Wind power T-type connection line ground fault setting method
A grounding fault and line connection technology, applied in the fault location, detecting faults according to conductor type, measuring electricity, etc., can solve problems such as increased line loss, increased investment cost of power grid transformation, and the peer end cannot receive blocking signals.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
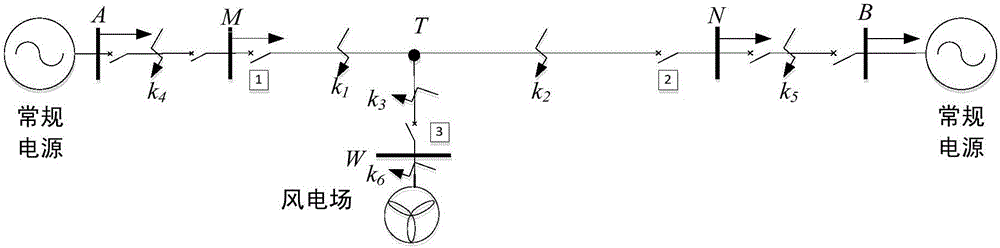
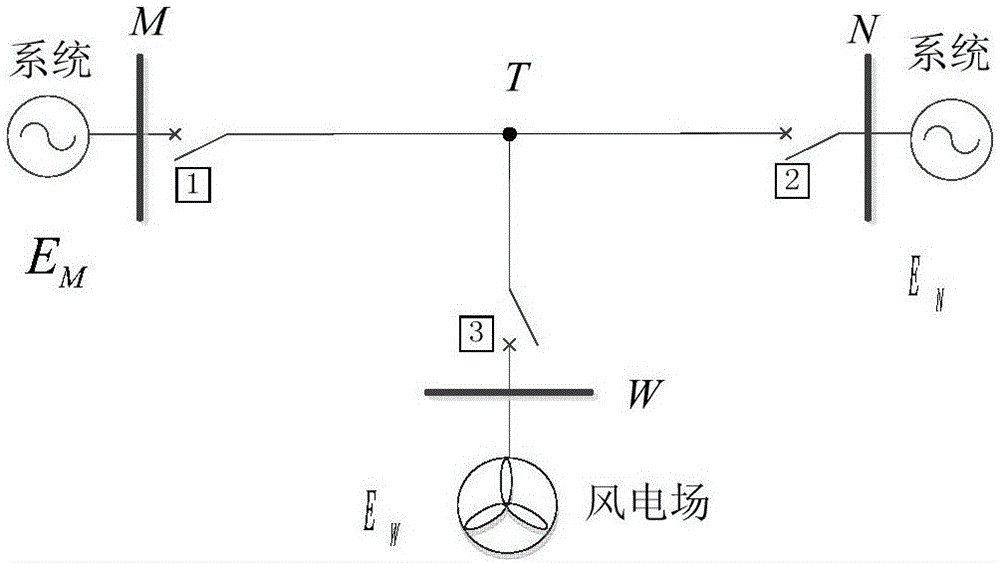
[0106] according to figure 1 In the distribution network simulation model with T-connected wind power, the system voltage level is 110kV, the capacity of conventional power sources on both sides is 90MW, the capacity of wind farm is 12MW, the load is 22MW, and the power factor is 0.85. The line parameter is Z 1 =0.21+j0.419Ω / km, Z 0 =0.63+j1.257Ω / km, b 1 =2.85e-6S / km, b 0 =6e-6S / km. The lengths of lines AM, MT, NT, WT, and NB are 20km, 30km, 50km, 20km, and 20km, respectively.
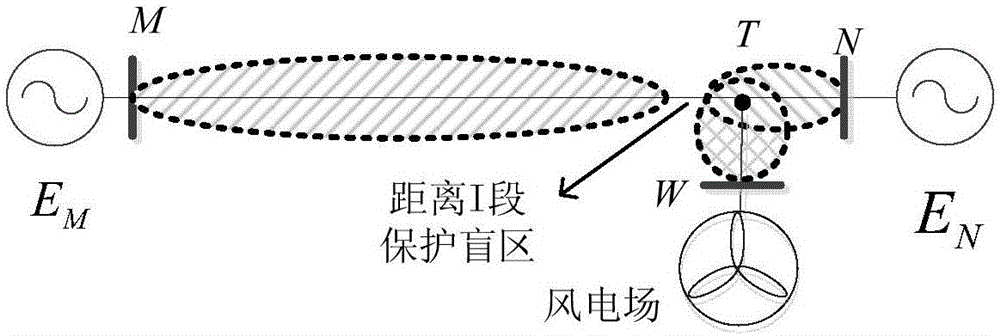
[0107] For wind power T-connection line area k 1 point and outside k 4 When a single-phase metallic ground short circuit occurs at the point, adopt the above-mentioned setting method for fault discrimination, including the following steps:
[0108] 1) Extract the zero-sequence voltage and zero-sequence current at the protection installation place of the wind power T-connection line, calculate the analog impedance and the signaling threshold of the transmitter according to the system parameters, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com