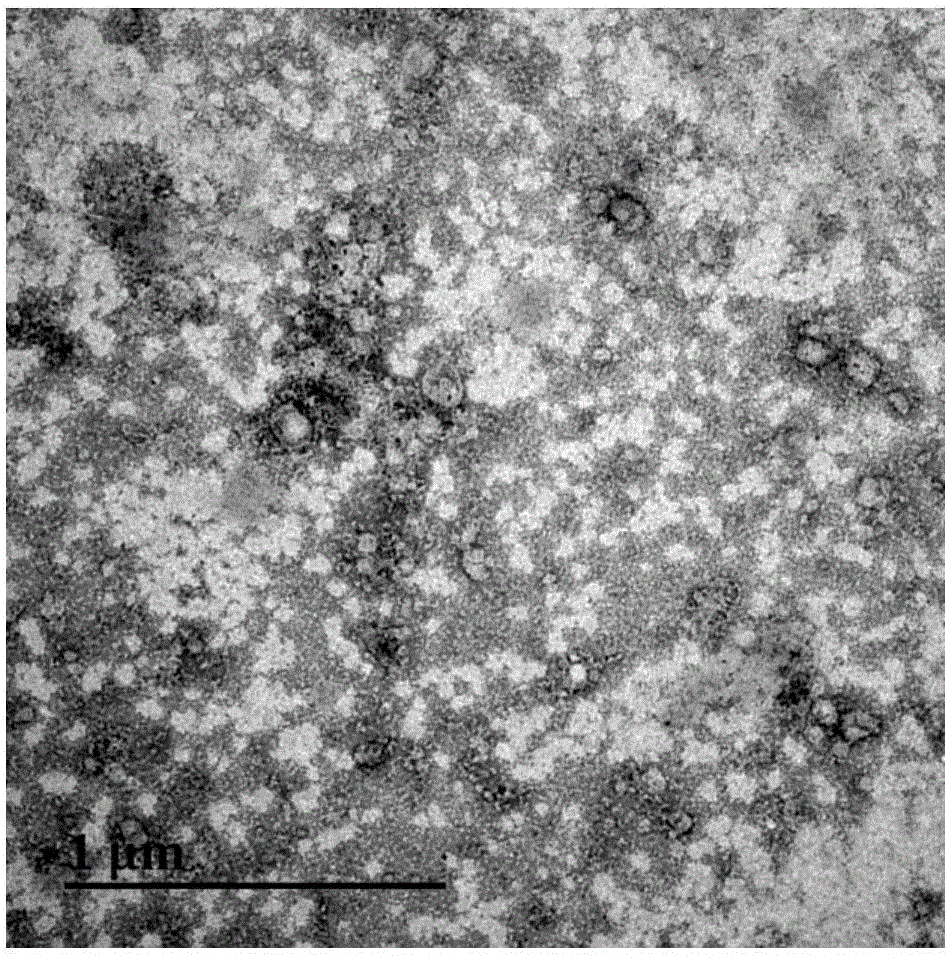
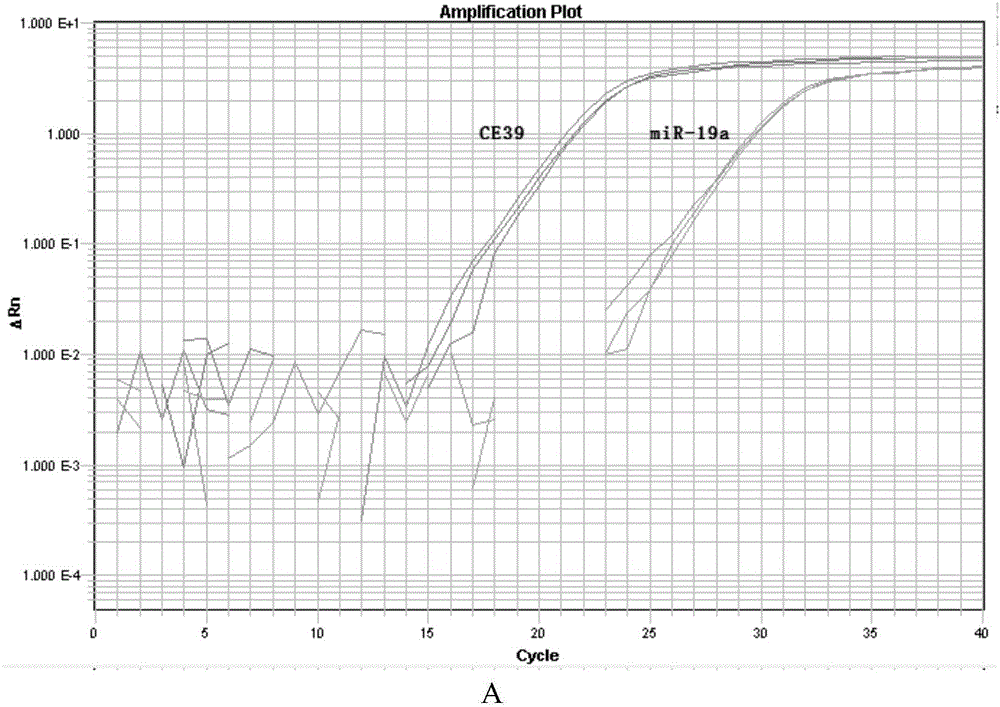
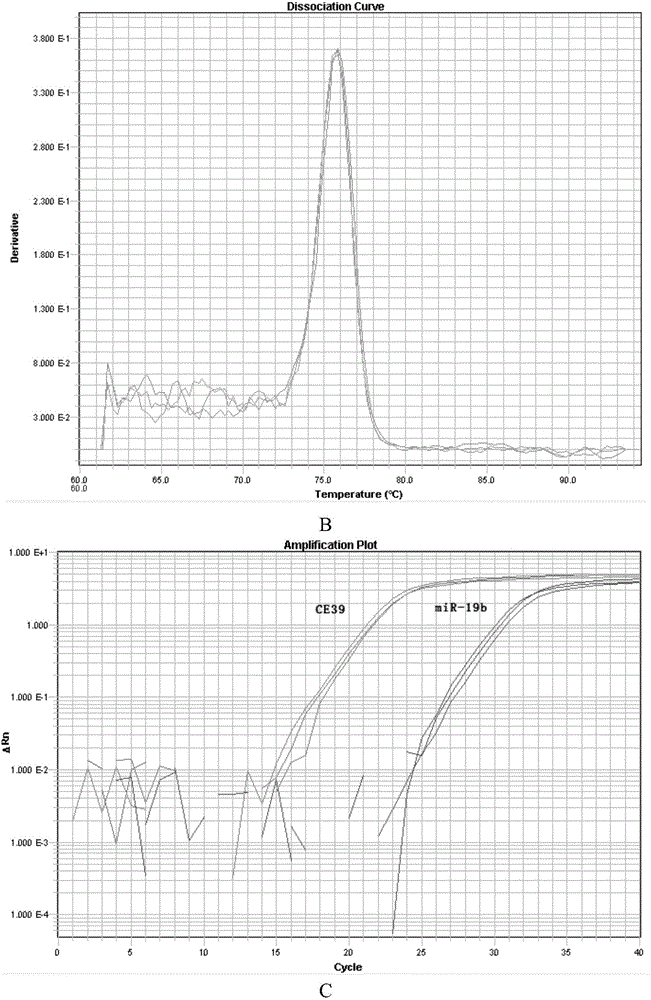
Method for separating MVs (microvesicles) and MV exosomes from tumor cell supernatant
A technology of tumor cells and microvesicles, applied in the preparation of test samples, etc., can solve the problems of low content, influence of subsequent analysis of microvesicles, low purity of microvesicles, etc., achieve high yield, improve extraction efficiency and research value effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1 Microvesicles
[0043] (1) For the preparation of ferroferromagnetic microspheres coupled with DIO, refer to examples 1-6 of patent application CN200880105993.1. By calculating the content of unbound and coupled lipophilic carbocyanine dye, the DIO of lipophilic carbocyanine dye coupled on 1 mg magnetic microspheres was 3.51×10 -5 mol, and suspended in 1xPBS solution to make 100mg / ml DIO-coupled ferroferric oxide magnetic microsphere suspension.
[0044] (2) will 1*10 6 Individual gastric cancer cells MGC80-3 were inoculated at 75cm 2 In the cell flask, add RPMI-1640 culture medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum (purchased from Gibco's RPMI-1640 culture medium and Gibco's fetal bovine serum), and place at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultivate in an incubator for 24 hours, collect 10ml of cell culture solution, add it to the first centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 200×g for 10 minutes, and separate to obtain 9.5ml of supernatant a;
[0045] (3) Add 10ml of supernatant a ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] (1) will 1*10 6 Individual gastric cancer cells AGS were inoculated at 75cm 2 Add RPMI-1640 culture medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum to the cell bottle, and place at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultivate in an incubator for 24 hours, collect 10ml of cell culture solution, add it to the first centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 200×g for 10 minutes, and separate to obtain 9.5ml of supernatant a;
