Cutting force prediction method considering tooth spacing angles, helical angles and eccentricity of cutter
A prediction method and inter-tooth angle technology, applied in manufacturing tools, measuring/indicating equipment, metal processing equipment, etc., can solve the problems of high experimental cost, high cost, low efficiency, etc., to improve efficiency, high accuracy, reduce cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific example 1
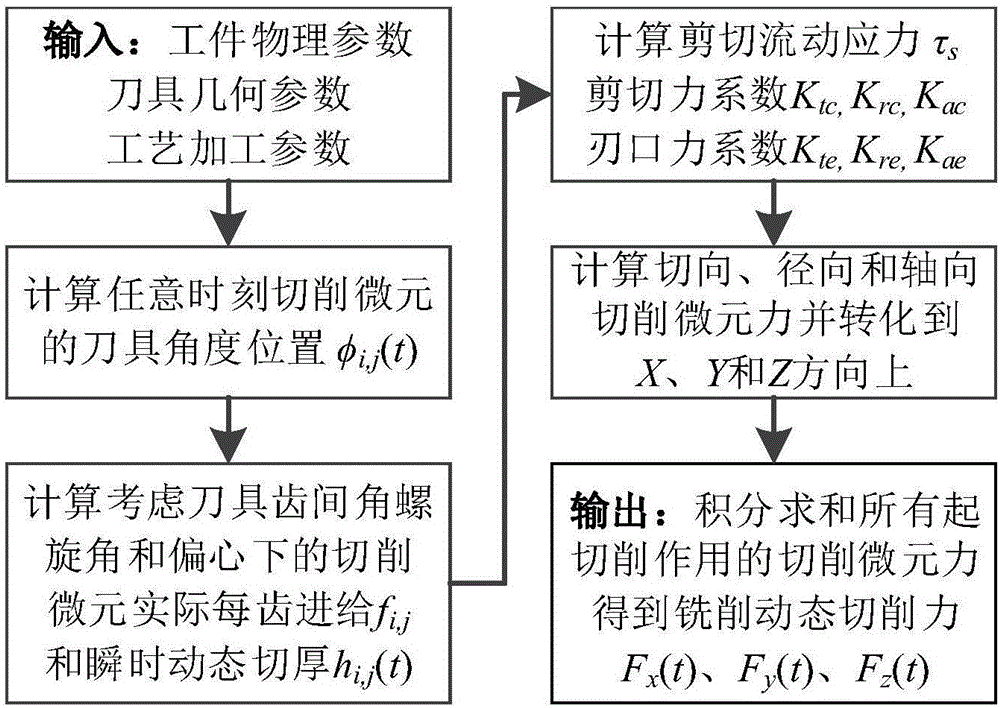
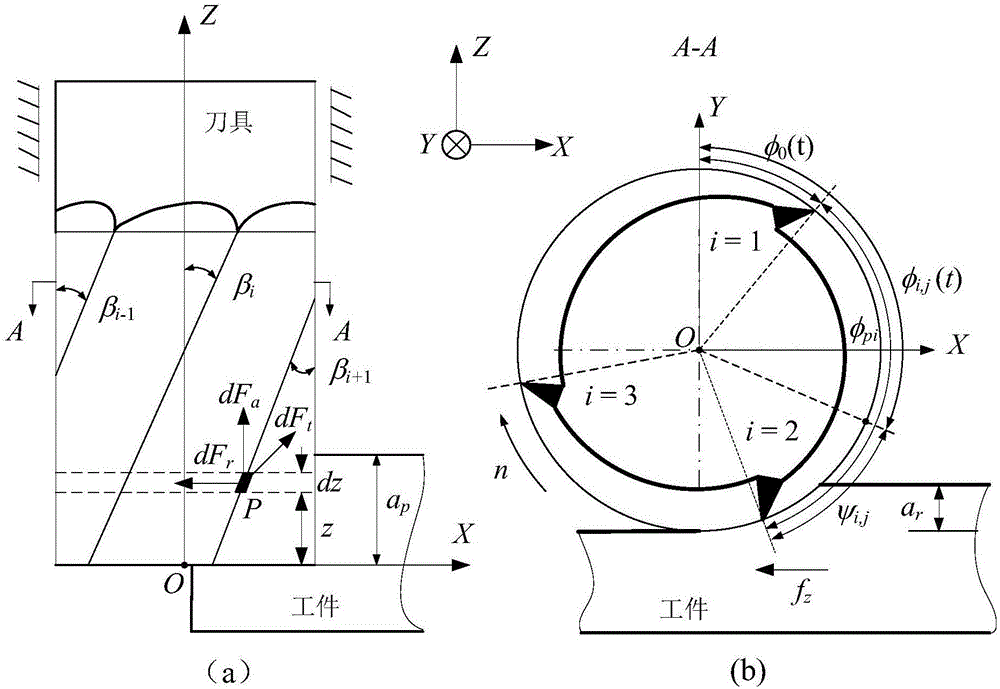
[0067] see image 3 , to predict the milling force of the cemented carbide tool on the aluminum alloy 6061-T6 in the five-axis machining center, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0068] (1) Determine the relevant parameters, the cemented carbide tool is a 3-tooth tool, where the tool diameter D = 8mm, the radial rake angle α n =5°, cutting edge radius r e =20um, inter-tooth angle φ pi =120° / 100° / 140°, helix angle β i =35° / 40° / 30°; spindle speed n=1000RPM, single tooth feed f z =0.1mm / z, axial depth of cut a p =0.5mm, radial cutting width a r = 7mm; After the tool is installed on the spindle, the laser displacement sensor is used to measure the tool eccentricity parameters as eccentricity distance ρ = 2.3mm and eccentricity angle λ = 32.3°, see Table 1 for details.
