Patents
Literature
283 results about "Hot cathode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
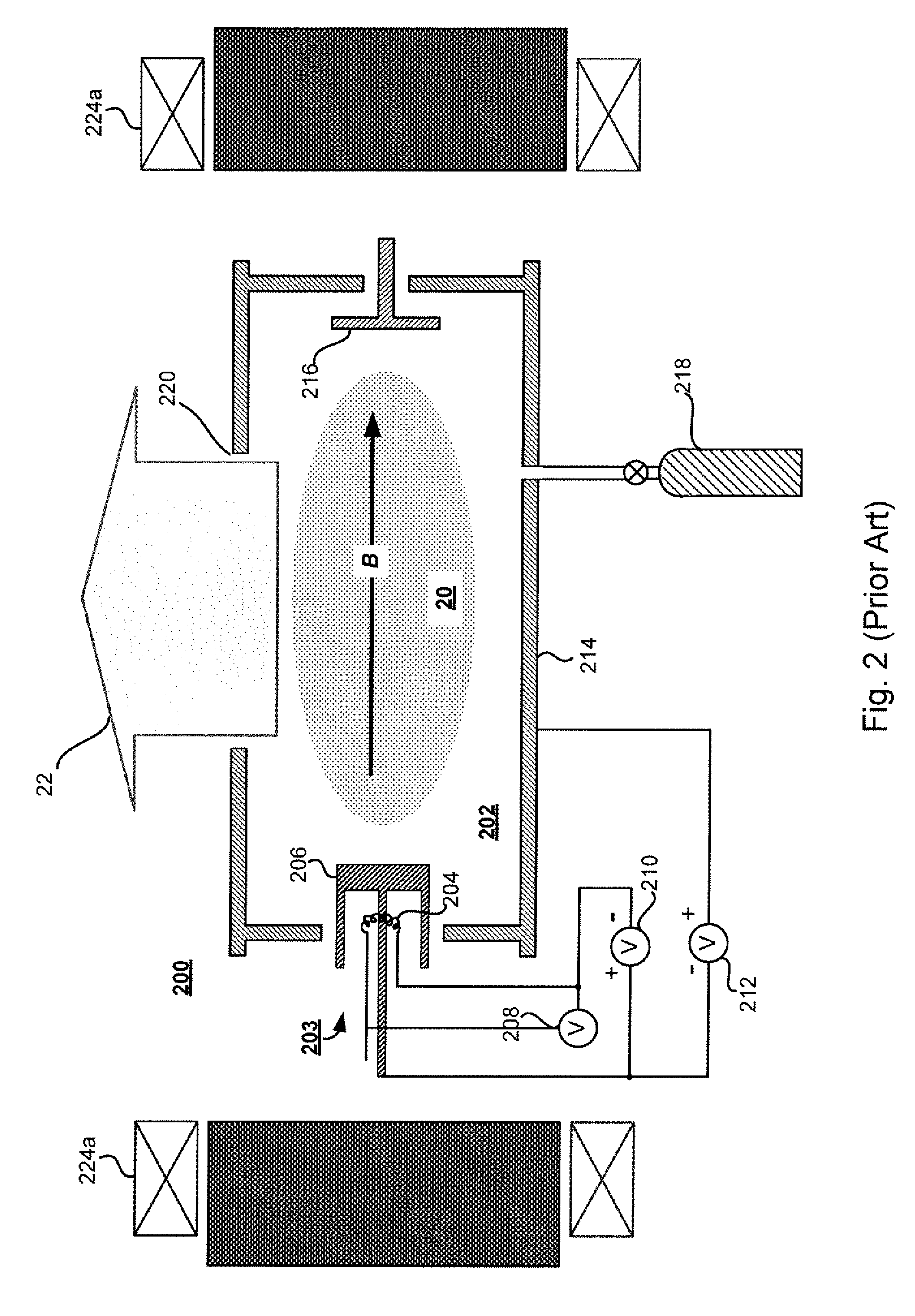
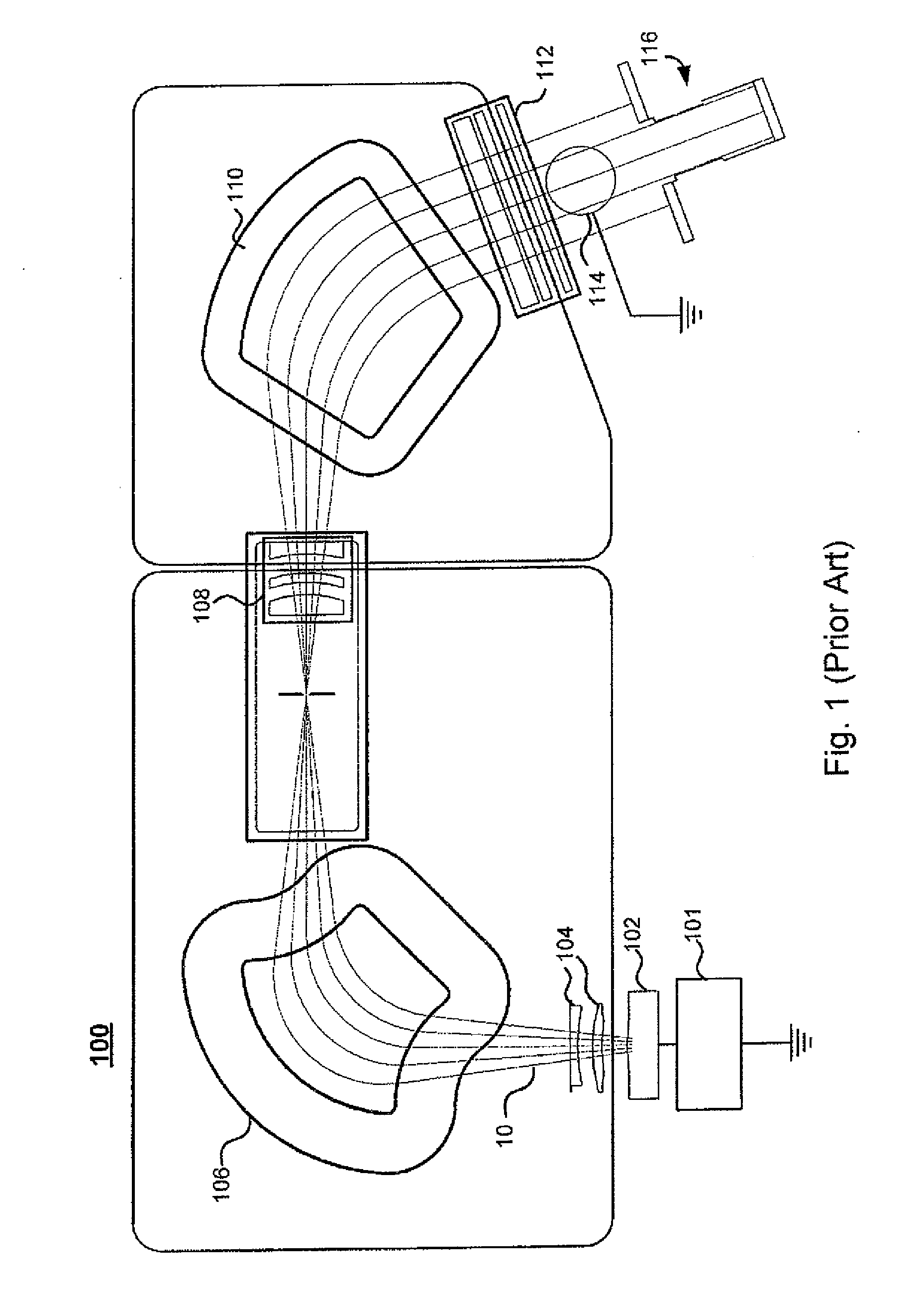
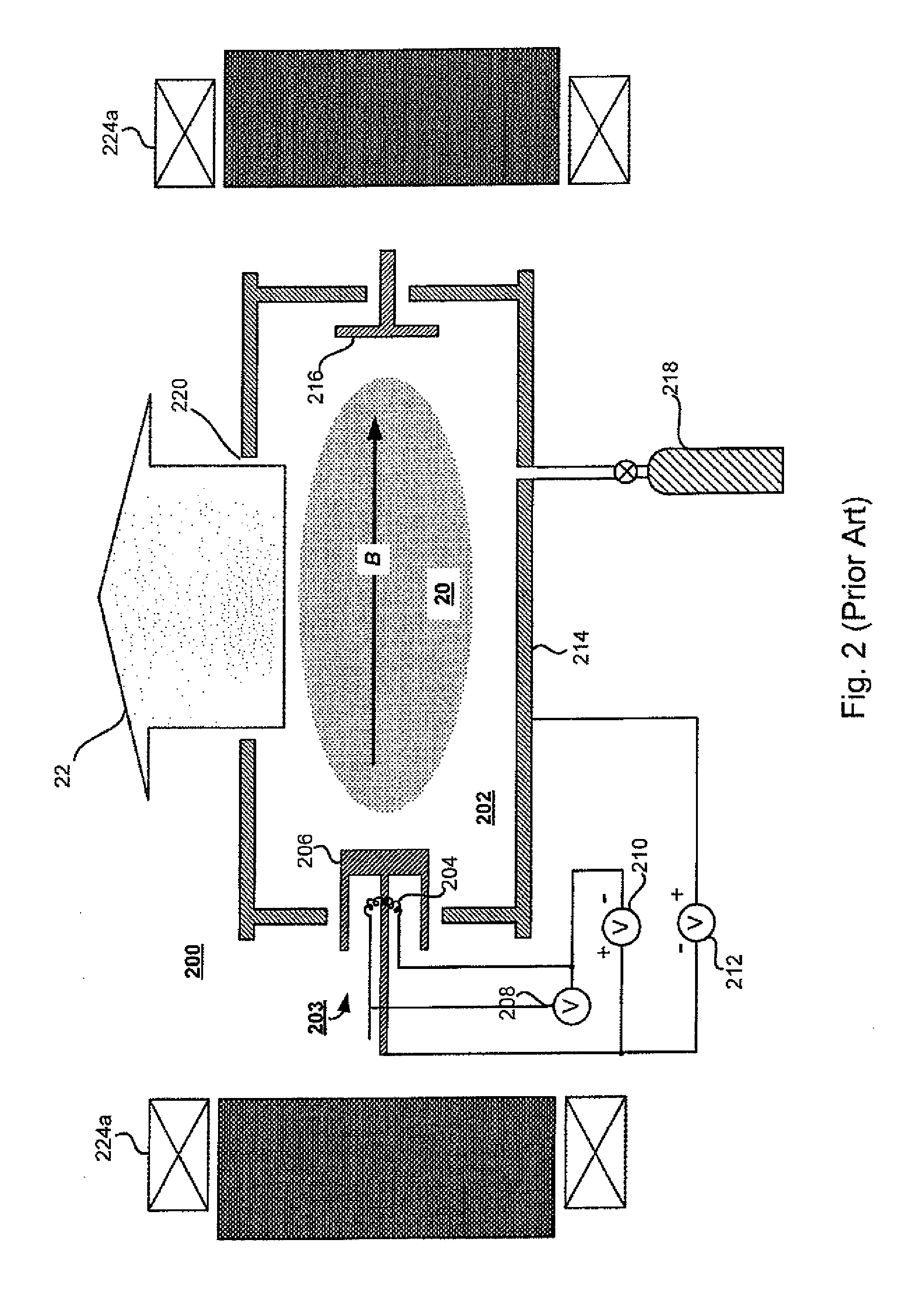
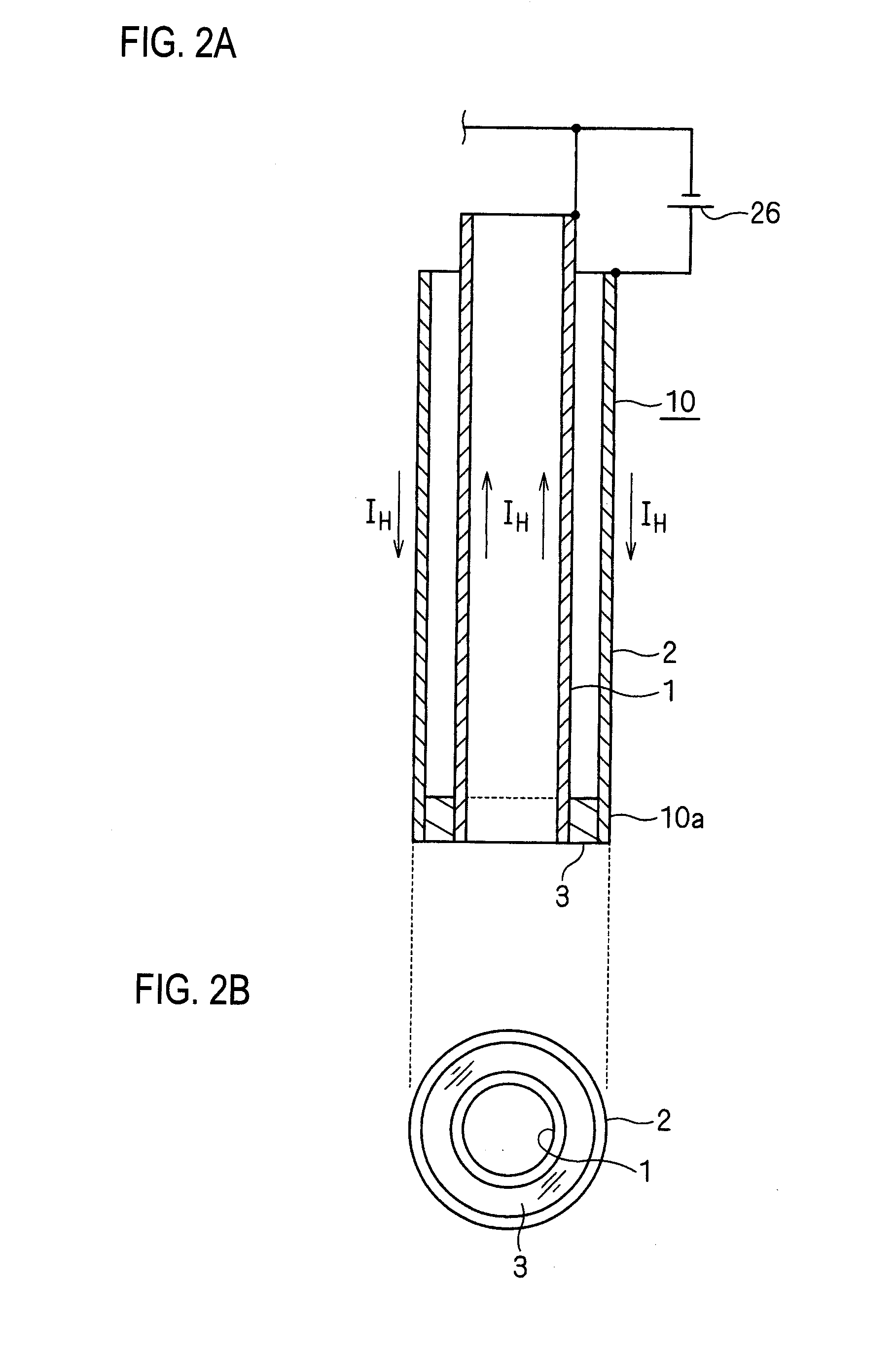
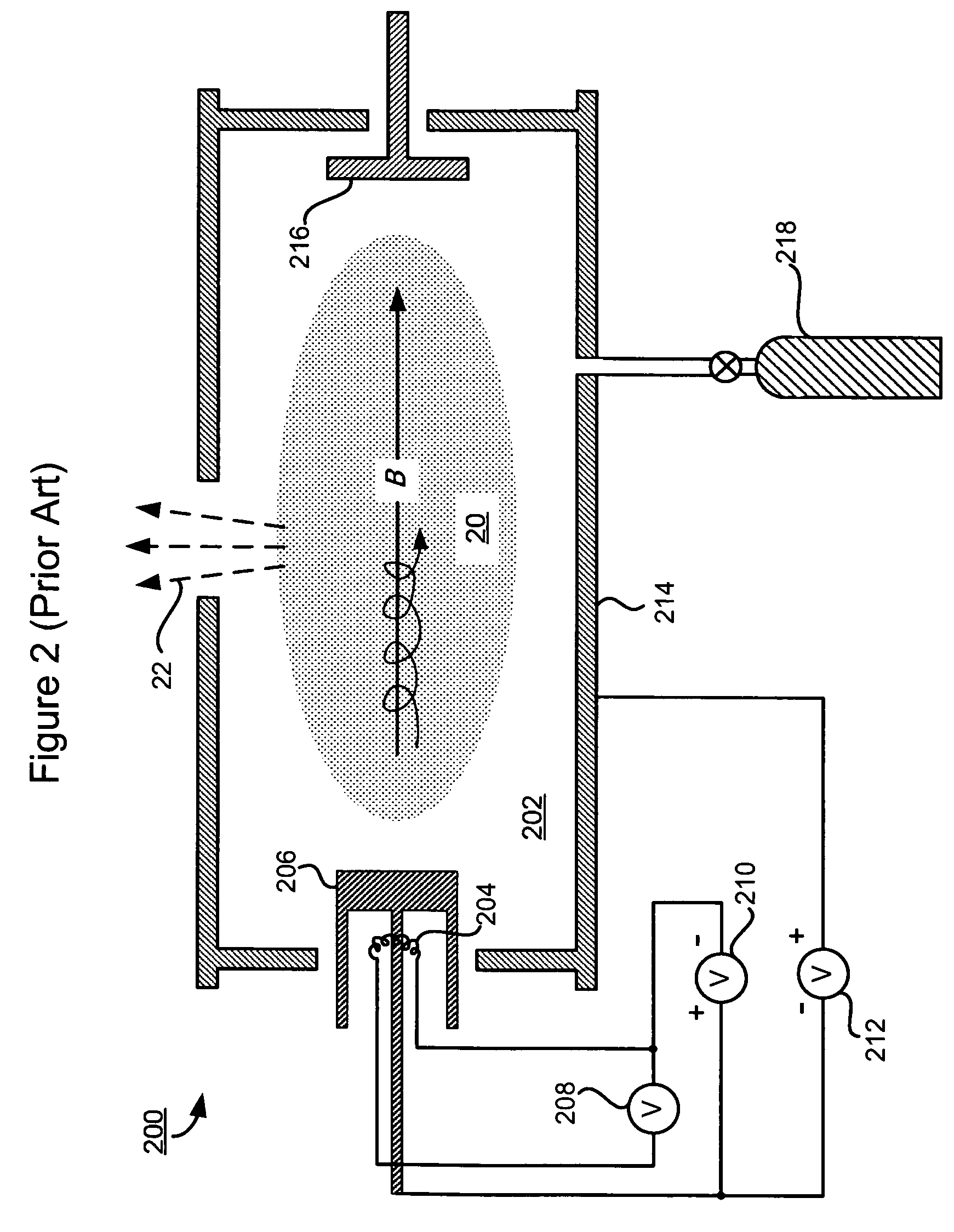
