Method used for producing nickel chloride products taking waste printing nickel screens as raw materials
A technology of nickel chloride and nickel mesh, applied in the direction of nickel halide, etc., can solve the problem of inability to produce chemical reactions, and achieve the effect of broadening the types of raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
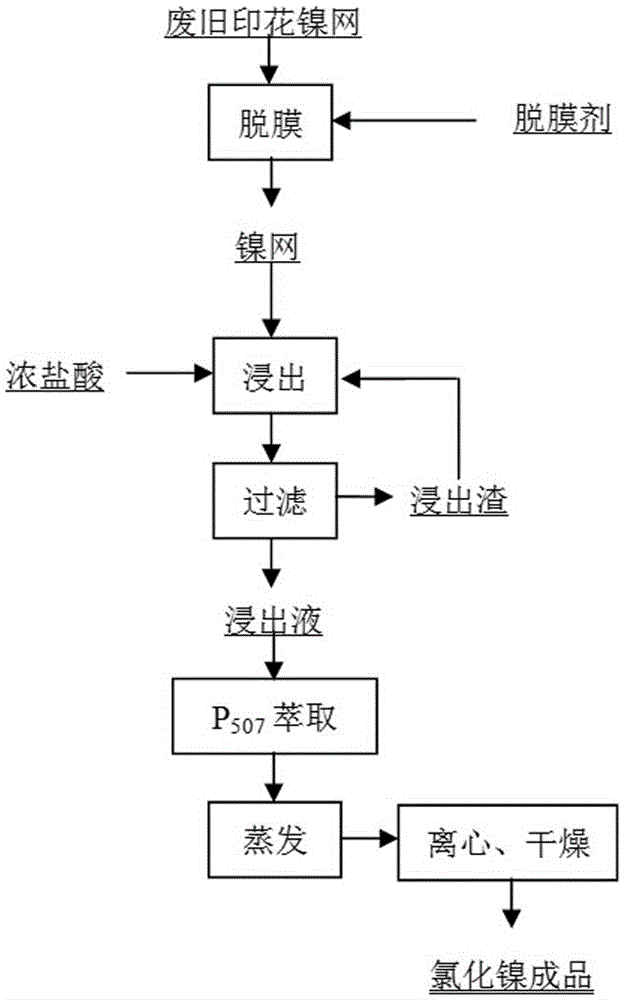
[0013] A kind of method that is raw material production nickel chloride product with waste printing nickel mesh, comprises the following steps:
[0014] a. Configure printing nickel mesh release agent
[0015] Add 30kg of hydrogen peroxide, 8kg of sodium dodecylsulfonate, 4kg of fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether (Pingpingjia o-20), 8kg of ethanol, and 12.5kg of water into the stripping agent configuration kettle, start mechanical stirring and mixing, and add hydroxide Nickel adjusts the pH value of the release agent to 12.5. After the mixture is uniform and the pH value is 12.5, the preparation of the release agent is completed.
[0016] b. Printed nickel mesh stripping
[0017] Take 5kg of the nickel mesh to be stripped and completely immerse it in the stripping agent, raise the temperature to 70°C at a constant speed and keep it warm to remove the photosensitive adhesive for 2 hours. After 2 hours, take out the nickel mesh and wash it with high-pressure water.
[0018] c...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Embodiment 2 step process is the same as embodiment 1, specifically:
[0027] The difference between step a and Example 1 is that the pH value of the release agent is controlled to be 12.3.
[0028] The difference between step b and Example 1 lies in that the temperature is controlled at 75° C. and the time is 2.5 h during the stripping process.
[0029] The difference between step c and Example 1 is that the temperature of the leaching process is controlled at 80° C., and the pH of the leaching solution is 4.0.
[0030] The difference between step d and Example 1 is that adding Ni ion concentration to the organic after saponification is the nickel chloride solution of 85.5g / L to produce nickel soap, and the organic after the nickel soap is mixed with the nickel mesh leaching solution for extraction. After the 7-stage countercurrent extraction of the extraction box, the extraction ratio is O:A=2:1. After the extraction, the loaded organic and 6.8mol / L hydrochloric acid...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 2 step process is the same as embodiment 1, specifically:
[0035] The difference between step a and Example 1 is that the pH value of the release agent is controlled to be 13.
[0036] The difference between step b and Example 1 is that the temperature is controlled at 80° C. and the time is 2.8 h during the stripping process.
[0037] The difference between step c and Example 1 is that the temperature of the leaching process is controlled at 78° C., and the pH of the leaching solution is 3.6.
[0038] The difference between step d and Example 1 is that adding Ni ion concentration to the organic after saponification is the nickel chloride solution of 88g / L to prepare nickel soap, and the organic after the nickel soap is mixed with the nickel mesh leaching solution for extraction, after The 7-stage countercurrent extraction of the extraction box, the extraction ratio O:A=1.5:1, the extracted loaded organic and 7mol / L hydrochloric acid are regenerated by the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com