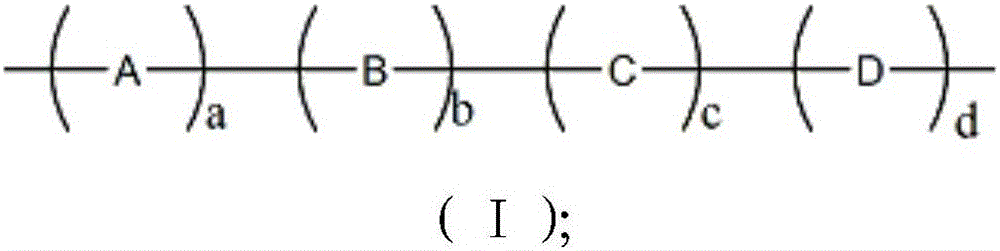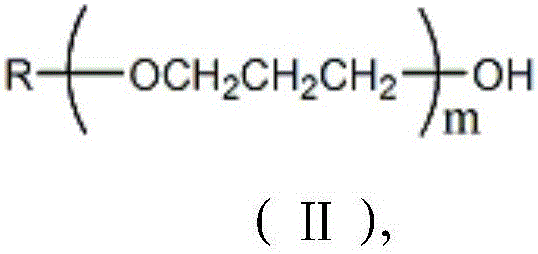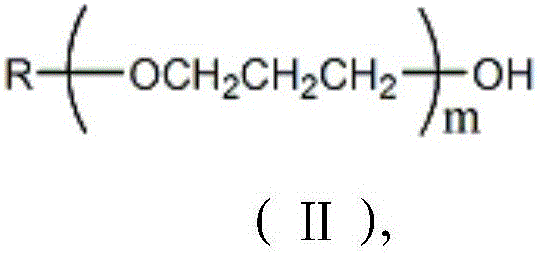Water-retaining shrinkage-reducing polycarboxylic acid water reducing agent and preparation method thereof
A technology of polycarboxylic acid and water retention, applied in the field of water reducing agent, can solve the problems of complex synthesis process and large increase in engineering cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0080] An embodiment of the preparation method of the water-retaining shrinkage-reducing polycarboxylate superplasticizer of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0081] (1) In a closed autoclave, replace the air in the reactor with high-purity nitrogen repeatedly twice, inject 1 mol of propylene alcohol and 0.2 g of catalyst NaOH, raise the temperature of the reactor to 100-115 ° C, and start slowly dropwise adding 1 mol of ring Oxygen, so that the reaction temperature is controlled within the range of 70°C, the pressure in the kettle is controlled at 0.2MPa, and the amount of ethylene oxide required for dropwise addition is controlled by the decrement method. After the dropwise addition of ethylene oxide is completed, the temperature Controlling at 80°C, the reaction was continued for 5h to obtain an intermediate product with the desired molecular weight.
[0082] (2) Keep the temperature at 80°C, start to slowly add 1mol of glycidol dropwise, and control th...
Embodiment 2
[0085] An embodiment of the preparation method of the water-retaining shrinkage-reducing polycarboxylate superplasticizer of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0086] (1) In a closed autoclave, replace the air in the reactor with high-purity nitrogen repeatedly for 3 times, inject 1mol of prenyl alcohol and 0.5gmol of catalyst KOH, raise the temperature of the reactor to 110°C, and start to slowly add 40mol of ring Oxygen, so that the reaction temperature is controlled within the range of 115°C, the pressure in the kettle is controlled at 0.4MPa, and the amount of ethylene oxide required for dropwise addition is controlled by the decrement method. After the dropwise addition of ethylene oxide is completed, the temperature Controlling at 110°C, the reaction was continued for 2h to obtain an intermediate product with the desired molecular weight.
[0087] (2) Lower the temperature to 80° C., start to slowly add 2 mol of glycidol dropwise, and control the drop...
Embodiment 3
[0090] An embodiment of the preparation method of the water-retaining shrinkage-reducing polycarboxylate superplasticizer of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0091] (1) In a closed autoclave, replace the air in the reactor with high-purity nitrogen repeatedly twice, inject 1mol of isobutenol and 2g of catalyst potassium carbonate, raise the temperature of the reactor to 115°C, and slowly add 80mol of ethylene oxide dropwise Alkanes, so that the reaction temperature is controlled within the range of 130 °C, the pressure in the kettle is controlled at 0.6MPa, and the amount of ethylene oxide required for dropwise addition is controlled by the decrement method. After the dropwise addition of ethylene oxide is completed, the temperature is controlled at At 120°C, the reaction was continued for 0.5h to obtain an intermediate product with the desired molecular weight.
[0092] (2) Lower the temperature to 80° C., start to slowly add 3 mol of glycidol dropwise, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com