Cold cathode structure for magnetron and millimeter wave magnetron
A cold cathode and magnetron technology, applied to the cathode of the time-of-flight electron tube, etc., can solve the problems of inability to provide secondary electron emission, unsuitable application of magnetron, and evaporation of materials emitted by the cathode, so as to improve the control of fighters ability, strong resistance to electron return bombardment and ion bombardment, and large emission current
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
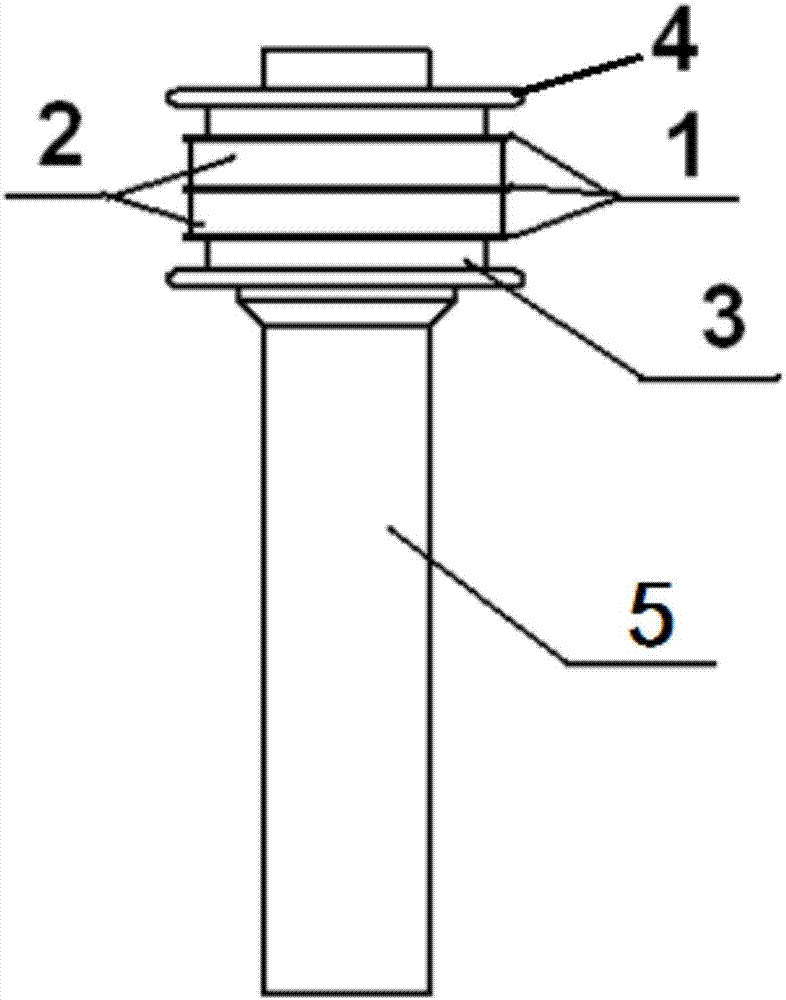
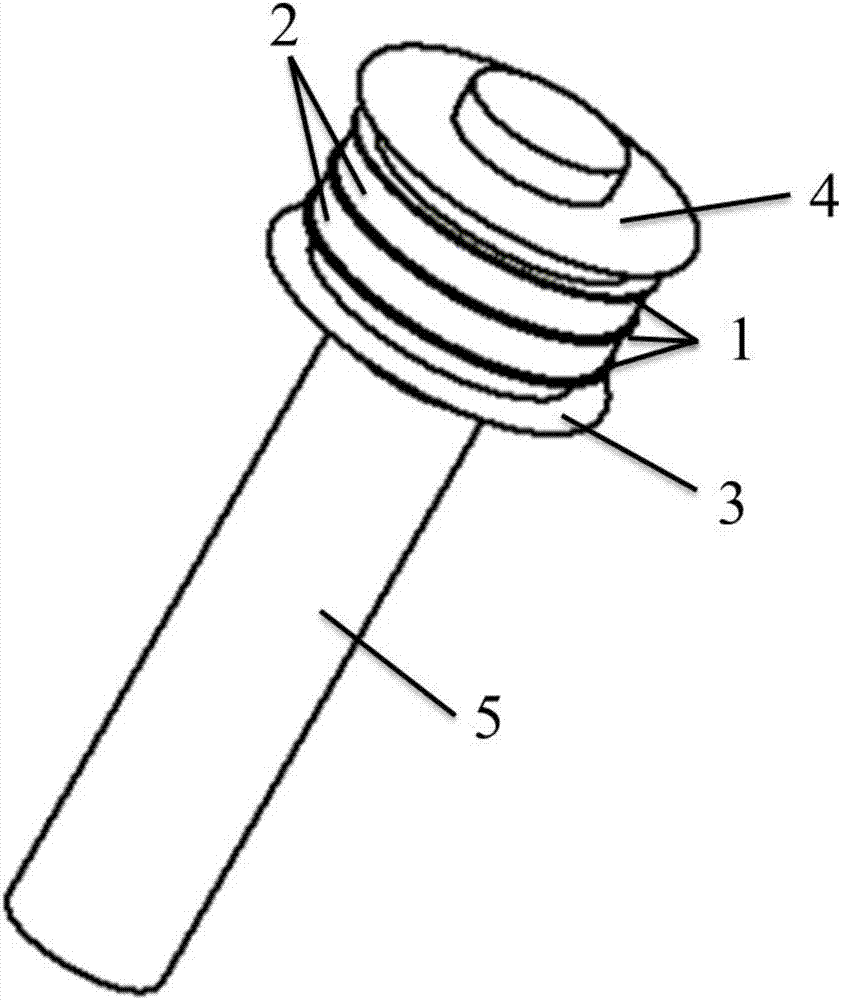
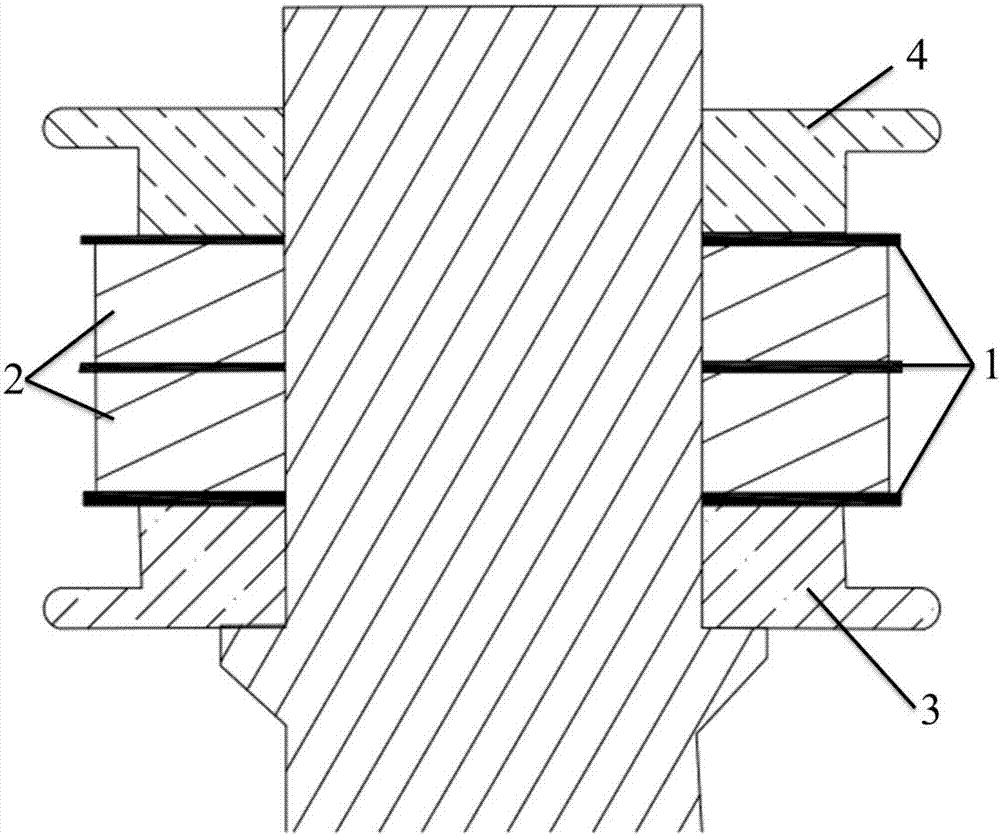
[0045] A cold cathode structure for millimeter wave magnetrons, such as Figure 1~3 As shown, it includes a bottom metal rod 5, an upper shield cap 4 and a lower shield cap 3 sheathed at one end of the bottom metal rod, and a cold cathode emitter arranged between the upper shield cap and the lower shield cap.
[0046] The cold cathode emitter includes three tantalum rings 1 and two palladium-barium rings 2. The tantalum rings and the palladium-barium rings are alternately arranged; the cold cathode emitter is shielded from the upper through the upper end surface of the top tantalum ring and the lower end surface of the bottom tantalum ring The cap 4 and the lower shield cap 3 are tightly connected.
[0047] The cold cathode emitter, the upper shielding cap and the lower shielding cap are all fixed on the bottom metal rod 4 by means of laser welding.
[0048] The bottom metal rod is a cylinder with a diameter of 2.8mm and a height of 20mm. The diameter of the tantalum ring 1 is 5.1 ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The cold cathode structure of Example 1 is used to replace the hot cathode component in the hot cathode magnetron to obtain a new cold cathode magnetron.
