Method for increasing heme synthesized from escherichia coli
A technology of Escherichia coli and recombinant Escherichia coli, which is applied in the field of metabolic engineering, can solve the problem of not considering the relationship between gene expression intensity of heme synthesis pathway and synthetic heme
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
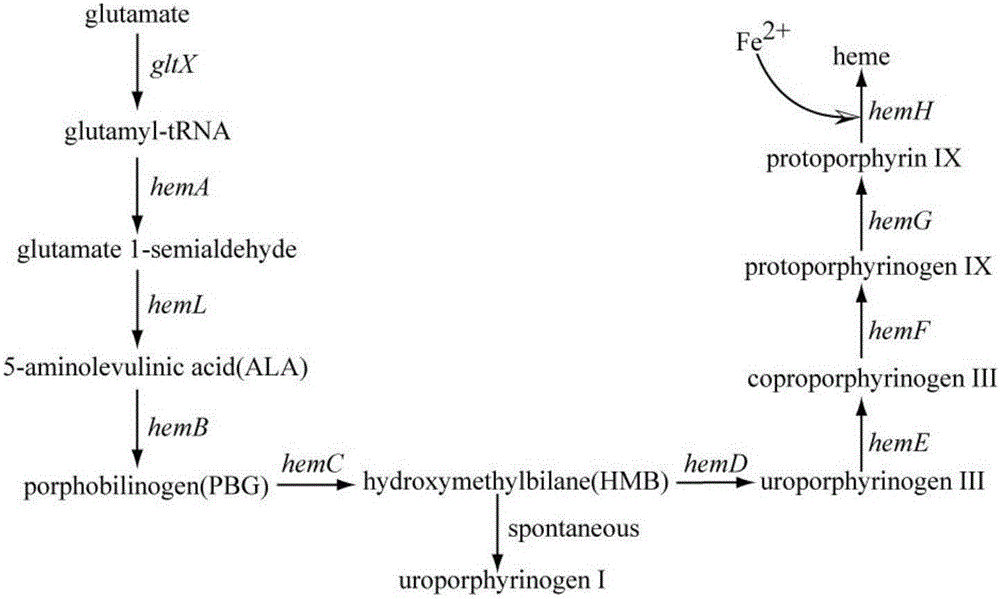
[0059] Example 1 Amplification of gene fragments related to heme synthesis pathway
[0060] Using the E.coli DH5α genome as a template, hemB (989bp), hemC (956bp), hemD (755bp), hemE (1079bp), hemF (914bp), hemG (560bp ), hemH (977bp ) genes were amplified respectively, and then fused PCR fused the hemC and hemD fragments into hemC-hemD, and the hemG and hemH fragments into hemG-hemH. Primers are shown in Table 1.
[0061] Table 1 Primers
[0062]
Embodiment 2
[0063] Example 2 Construction of Escherichia coli Synthetic Heme Related Recombinant Engineering Strains
[0064]The fragment hemC-hemD was connected with the expression vectors pRSFDuet-2, pCDFDuet-2, pACYCDuet-2 respectively by using restriction sites PstⅠ and HindⅢ to obtain recombinant vectors pRSFDuet-2-hemC-hemD, pCDFDuet-2-hemC-hemD, pACYCDuet -2-hemC-hemD. The fragment hemB was connected with the vectors pRSFDuet-2-hemC-hemD, pCDFDuet-2-hemC-hemD, pACYCDuet-2-hemC-hemD respectively by BamHI and SacⅠ, and the recombinant vectors pRSFDuet-2-hemB-hemC-hemD, pCDFDuet- 2-hemB-hemC-hemD, pACYCDuet-2-hemB-hemC-hemD. The amplified hemE fragments were ligated into pRSFDuet-2-hemB-hemC-hemD, pCDFDuet-2-hemB-hemC-hemD, and pACYCDuet-2-hemB-hemC-hemD through restriction sites NdeI and XhoI, respectively, to obtain Recombinant plasmids pRSFDuet-2-hemB-hemC-hemD-hemE, pCDFDuet-2-hemB-hemC-hemD-hemE, pACYCDuet-2-hemB-hemC-hemD-hemE.
[0065] The fragment hemF amplified from the Es...