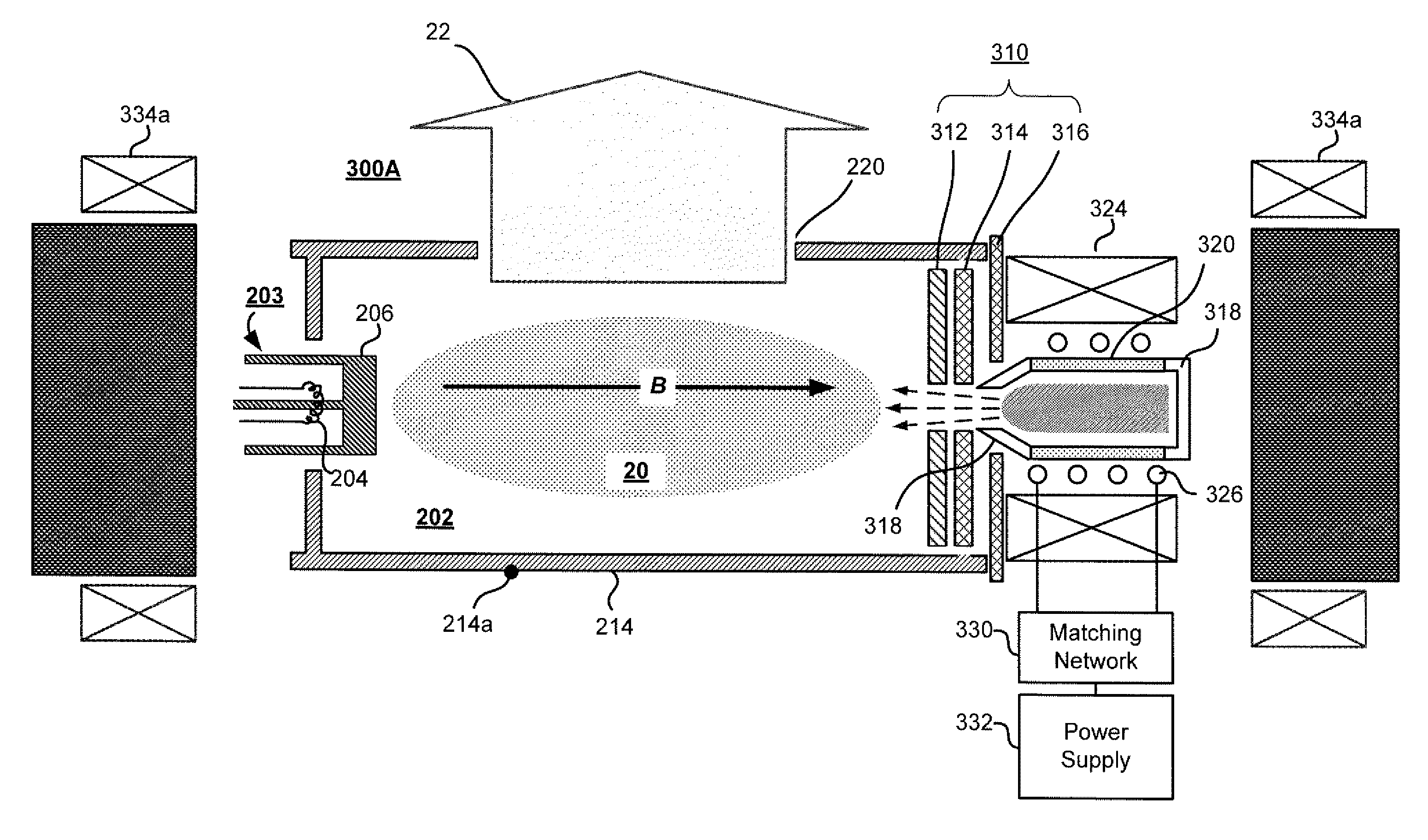
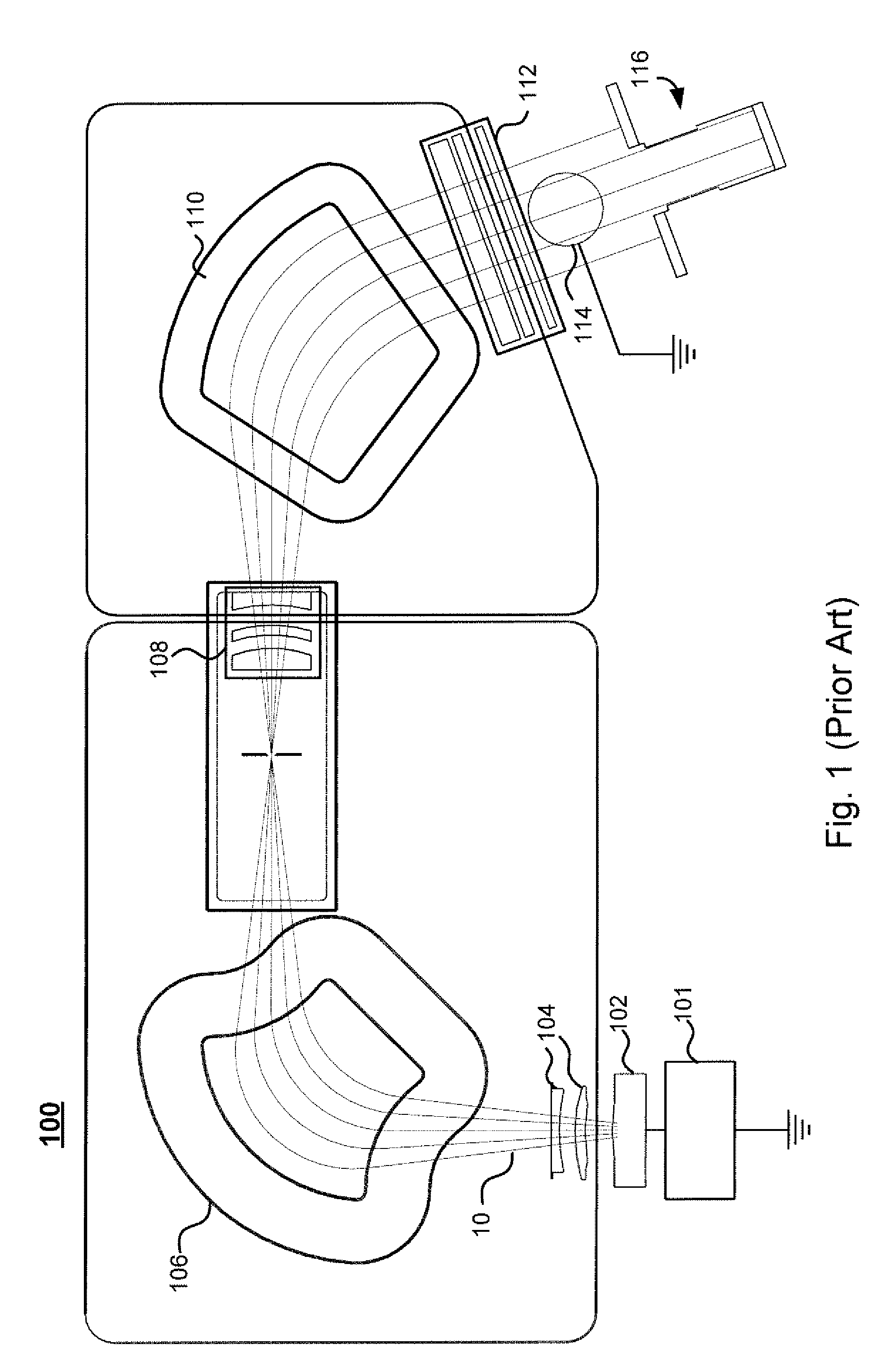
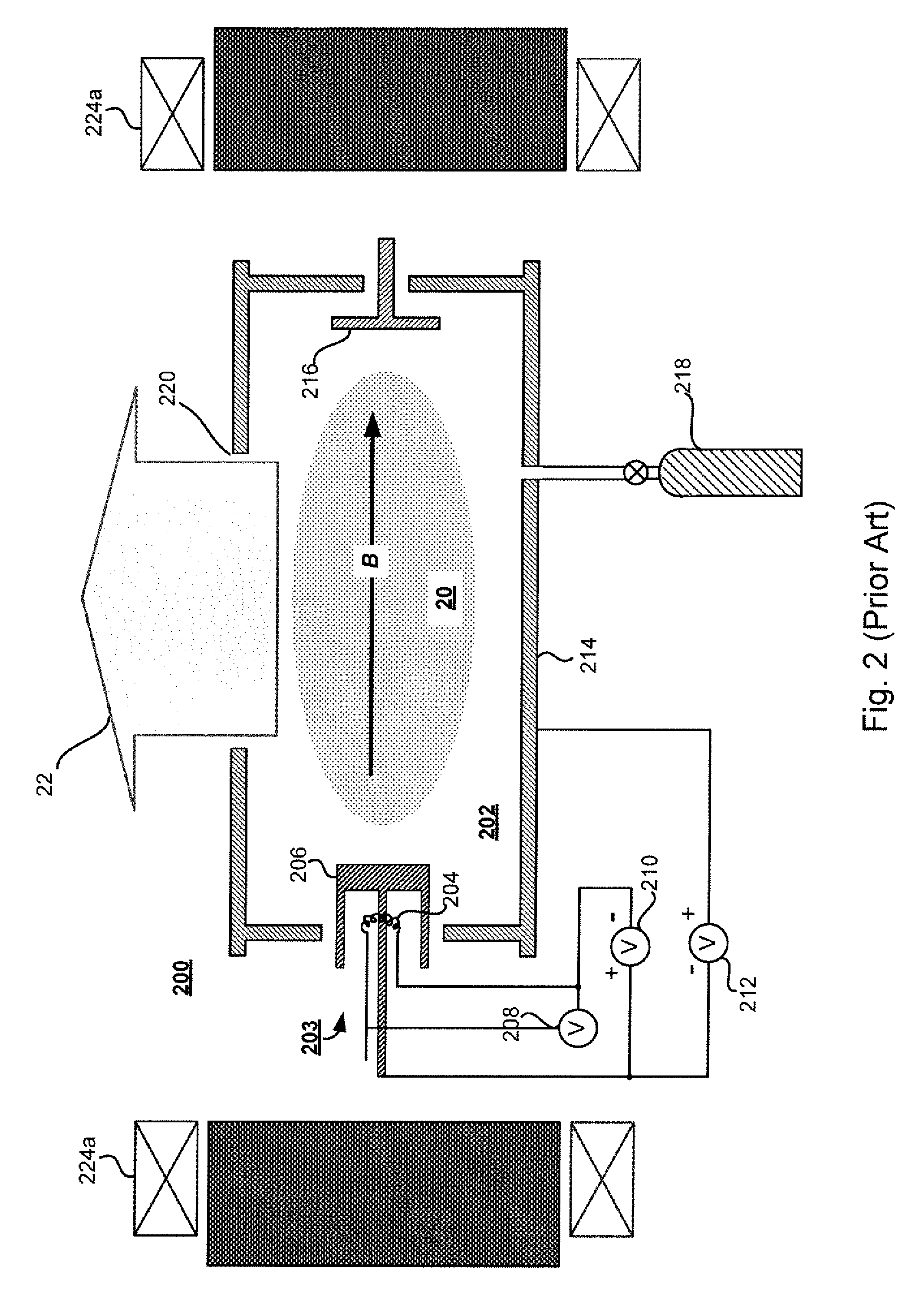
In vacuum tubes and gas-filled tubes, a hot cathode or thermionic cathode is a cathode electrode which is heated to make it emit electrons due to thermionic emission. This is in contrast to a cold cathode, which does not have a heating element. The heating element is usually an electrical filament heated by a separate electric current passing through it. Hot cathodes typically achieve much higher power density than cold cathodes, emitting significantly more electrons from the same surface area. Cold cathodes rely on field electron emission or secondary electron emission from positive ion bombardment, and do not require heating. There are two types of hot cathode. In a directly heated cathode, the filament is the cathode and emits the electrons. In an indirectly heated cathode, the filament or heater heats a separate metal cathode electrode which emits the electrons.