[0069] Table 1 Milling related parameters
[0070]
[0071](2) The dynamic force measuring instrument 9257A is used to collect the piezoelectric signal in the process of processing in rea...
specific example 2
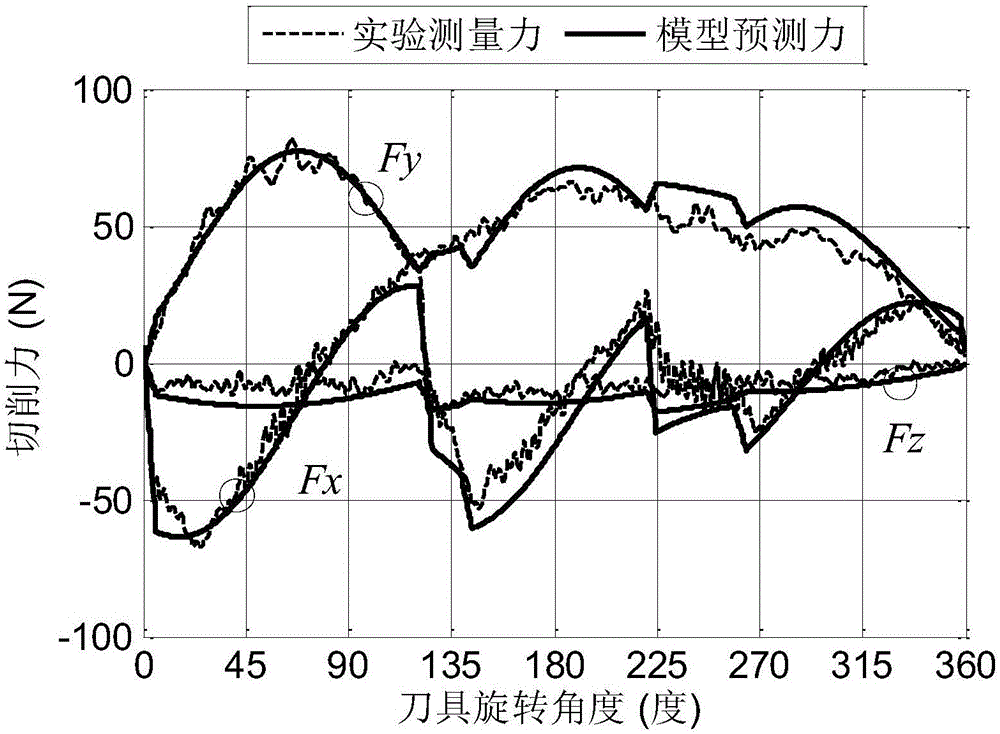
[0089] see Figure 4 , the specific example 2 uses a 3-tooth variable inter-tooth angle cutter to perform down milling on aluminum alloy 6061-T6, and the physical parameters of the workpiece are the same as those in specific example 1; the inter-tooth angle φ pi =120° / 100° / 140°, the rest of the geometric parameters of the tool are the same as in the specific example 1; the process parameter is the axial depth of cut a p =1.5mm, radial cutting width a r =4mm, the eccentric distance ρ=4.3mm and the eccentric angle λ=20.6°, and the rest of the processing parameters are the same as those in the specific example 1.
[0090] Depend on Figure 4 It can be seen that the milling force prediction method considering the interdental angle, helix angle and eccentricity of the tool provided by the present invention is very close to the experimental value for the milling force prediction value of the variable interdental angle tool. It can be seen that the accuracy of the milling force pre...
specific example 3
[0092] see Figure 5 , the specific example 3 uses a 3-tooth variable helix angle tool for down milling of aluminum alloy 6061-T6, the physical parameters of the workpiece are the same as the specific example 1; the tool helix angle β i = 30° / 35° / 40°, the rest of the geometric parameters of the tool are the same as in Example 1; the process parameter is the axial depth of cut a p =1mm, radial cutting width a r =6mm, the eccentricity distance ρ=3.5mm and the eccentricity angle λ=30.8°, and the rest of the processing parameters are the same as those of the concrete example 1.
[0093] Depend on Figure 5 It can be seen that the milling force prediction method considering the interdental angle, helix angle and eccentricity of the tool provided by the present invention is very close to the experimental value for the milling force prediction value of the variable helix angle tool, and it can be seen that the accuracy of the milling force prediction method is relatively high , it...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com