Core SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) marker for distinguishing brucella melitensis and brucellaa bortus and application of core SNP marker
A technology for Brucella bovis and Brucella melis, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of complex operation and long time required, and achieve efficient identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1 is used to distinguish the acquisition of the core SNP marker of sheep species and brucella bovis
[0027] 1. Brucella strain selection
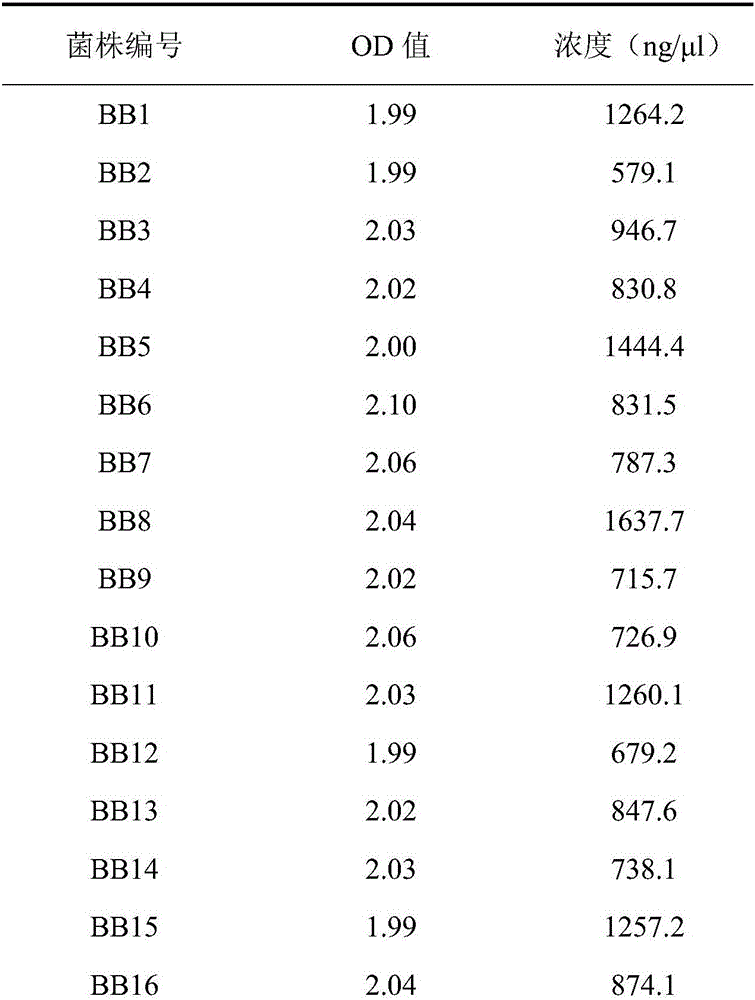
[0028] The research subjects selected 20 strains of Brucella preserved in the Brucella strain collection of the Institute of Brucella Infectious Diseases Prevention and Control, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Among them, there are 15 sheep breeds, 3 cattle breeds and 2 pig breeds. The strains were collected and isolated from 10 provinces (autonomous regions) including Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Heilongjiang Province, Shandong Province, and Gansu Province, and verified by morphological and biochemical identification to determine the type of the strain. The other 55 bacteria (including one reference strain) in this example were downloaded from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) GenBank database (http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / genome / ).
[0029] 2. Genomic DNA extraction of Bru...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Example 2 Two pairs of primer detection sensitivity and specificity evaluation
[0066] 1. Sensitivity evaluation of two pairs of primers
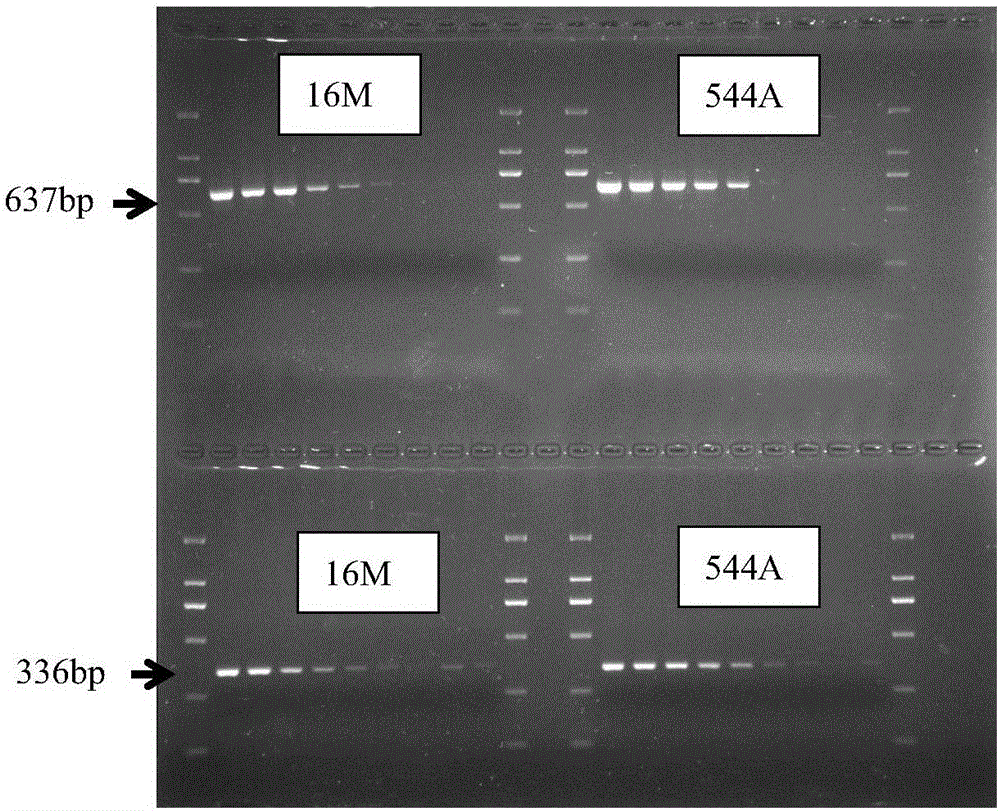
[0067] The nucleic acids of the standard strains of Brucella melis 16M and Brucella bovis 544A were respectively diluted to a concentration of 1:1, 1:10, 1:100, 1:1000, 1:10 4 , 1:10 5 , 1:10 6 , 1:10 7 , 1:10 8 . Two pairs of primers were used to amplify, and the amplification results were shown in figure 1 (Upper is BOV_A0392 primer, lower is BOV_0551 primer). The results showed that the sensitivity of BOV_0551 primer was higher than that of BOV_A0392, and it was preferentially used as a primer for identification (Table 3).
[0068] table 3
[0069]
[0070] 2. Evaluation of detection specificity of two pairs of primers
[0071] Bartonella henselae, Vibrio cholerae, Francisella tularensis, Escherichia coli O:157, Escherichia coli O:16, Enterocolitica yeres that have serological cross-reactivity with Brucella or are clo...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Application of two pairs of primers in the detection of local brucella bacterial strains in embodiment 3
[0073] PCR was performed on the DNA of 100 strains of Brucella (60 strains of Goreum, 50 strains of Bovis, 30 strains of Suis and 20 strains of Canis) isolated in different ages and regions and had been biochemically identified Post-amplification sequencing evaluation. Specific SNP information appeared in all M. melis and B. bovis, with a specificity of 100%. For the sequence comparison results of the amplified products of some strains to be tested, see figure 2 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com