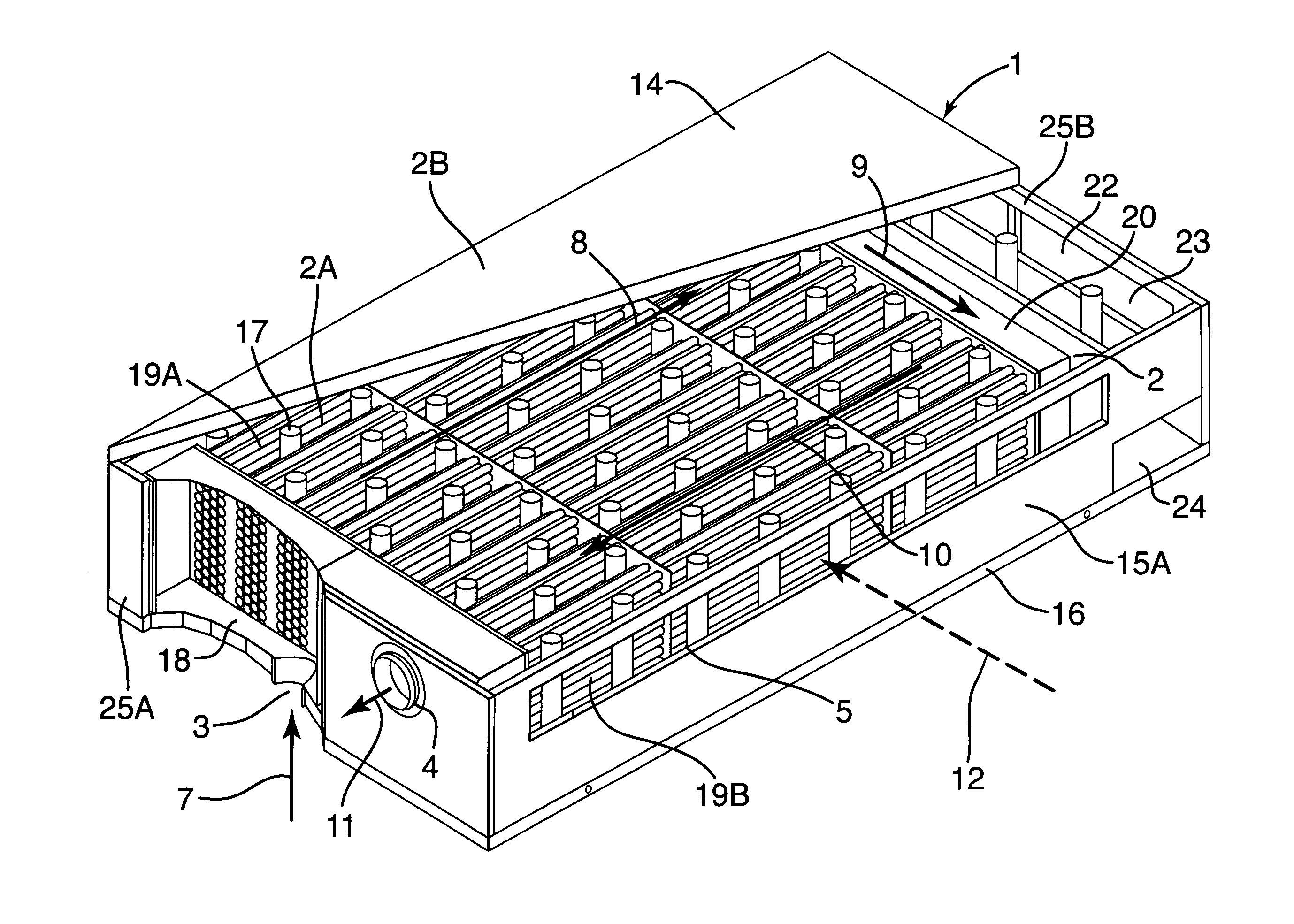
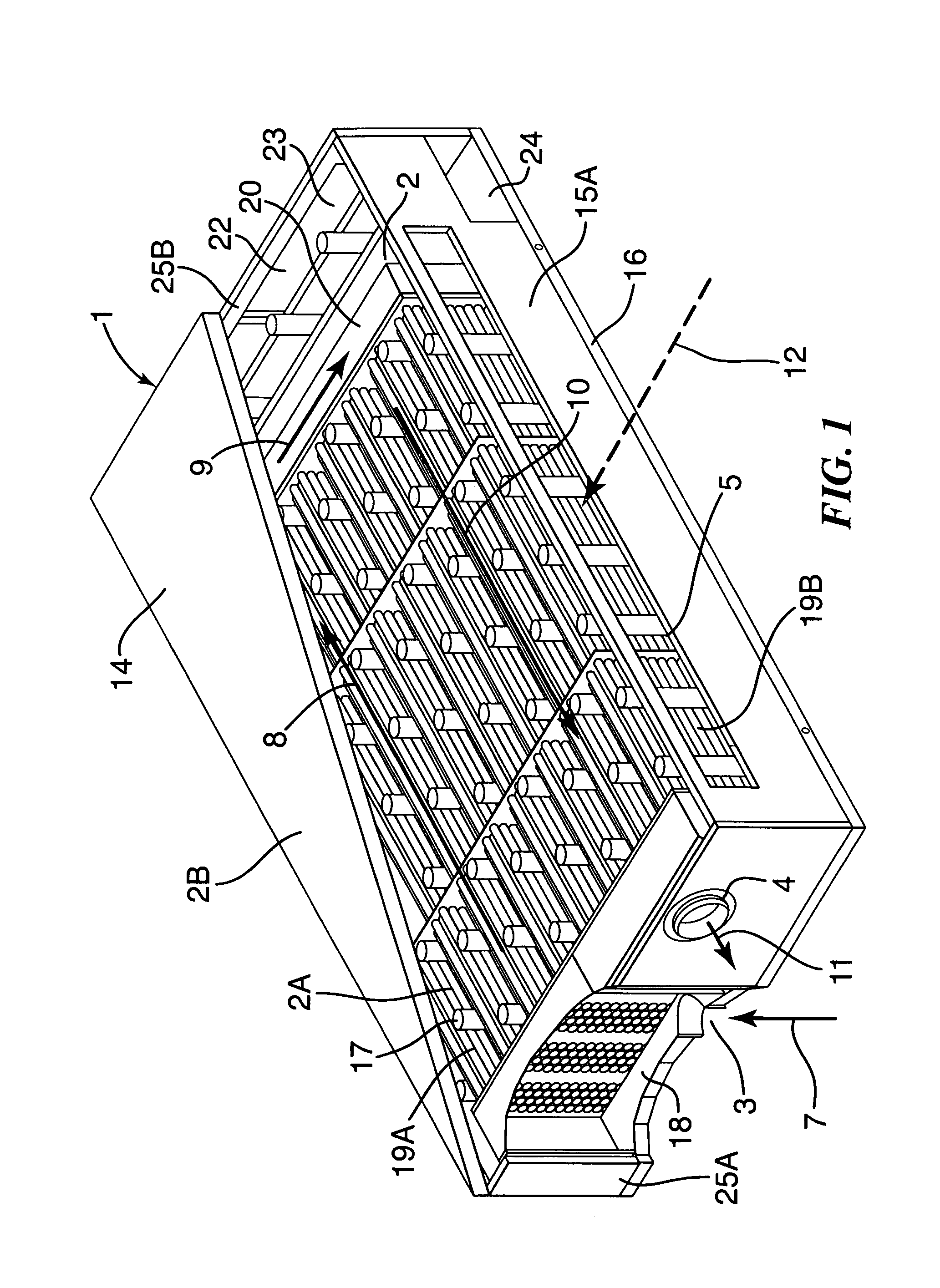
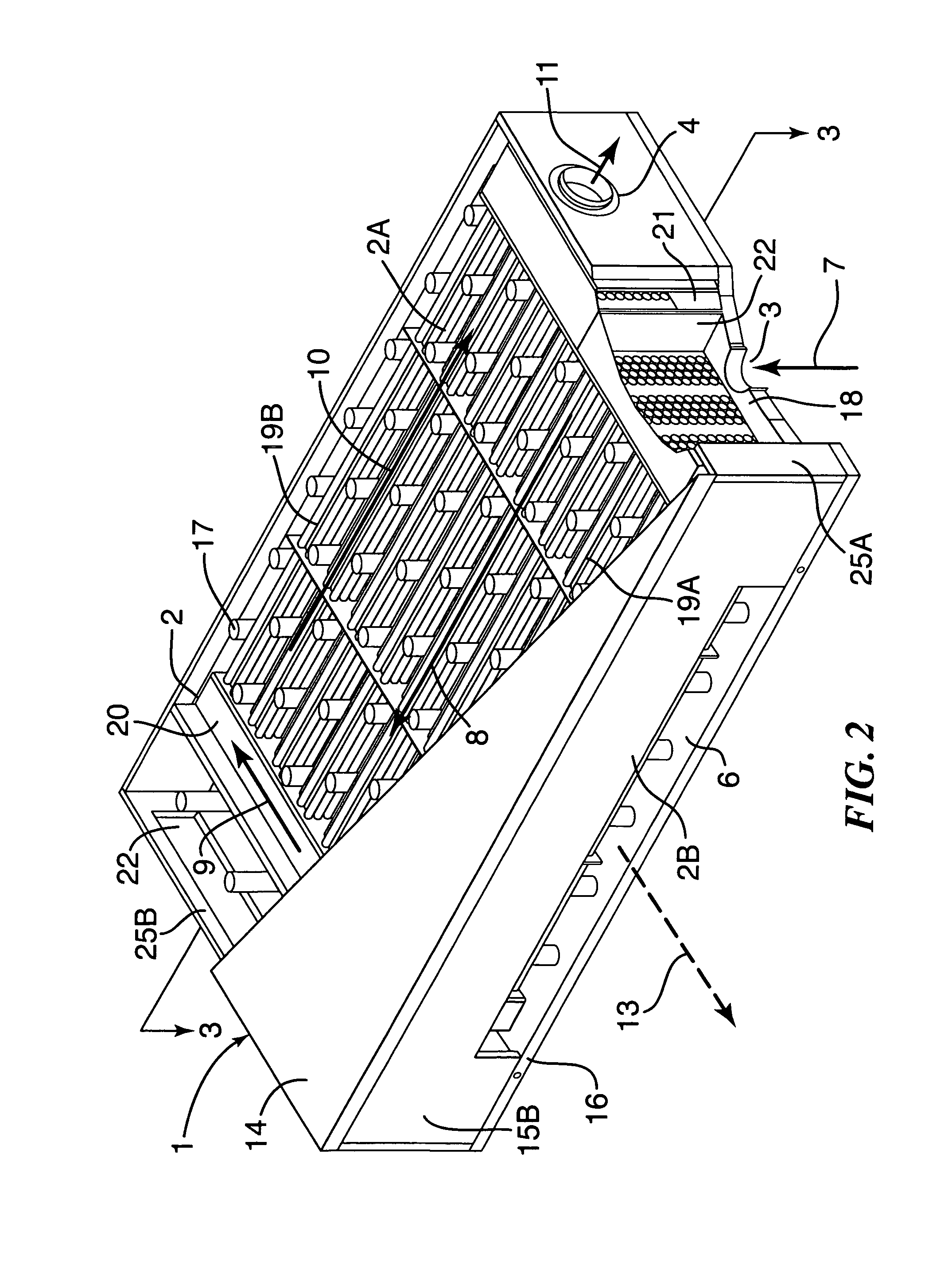
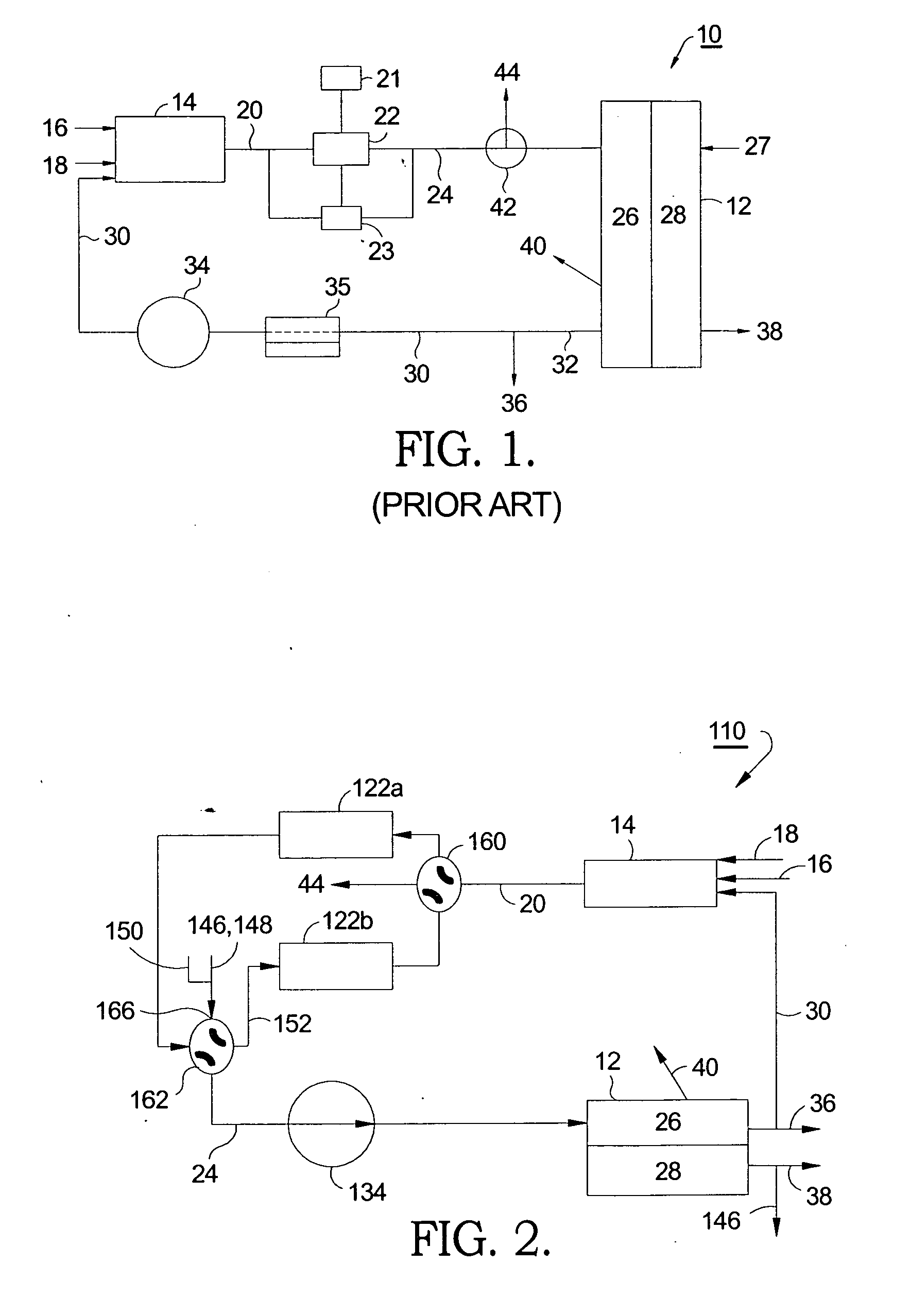
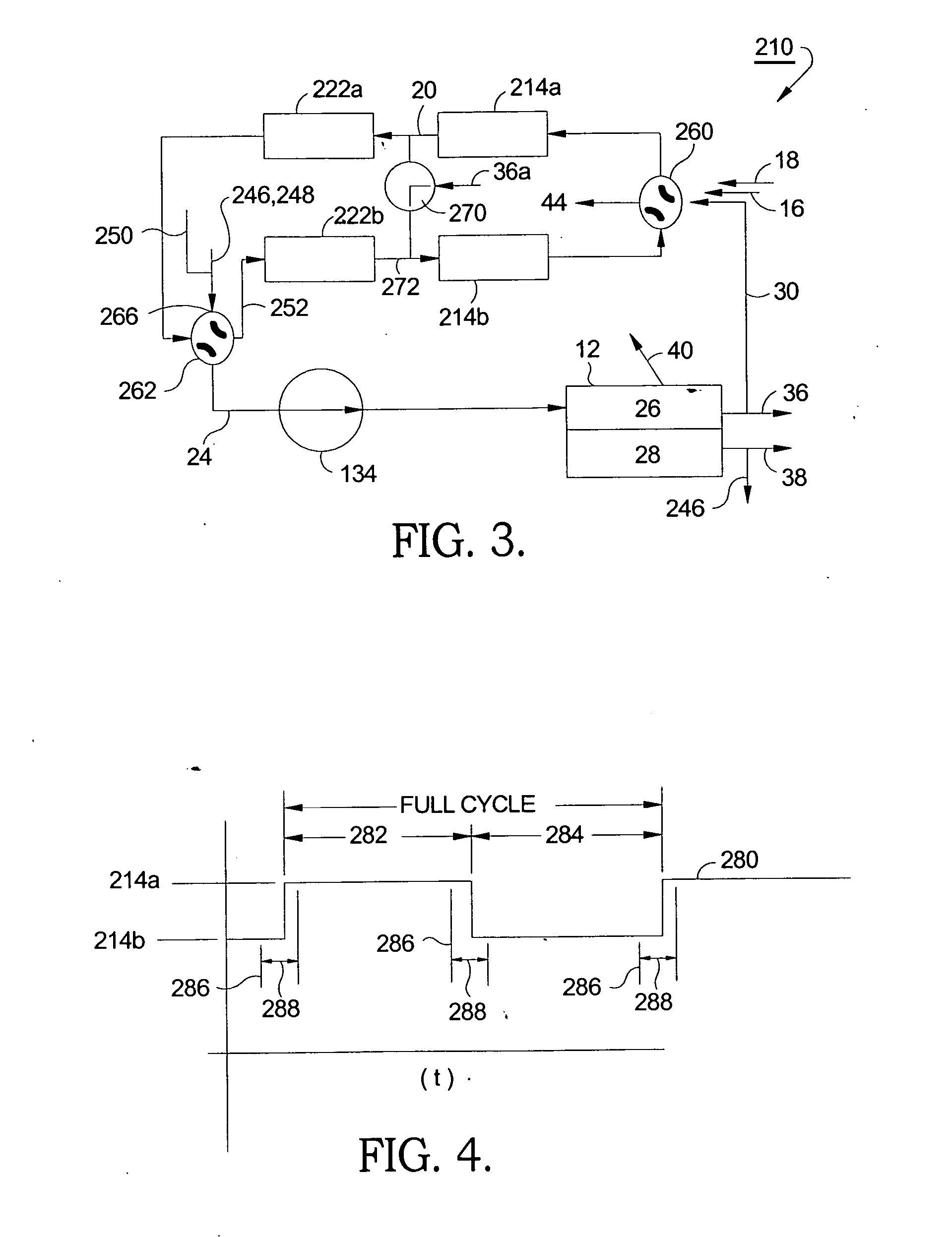
Fuel cell end unit with integrated heat exchanger
An end unit for a fuel cell stack is described that contains an integrated heat exchanger for superheating the fuel gas before delivery to the stack. Heat is transferred from the hot cathode outlet stream to the cool fuel inlet stream in a space adjacent the stack's end plate. The end unit is designed as a hollow box forming the shell of the exchanger with the heat exchanger inside. The end unit has openings