[0052] The magnetron is tested, and the magnetron has normal vibration characteristics without obvious hysteresis. The vibration time is less than 5s, and the magnetron works stably. When high voltage (voltage waveform such as Figure 4 After A), the RF envelope is as Figure 4 As shown in middle B, this envelope is consistent with the normal envelope of a hot cathode magnetron, the pulse width reaches the normal pulse width of 400ns, and other electrical parameters are also normal.
[0053] In order to verify the vibration characteristics of this cold cathode, a cold cathode magnetron life test was carried out. The magnetron was cold-started 200 times. After 500 hours of normal operation, the magnetron cold-started normally, and all electrical parameters met the index requirements. Figure 5 It is the output power change c...
Embodiment 3
[0055] A cold cathode structure for a millimeter-wave magnetron is the same as Embodiment 1, except that the bottom metal rod is a cylinder with a diameter of 2.0 mm and a height of 15 mm. The diameter of the tantalum ring is 5.0mm and the thickness is 0.01mm. The diameter of the palladium barium ring is 5.0mm and the thickness is 1.5mm. The total thickness of the cold cathode emitter is 3.03 mm.
[0056] The cold cathode structure is used to replace the hot cathode component in the hot cathode magnetron, and a new cold cathode magnetron is obtained. The magnetron was tested, and the test results met the requirements.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com