Method for constructing three-dimensional model based on tissue slices
A technology of tissue slices and three-dimensional models, applied in the field of biochemistry, can solve the problems of easy deformation of tissues, inability to display the three-dimensional shape and distribution of antigens, expensive experimental equipment, etc., and achieve the effect of low application threshold
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] In this embodiment, the bright-field 3D reconstruction of cholinergic neurons in mouse brain tissue is taken as an example for illustration.
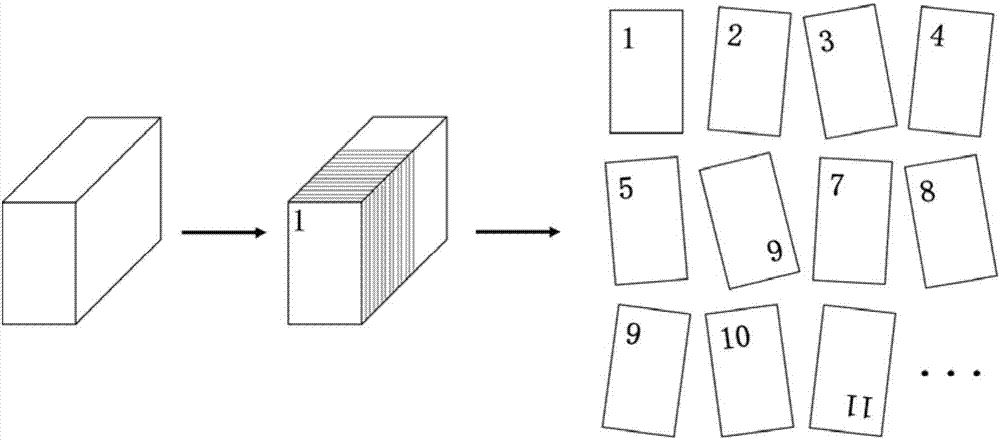
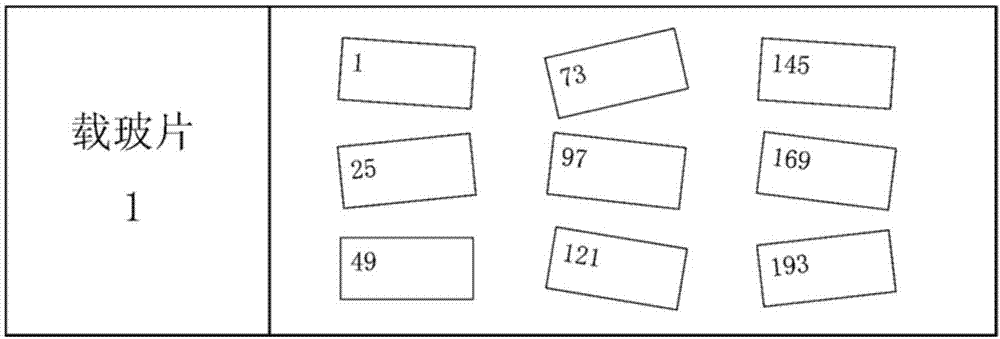
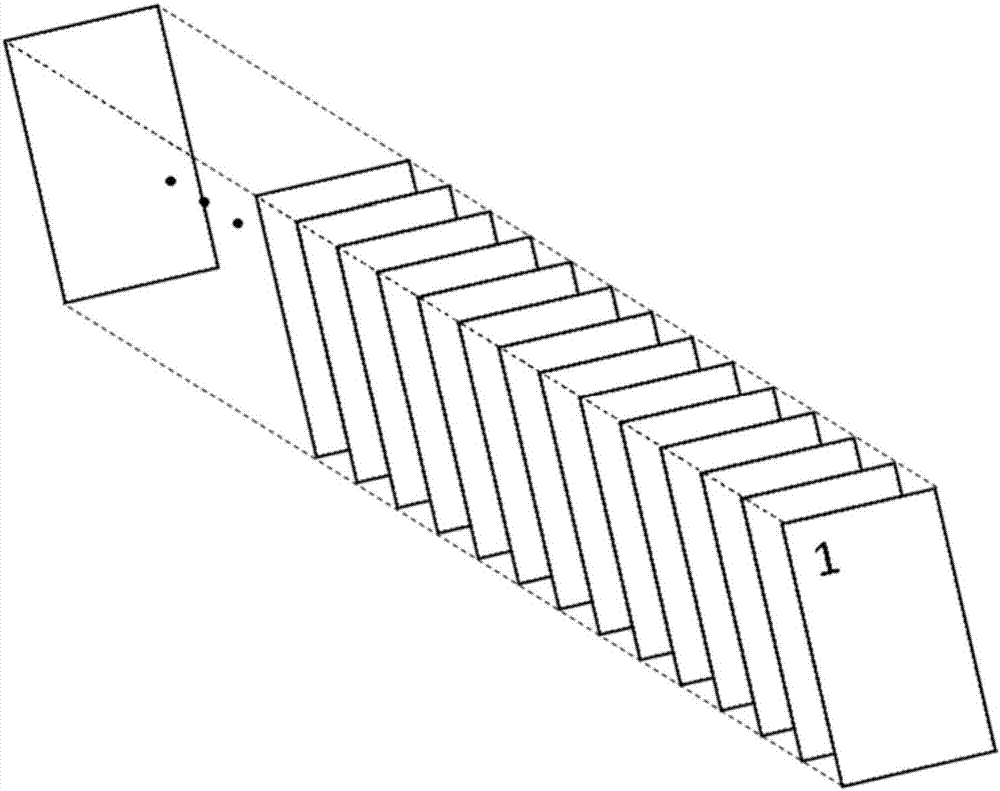
[0032] In the first step, the mouse brain tissue was first sliced serially with a frozen microtome, and the slice thickness was 16 microns, and divided into 24 equal parts. The specific steps were as follows (such as figure 1 as shown, figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of continuous sectioning of animal tissue blocks in an embodiment of the present invention. ):
[0033] 1. Set the parameters of the cryostat (Leica, Germany) (the temperature of the fixed base is 16°C, the temperature of the chassis is 20°C, and the slice thickness is 16 microns), and install a brand-new blade (Leica, Germany), and then wait for 1 hour ;
[0034] 2. Coat the surface of the microtome base with frozen section embedding agent (Sakura, Japan), about 1 mm thick, and use a microtome to flatten the surface after it solidifies;
[0035] ...
Embodiment 2
[0071] In this example, the fluorescent 3D reconstruction of somatostatin-positive neurons in mouse brain tissue is taken as an example for illustration.