that allow fuel cell process gas to be taken directly from the stack without requiring piping or ductwork to be attached to thin manifolds. Separate chambers are provided for both the cathode outlet and anode outlet gas, thereby allowing all process connections to be made at one end of the stack. The end unit also features a current collection post that is separated from the end cell of the stack by a multitude of members which provide structural support for the end unit and act to more uniformly collect electrical current than would a single, large current post.
Owner:FUELCELL ENERGY INC
Super heat-conductive pipe lamp
InactiveCN1359137AEfficient extractionEffective divergenceElectric discharge tubesElongate light sourcesElectricityCold cathode
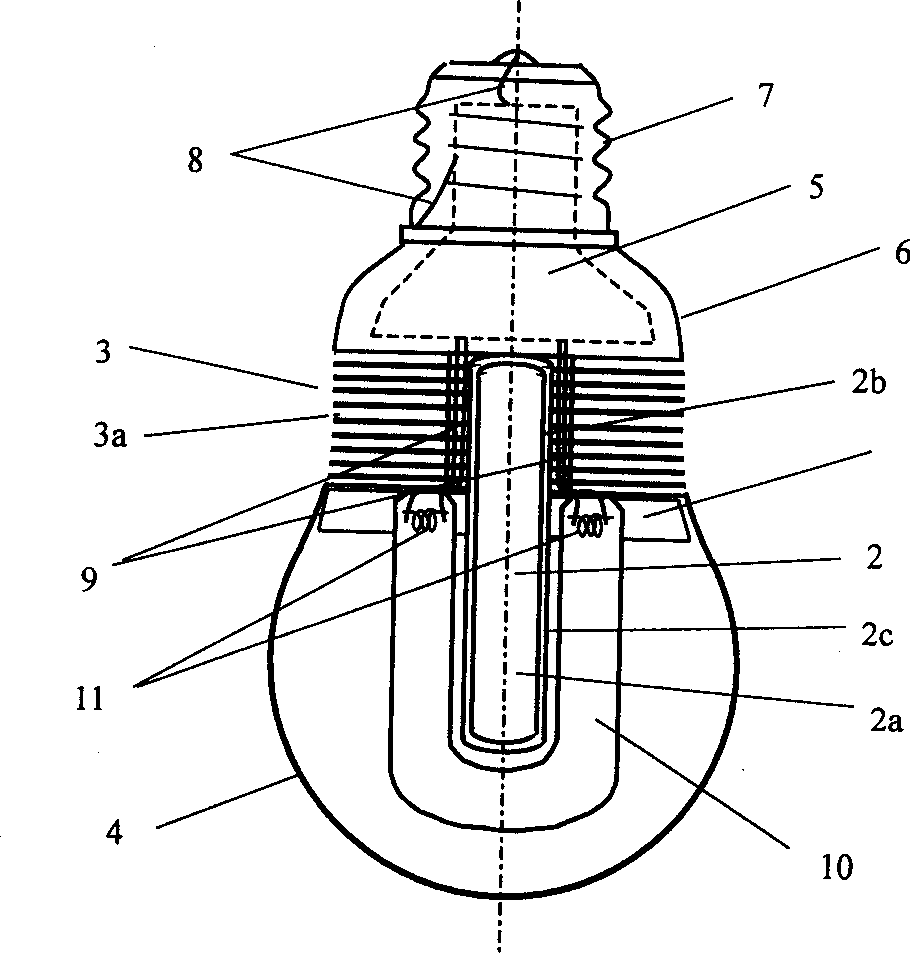
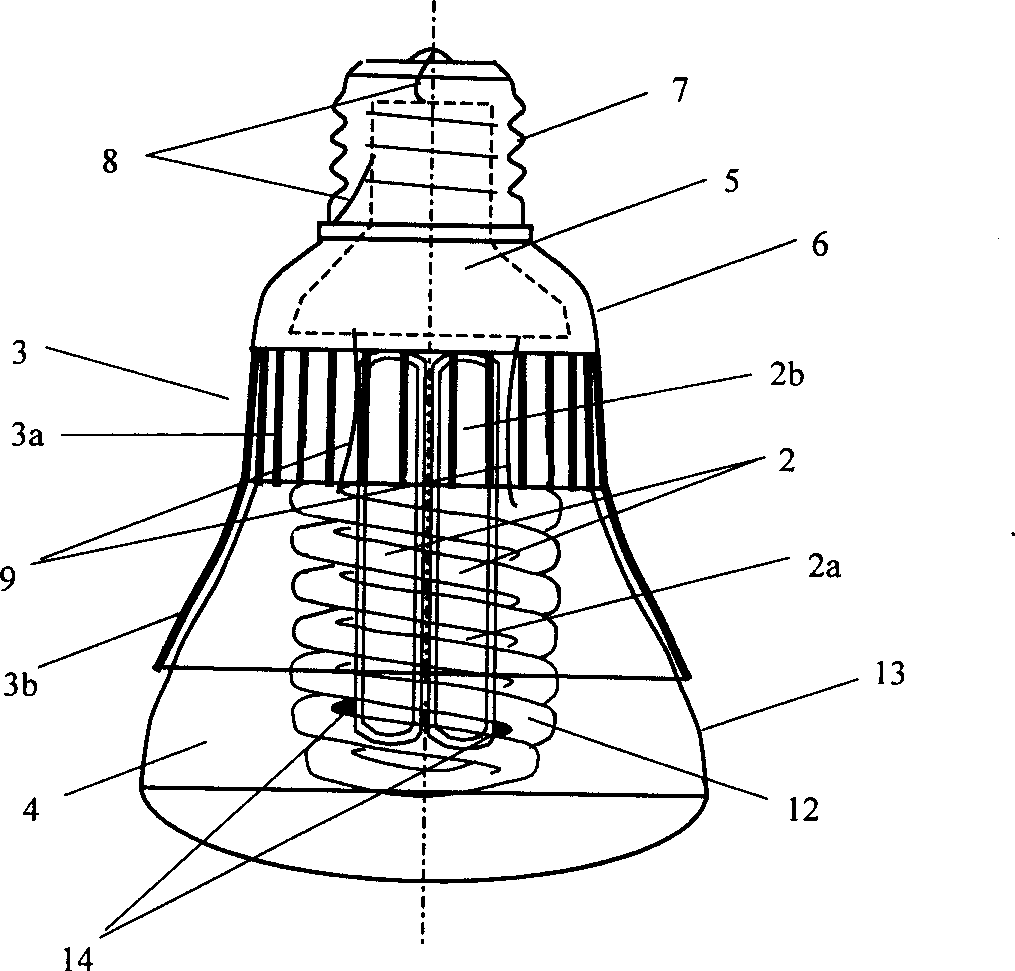
The present invention relates to a heat superconducting tube lamp, including a luminou device, for example, at least a hot-cathode or cold-cathode fluorescent light tube or at least a light-emitting diode, a light transmission bulb shell, a driver and its shell and an electric connector, also including at least one heat superconducitng tube, the luminous device is positioned on the surface of heat-absorbing end of the heat superconducting tube or near by it and a heat abstrator