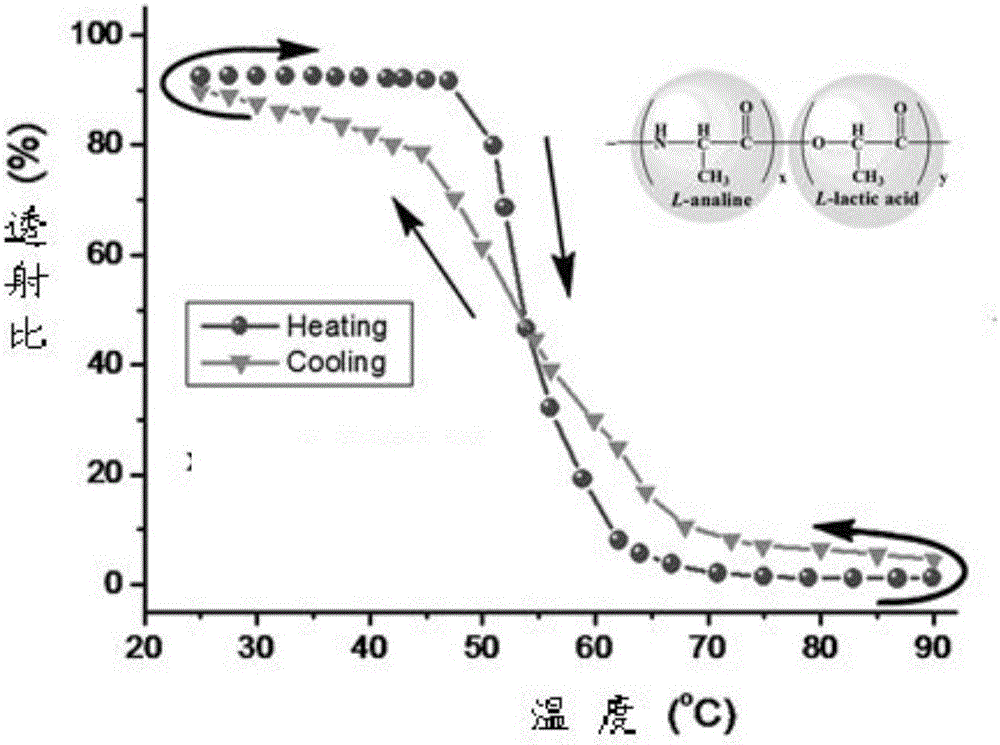
Temperature sensitive material preparation method
A temperature-sensitive material, lactic acid technology, applied in the field of temperature-sensitive materials, can solve the problems of achieving the best, reducing the temperature-sensitive properties of materials, and not being able to have both biocompatibility and temperature-sensitive properties.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0028] The invention provides a method for preparing a temperature-sensitive material, comprising the following steps:
[0029] Dehydrating lactic acid to obtain dehydrated lactic acid;
[0030] The anhydrous lactic acid and alanine are subjected to a copolymerization reaction under the condition of a catalyst to obtain a temperature-sensitive material.
[0031] In the present invention, lactic acid is dehydrated to obtain dehydrated lactic acid. The present invention has no special requirements on the source of the lactic acid, and lactic acid well known to those skilled in the art can be used, specifically, a commercially available product of lactic acid. In the present invention, the lactic acid contains 10-15% water. The present invention has no special requirements on the configuration of the lactic acid, specifically, it can be one, two or three of L-type lactic acid, D-type lactic acid and DL-type lactic acid.
[0032] In the present invention, the dehydration temper...
Embodiment 1
[0064] (1) Dehydration and pre-polymerization stage
[0065] In a microwave reactor (CEM microwave synthesizer, DISCOVER SP, power 150w, stirring rate High), 5.04g of lactic acid was placed in a 100mL long-necked flask, and a magnetic stirrer was placed. After 30 minutes of treatment at a vacuum of 0.065MPa and a temperature of 120°C, impurities such as water in the system can be removed. Then, add 4.2036g of alanine, 0.056g of stannous chloride and 0.047g of p-toluenesulfonic acid into the reaction flask, and react for 45 minutes at a vacuum degree of 0.083MPa and a temperature of 160°C.
[0066] (2) Polymerization stage
[0067] The reaction was continued at a vacuum of 0.088 MPa and a temperature of 170° C. for 30 minutes.
[0068] (3) Insulation stage
[0069] The reaction was maintained for 60 minutes at a vacuum of 0.085 MPa and a temperature of 160°C. When the reaction temperature drops below 50°C, fully dissolve it with 8mL of anhydrous methanol, then add it dropwi...
Embodiment 2
[0076] (1) Dehydration and pre-polymerization stage
[0077] In a microwave reactor (CEM microwave synthesizer, DISCOVER SP, power 150w, stirring rate High), 5.18g of lactic acid was placed in a 100mL long-necked flask, and a magnetic stirrer was placed. React for 40 minutes at a vacuum of 0.076 MPa and a temperature of 125° C. to remove free water in the reaction solution. Then, add 3.82g of alanine, 0.06g of stannous chloride and 0.05g of p-toluenesulfonic acid into the reaction flask, and react for 50 minutes at a vacuum degree of 0.092MPa and a temperature of 165°C.
[0078] (2) Polymerization stage
[0079] The reaction was continued at a vacuum of 0.089 MPa and a temperature of 175° C. for 40 minutes.
[0080] (3) Insulation stage
[0081] The reaction was maintained for 65 minutes at a vacuum of 0.090 MPa and a temperature of 170°C. When the reaction temperature drops below 50°C, fully dissolve it with 12mL of anhydrous methanol, then dropwise add it into 180mL of die...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com