Embodiment 3
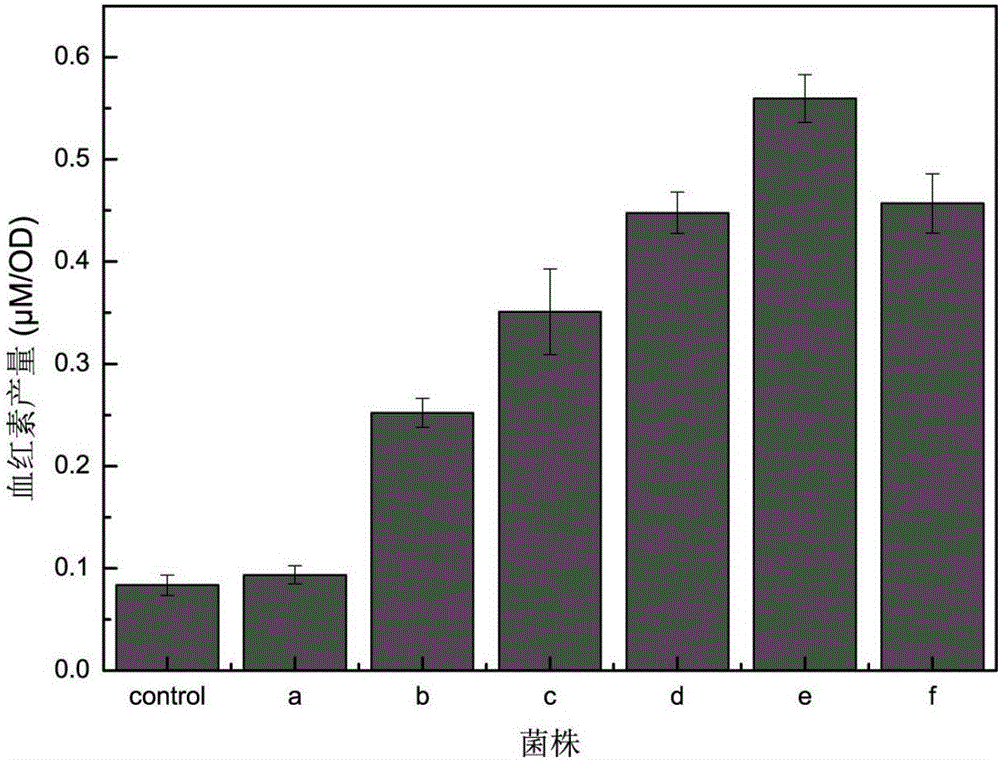
[0072] Embodiment 3 Recombinant bacteria shaking flask fermentation verification
[0073] With E.coli DH5α: pUC19-hemA-hemL as the control,
[0074] Recombinant strains:
[0075] (a) E.coli DH5α: pUC19-hemA-hemL+pRSFDuet-2-hemB-hemC-hemD-hemE+pCDFDuet-2-hemF-hemG-hemH;
[0076] (b) E.coli DH5α: pUC19-hemA-hemL+pRSFDuet-2-hemB-hemC-hemD-hemE+pACYCDuet-2-hemF-hemG-hemH;
[0077] (c) E.coli DH5α: pUC19-hemA-hemL+pCDFDuet-2-hemB-hemC-hemD-hemE+pRSFDuet-2-hemF-hemG-hemH;
[0078] (d) E.coli DH5α: pUC19-hemA-hemL+pCDFDuet-2-hemB-hemC-hemD-hemE+pACYCDuet-2-hemF-hemG-hemH;
[0079] (e) E.coli DH5α: pUC19-hemA-hemL+pACYCDuet-2-hemB-hemC-hemD-hemE+pRSFDuet-2-hemF-hemG-hemH;
[0080] (f) E. coli DH5α: pUC19-hemA-hemL+pACYCDuet-2-hemB-hemC-hemD-hemE+pCDFDuet-2-hemF-hemG-hemH.
[0081] Ferment the recombinant Escherichia coli (a), (b), (c), (d), (e), (f) and the control strain in 250mL Erlenmeyer flasks respectively, the inoculum size is 1%, and the initial glucose concentration is 20...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com