Method for determining influence of genetic variation on function based on genomic environment
A genetic variation and genome technology, applied in the field of determining the functional impact of genetic variation based on the genome environment, can solve the problem of not being able to accurately and directly point out the specific impact of variation on biological pathways, avoiding annotation errors and improving accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1: Annotation of protein-coding genes
[0028] In this example, the method of the present invention is used to annotate protein-coding genes.
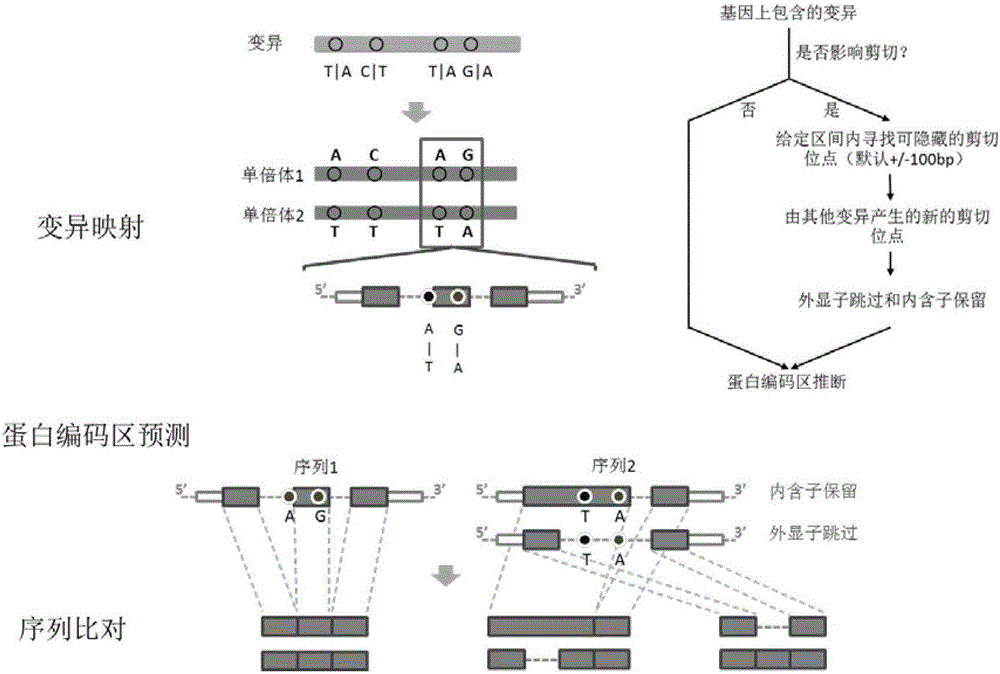
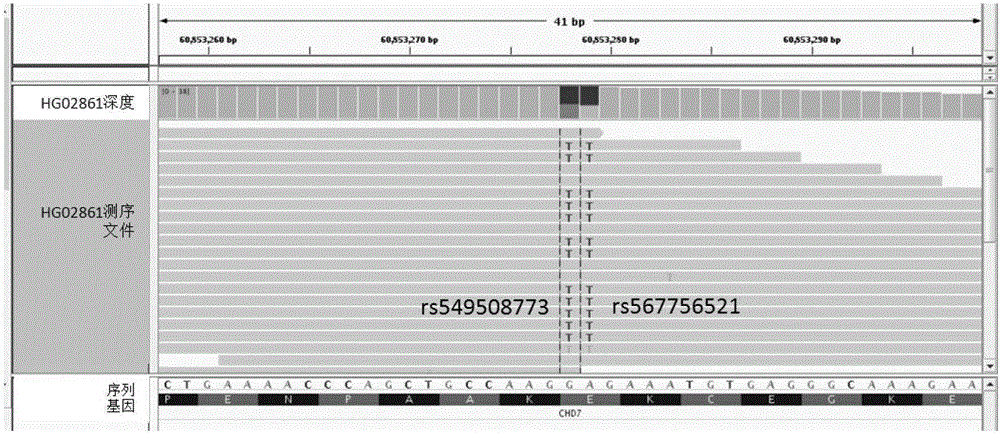
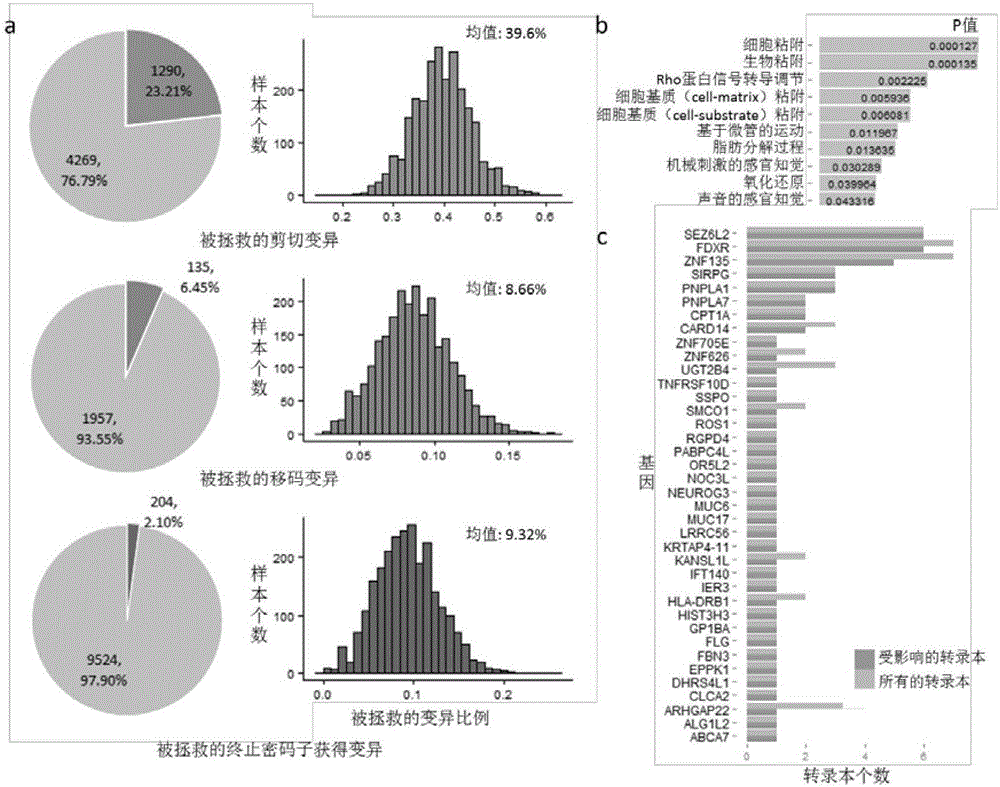
[0029] For the annotation of protein-coding genes, the following steps can be carried out: 1) Map the variation to each gene of a given gene model according to its coordinate position; 2) Infer the protein-coding region of the gene according to all the variations on each gene; specifically Specifically, for transcripts containing variants that affect splicing, search for hidden splicing sites within a given interval (+ / -100bp by default), as well as new splicing sites caused by other variants. For transcripts for which no alternative splice sites could be found, both exon skipping and intron retention were considered. 3) Translate it into a protein sequence according to the sequence of the obtained protein coding region; 4) Compare the obtained protein sequence with the known reference protein sequence to determine the ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2: Annotation of transcription factor binding sites
[0033] In this example, the method of the present invention is used to annotate transcription factor binding sites.
