Statistics-based method for improving one-dimensional spectral signal-to-noise ratio of nuclear magnetic resonance
A kind of nuclear magnetic resonance and signal-to-noise ratio technology, which is used in magnetic resonance measurement, measurement using nuclear magnetic resonance imaging system, measurement of magnetic variables, etc. Line broadening effect, signal-to-noise ratio improvement effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
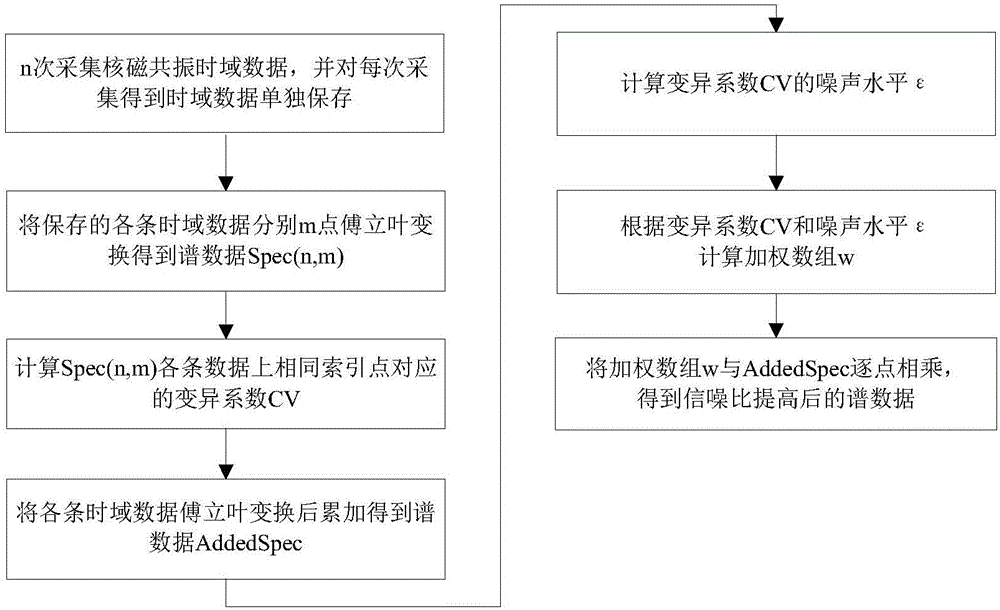
[0039] A method for improving the signal-to-noise ratio of one-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum based on statistics, the overall flow chart is as follows figure 1 As shown, the method generally includes the following steps:
