High-temperature compound polymerization inhibitor used in rectification process of aromatic alkene monomer and application thereof
A rectification process, a technology for aromatic olefins, which is applied in the purification/separation of hydrocarbons, hydrocarbons, chemical instruments and methods, etc. Reduce the cost of use, avoid potential safety hazards, avoid the effect of explosion or blockage of pipelines
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with embodiment, but it does not limit the implementation of the present invention.
Embodiment 1~12
[0033] Weigh the three components A, B, and C according to a certain proportion, add them into the four-necked flask together with styrene, add a condenser above the four-necked flask, and replace the air in the system with nitrogen for 5 minutes to Reduce the oxygen content in the flask, then seal the system, heat the four-neck flask in a constant temperature heater, and heat it at a constant temperature at 125°C for 2 hours, and take samples to analyze the content of polystyrene in styrene.
[0034] Determination of the amount of polymer produced by gravimetric method: taking advantage of the property that the polymer is insoluble in methanol, add enough dry methanol to the sample to completely precipitate the polymer, then filter, dry, weigh, and keep the weight constant to obtain The mass of polymer produced.
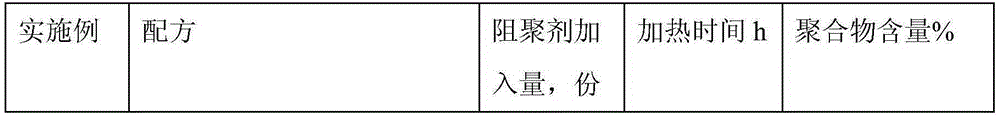
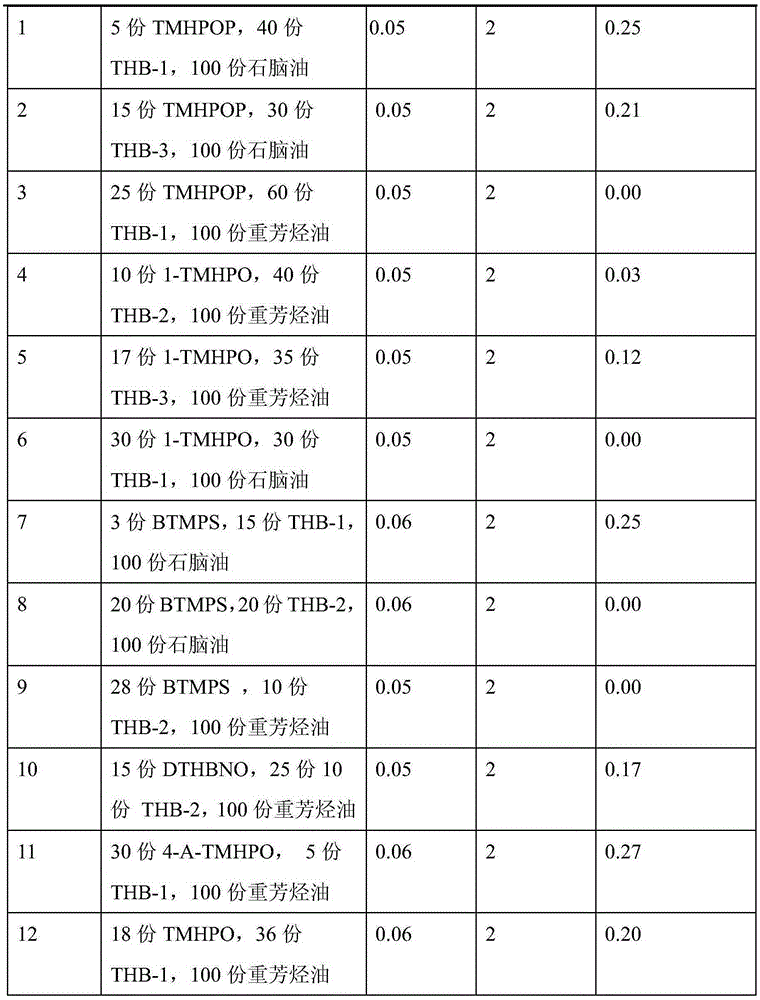
[0035] The formula of embodiment 1-12 and experimental result thereof are as shown in table 1, and in the table, the distribution ratio of each component of polymer...
Embodiment 13
[0043] Prepare a polymerization inhibitor according to the process described in Example 1, and add it to styrene, keep the temperature at 125°C for 3 hours, sample and analyze the content of polystyrene in styrene, wherein the compounded polymerization inhibitor is: 20 parts 1-TMHPO (component A), 20 parts THB-3 (component B), 100 parts naphtha. Based on the mass of styrene as 100 parts, the changes in the polymerization inhibition effect under the conditions of different polymerization inhibitor dosages in Example 13 are shown in Table 2.
[0044] Table 2 Comparison of polymerization inhibition effects at different dosages
[0045] Amount of compounded polymerization inhibitor, parts by mass Polymer content% 0.005 1.21 0.010 0.80 0.030 0.25 0.040 0.06 0.050 0.00 0.070 0.00
[0046] It can be seen that with the increase of the amount of polymerization inhibitor, the effect of polymerization inhibition is obviously improved.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com