Plant dip dyeing liquid used for purifying nitrogen and phosphorus polluted water body and preparation method thereof
A technology for purifying water body and impregnating liquid, applied in water pollutants, chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of difficult separation, harsh regeneration conditions, long adsorption time, etc., to expand the scope of use, reduce Mass transfer resistance, the effect of enhancing the degree of treatment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
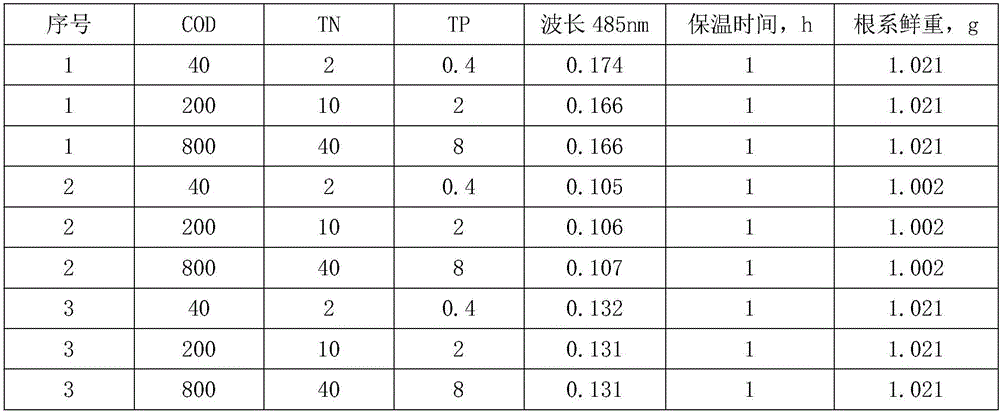
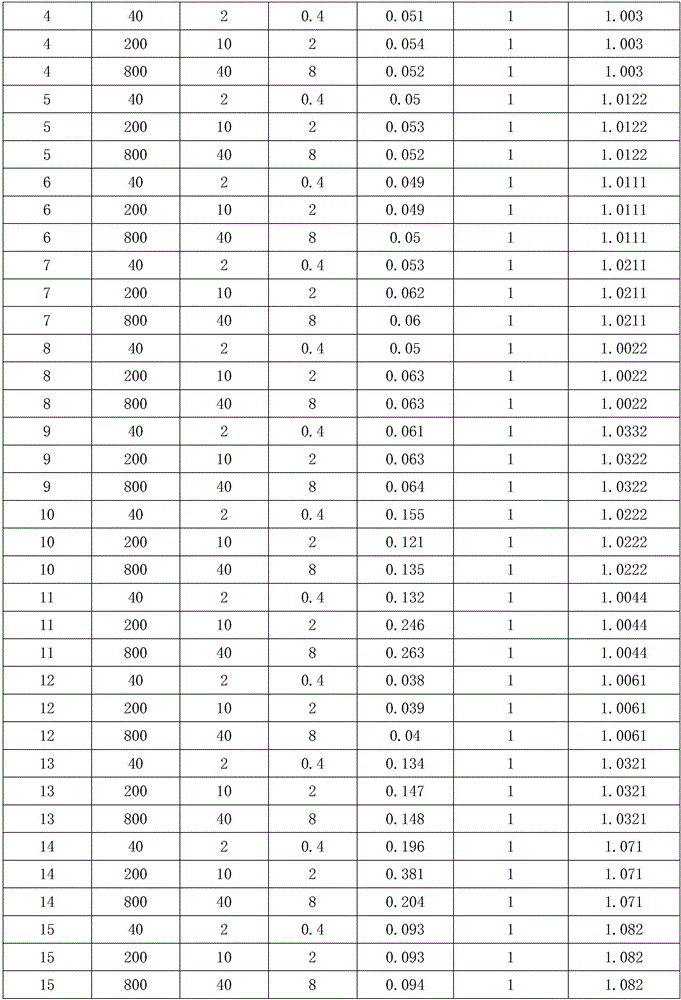
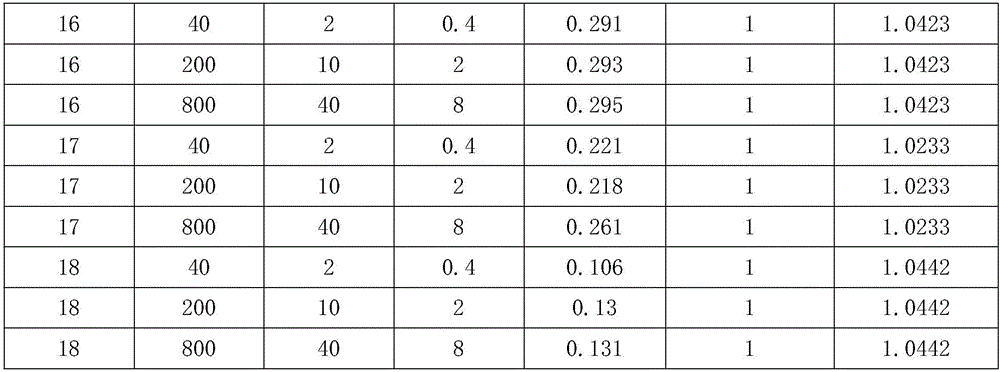
[0026] A plant liquid for purifying nitrogen and phosphorus pollution in water bodies, the formula of which consists of the following raw materials in parts by weight:
[0027] 10 parts of calamus, 10 parts of water spinach, 1 part of potassium permanganate solution, 100 parts of vinyl monomers, 60 parts of clay, 10 parts of auxiliary raw materials, and 500 parts of sterile water.
[0028] Its preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0029] (1) select two kinds of plants of calamus calamus and water spinach as the extracting raw material of liquid;
[0030] (2) The above two plants are completely picked, washed twice with clear water, and then soaked in clear water for 4 hours;
[0031] (3) After crushing and sieving with a micro-crusher, take 6 grams of plant meal;
[0032] (4) After soaking and extracting the obtained plant meal with 0.1% potassium permanganate solution at room temperature for 40 hours, filter the extract with filter paper;
[0033] (5) Add the...
Embodiment 2
[0037] A plant liquid for purifying nitrogen and phosphorus pollution in water bodies, the formula of which consists of the following raw materials in parts by weight:
[0038] 25 parts of calamus, 25 parts of water spinach, 5 parts of potassium permanganate solution, 150 parts of vinyl monomers, 90 parts of clay, 20 parts of auxiliary raw materials, and 750 parts of sterile water.
[0039] Its preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0040] (1) select two kinds of plants of calamus calamus and water spinach as the extracting raw material of liquid;
[0041] (2) The above two plants are completely picked, washed 3 times with clear water, and then soaked in clear water for 5 hours;
[0042] (3) After pulverizing and sieving with a micro-crusher, take 7 grams of plant meal respectively;
[0043] (4) After soaking and extracting the obtained plant meal with 0.1% potassium permanganate solution at room temperature for 50 hours, filter the extract with filter paper;
...
Embodiment 3
[0048] A plant liquid for purifying nitrogen and phosphorus pollution in water bodies, the formula of which consists of the following raw materials in parts by weight:
[0049] 50 parts of calamus, 50 parts of water spinach, 10 parts of potassium permanganate solution, 200 parts of vinyl monomers, 150 parts of clay, 30 parts of auxiliary raw materials, and 1000 parts of sterile water.
[0050] Its preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0051] (1) select two kinds of plants of calamus calamus and water spinach as the extracting raw material of liquid;
[0052] (2) The above two plants are completely picked, washed 5 times with clear water, and then soaked in clear water for 6 hours;
[0053] (3) After pulverizing and sieving with a micro-crusher, take 8 grams of plant meal respectively;
[0054] (4) After soaking and extracting the obtained plant meal with 0.1% potassium permanganate solution at room temperature for 60 hours, filter the extract with filter paper;...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com