[0034] The annotation of transcription factor binding sites is divided into loss of transcription factor binding sites (TFBS loss) and transcription factor binding site gain (TFBS gain). For the prediction of the loss of transcription factor binding sites, it is judged whether there is a loss of transcription factor binding sites by comparing the score of the site weight matrix corresponding to the sequence before and after the mutation. On the other hand, for the prediction of transcription factor binding sites, first find out all the variations in the promoter, and then reconstruct the promoter sequence. Then, the transcription factor binding sites were predicted according to the site weight matrix. Figure 4 A flowchart showing the annotation of transcription factor binding sites using th...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3: Annotation to microRNA
[0038] In this example, the method of the present invention is used to annotate microRNA.
[0039] For the annotation of miRNA, the individualized sequence is also reconstructed according to the given variation to comprehensively judge the impact of the variation on miRNA production and miRNA target sites. For the annotation of microRNA generation, it aims to predict the effect of genomic variation located on pre-microRNA on the minimum free energy of pre-microRNA secondary structure. The tool used here to calculate the minimum free energy of pre-microRNA is RNAfold. First, find all variants on the same pre-microRNA. Then, the real pre-microRNA sequence is reconstructed. Finally, calculate the change of the minimum free energy of the pre-microRNA before and after the genomic variation occurs, and take it as the influence on the generation of microRNA. MicroRNA target binding annotation refers to the effect of predicting variants o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com