Co-dominant SSR markers closely linked to tobacco TMV resistant gene N and application of co-dominant SSR markers
A resistance gene and co-dominant technology, applied in the direction of DNA / RNA fragments, recombinant DNA technology, microbial measurement / inspection, etc., can solve the problems of cumbersome detection system, PCR amplification failure, and inability to distinguish all genotypes, etc. Achieve the effect of low cost and fast cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Screening of co-dominant SSR markers N-linked to tobacco anti-TMV gene by Bulked Segregation Analysis (BSA)
[0031] 1. Experimental materials
[0032] The flue-cured tobacco Y3 with excellent comprehensive traits but susceptible to TMV was used as the female parent, and the TMV-resistant flue-cured tobacco material Coker176 (whose resistance was controlled by the N gene) was used as the male parent. In 2014, the TMV-resistant and susceptible parent materials were planted, and F1 was obtained by crossing. In 2015, F1 and two parents were planted, and Y3 was used as the recurrent parent, and the backcross generation (BC1F1) population was obtained by crossing. In 2016, two parents, F1 and BC1F1 generation materials were planted.
[0033] 2. Identification of TMV resistance in parents and BC1F1 isolates
[0034] The test materials were transplanted to the field after they became seedlings, with a row-to-plant spacing of 100cm × 50cm; 3 weeks after transplanting, artific...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Map Distance of Codominant Linkage Markers and Its Validation in Individual Plants of BC1F1 Population
[0052] 1. Data analysis
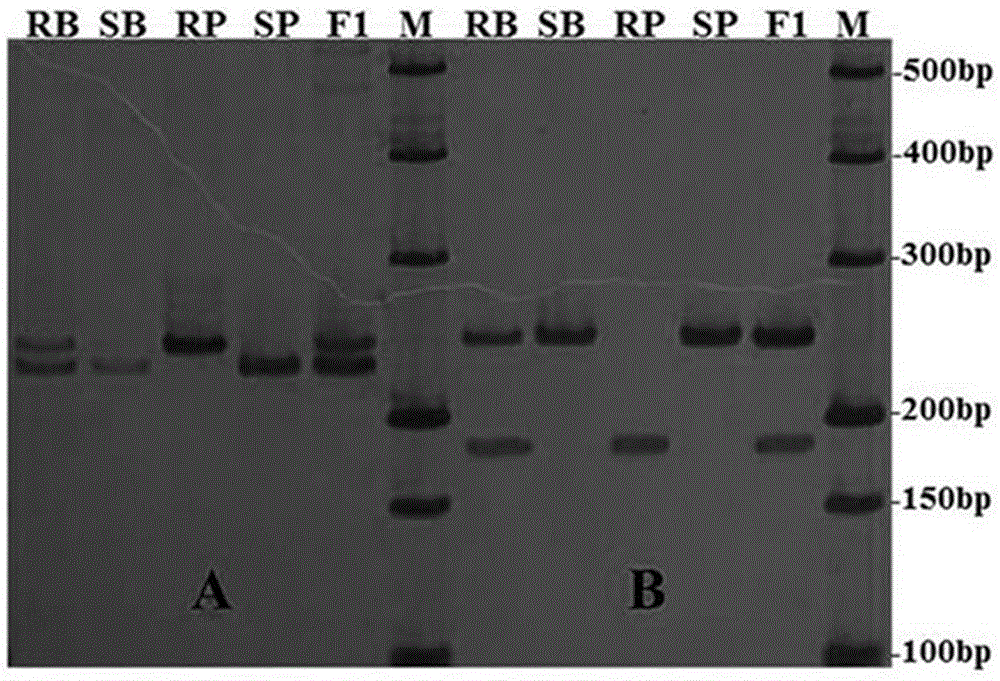
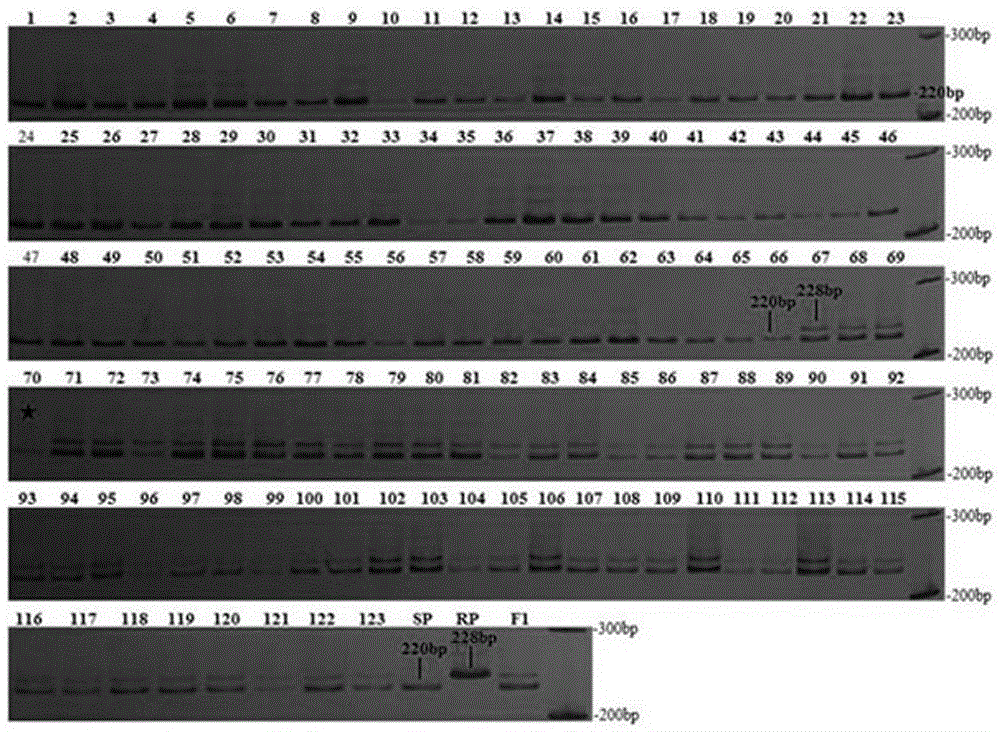
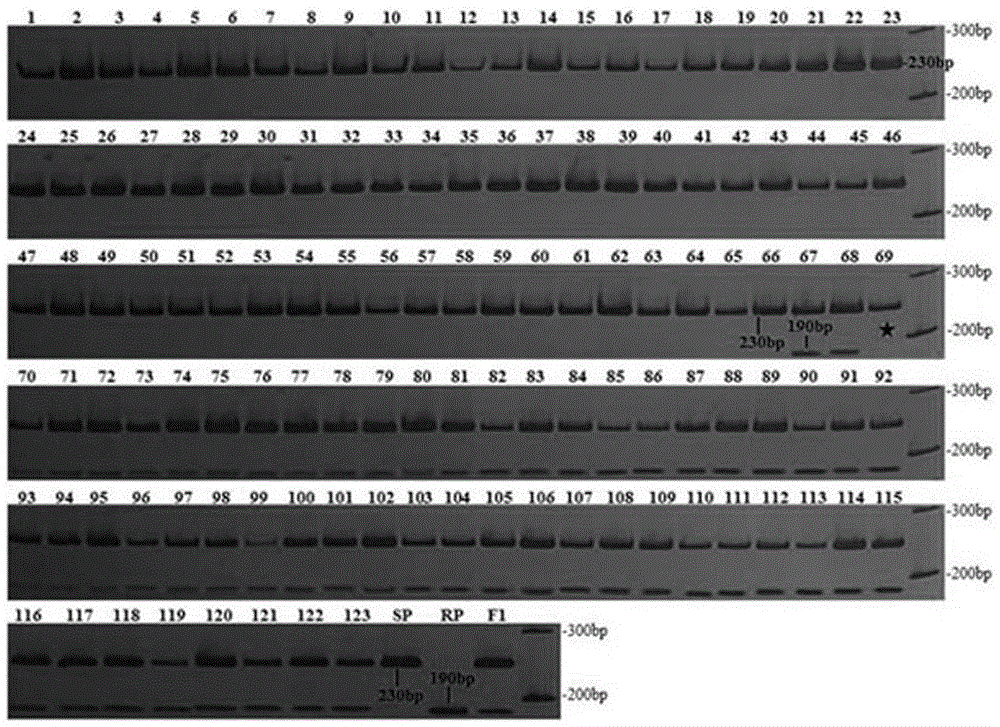
[0053] First, extract and purify tobacco genome DNA, identify TMV resistance of individual plants of BC1F1 population and analyze SSR markers according to the method described in Example 1. Secondly, 123 individual plants in the BC1F1 population were genotyped using the markers TM508-007 and TM508-118 obtained by BSA screening. Finally, carry out data statistics on the band type of each individual plant. The resistant heterozygous band is marked as "H", the susceptible band is marked as "A", and the bands with unclear or no amplification bands are marked as "U". ".
[0054] 2. Calculation of genetic distance of co-dominant linked markers
[0055] Using JoinMap 4.0 software combined with the TMV resistance identification data of individual plants in BC1F1 population, genetic linkage analysis was carried out on the genotype data of co-domin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com