[0040]Step 1, the nuclear magnetic resonance instrument loads the set pulse sequence and sampling parameters, and performs multiple scans and acquisitions on the nuclear magnetic resonance FID signal; (in this embodiment: the pulse sequence is a single pulse, and the sampling parameters mainly include the observation core = 13 C, spectral width sw=30kHz, sampling time acqutime=1s, number of sampling points=30k)
[0041] Step 2, saving the nuclear magnetic resonance FID signals collected by each scan in step 1 respectively;
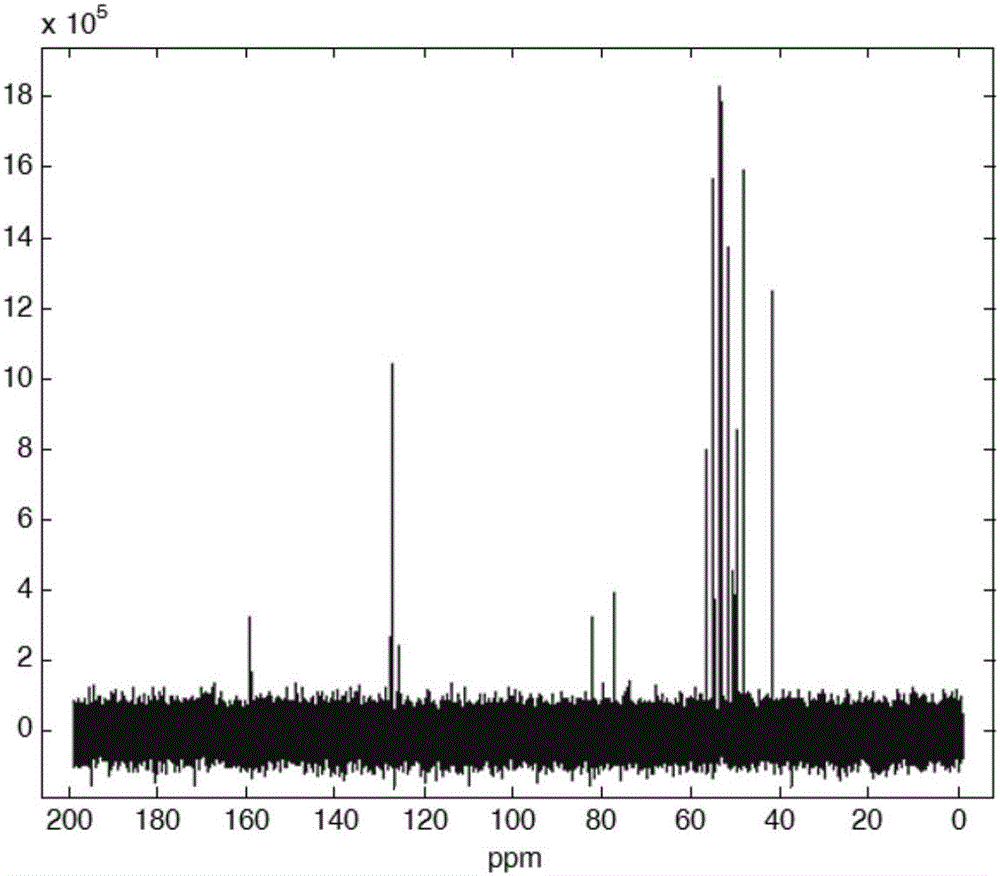
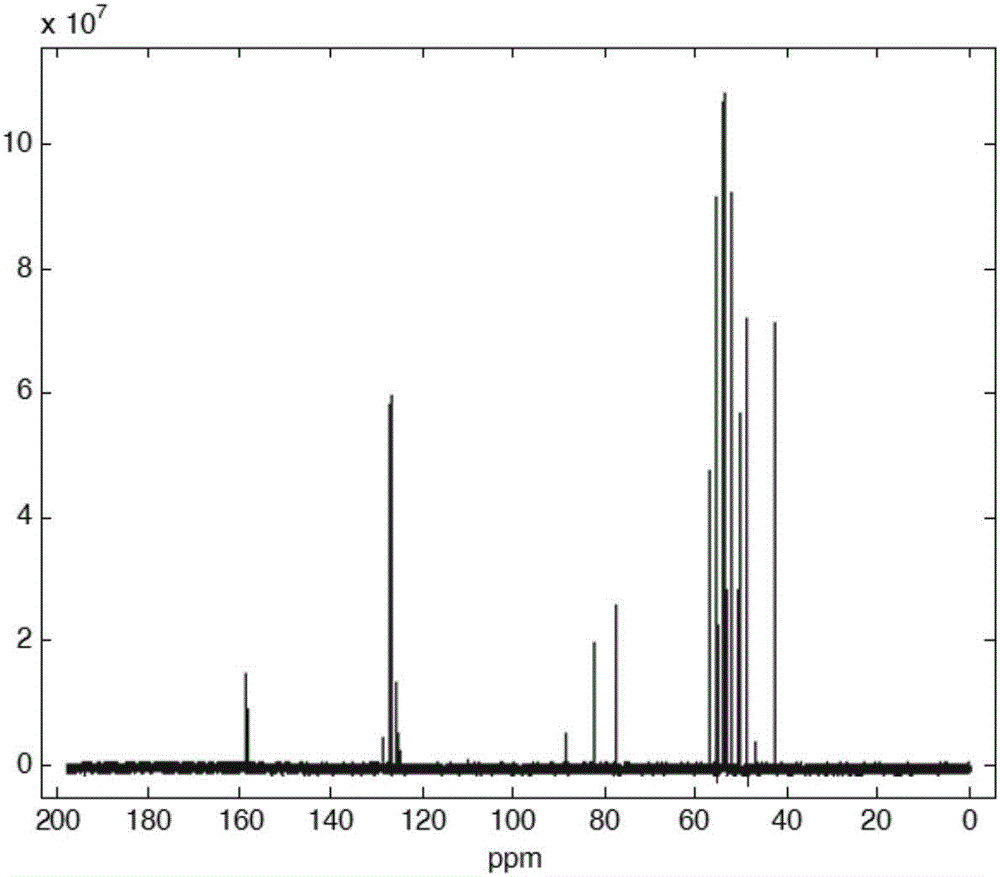
[0042] Step 3, perform Fourier transform on the nuclear magnetic resonance FID signal corresponding to each scan in step 2, obtain the corresponding spectral data of each scan and form a two-dimensional array Spec(n, m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com