[0072] In the first step, the mouse brain tissue was serially sliced with a frozen microtome with a thickness of 16 microns and divided into 24 equal parts. The specific steps are as follows:
[0073] 1. Set the parameters of the cryostat (Leica, Germany) (the temperature of the fixed base is 16°C, the temperature of the chassis is 20°C, and the slice thickness is 16 microns), and install a brand-new blade (Leica, Germany), and then wait for 1 hour ;
[0074] 2. Coat the surface of the microtome seat with tissue embedding agent (Sakura, Japan), about 1 mm thick, and use a microtome to flatten the surface after it solidifies;
[0075] 3. Cut the mouse brain tissue into two equal parts along the sagittal midline, and then poke two small holes in the brain tissue perpendicular to the right brain (or left brain) section (for...
Embodiment 3
[0099] In this example, the fluorescent 3D reconstruction of excitatory neurons in the brain tissue of transgenic mice is taken as an example for illustration.
[0100] In the first step, the mouse brain tissue was serially sliced with a frozen microtome with a thickness of 16 microns and divided into 24 equal parts. The specific steps are as follows:
[0101] 1. Set the parameters of the cryostat (Leica, Germany) (the temperature of the fixed base is 16°C, the temperature of the chassis is 20°C, and the slice thickness is 16 microns), and install a brand-new blade (Leica, Germany), and then wait for 1 hour ;
[0102] 2. Coat the surface of the microtome seat with tissue embedding agent (Sakura, Japan), about 1 mm thick, and use a microtome to flatten the surface after it solidifies;
[0103] 3. Cut the mouse brain tissue into two equal parts along the sagittal midline, and then poke two small holes in the brain tissue perpendicular to the right brain (or left brain) sectio...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com