[0050] (3) Add 9.5ml supernatant a into the second centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 2000×g for 15 minutes to obtain 9.0ml supernatant b;
[0051] (4) Add 9.0ml of supernatant b into a 100KDa ultrafiltration tube, and centrifuge at 5000rpm for 15 minutes. Pour off the filtrate, and collect about 1ml of the remaining liquid in the ultrafiltration tube into a third centrifuge tube. Add 0.1ml, 100mg / ml DIO-coupled ferric oxide magnetic microsphere suspension prepared in step (1) of Example 1, place at 4°C and 100rpm and incubate with horizontal shaking for 16 hours to ensure that the particl...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3 Extraction of Exosomes (50-150nm) Subclasses in Microvesicles
[0054] (1) will 1*10 6 Individual gastric cancer cells (undifferentiated) HGC-27 were seeded at 75cm 2 Add RPMI-1640 culture medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum to the cell bottle, and place at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultivate in an incubator for 24 hours, collect 10ml of cell culture solution, add it to the first centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 200×g for 10 minutes, and separate to obtain 9.5ml of supernatant A;
[0055] (2) Add 9.5ml supernatant A to the second centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 2000×g for 40 minutes to obtain 9.0ml supernatant B;
[0056] (3) Add 9.0ml supernatant B to the third centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 10000×g for 40 minutes to obtain 8.5ml supernatant C;
[0057] (4) Add 8.5ml of supernatant C into a 100KDa ultrafiltration tube, and centrifuge at 5000rpm for 15 minutes. The filtrate was discarded, and the remaining liquid in the ultrafiltration tube was collected in a third ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com