which is tightly and thermally contacted with heat-releasing end of heat superconducting tube, and the described heat superconducting tube can effectively pump out the heat quantity from luminous device and make the heat quantity pass through the heat abatractor to diserse so as to make luminous device work at low temp. It can be made into high-power high-efficiency and long-life lamp.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MANELUX LIGHTING
Transmitting Device for Free-Space Optical Transmission
InactiveUS20080063404A1Promote resultsElectric lighting sourcesClose-range type systemsLow voltagePower filter
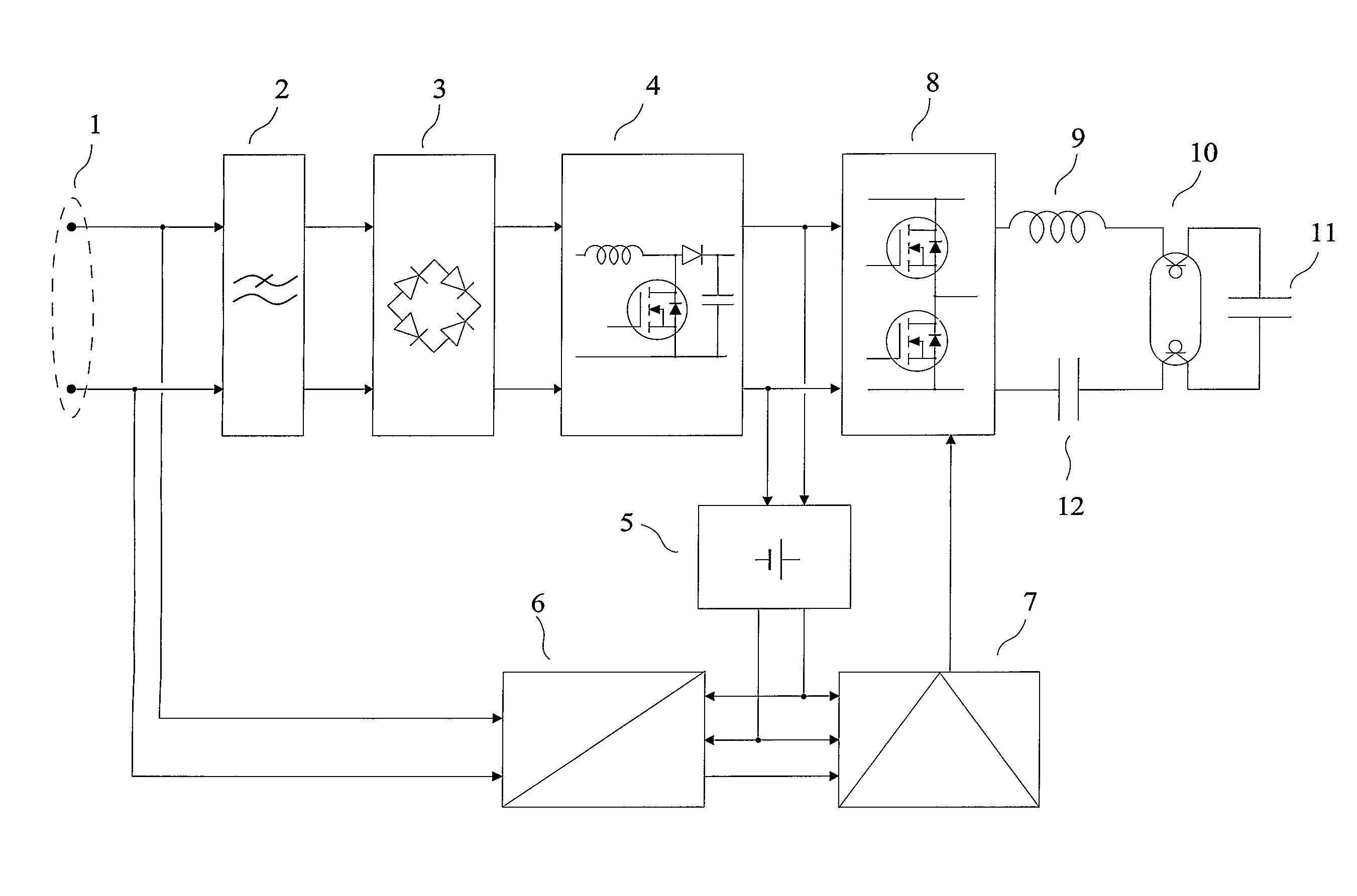
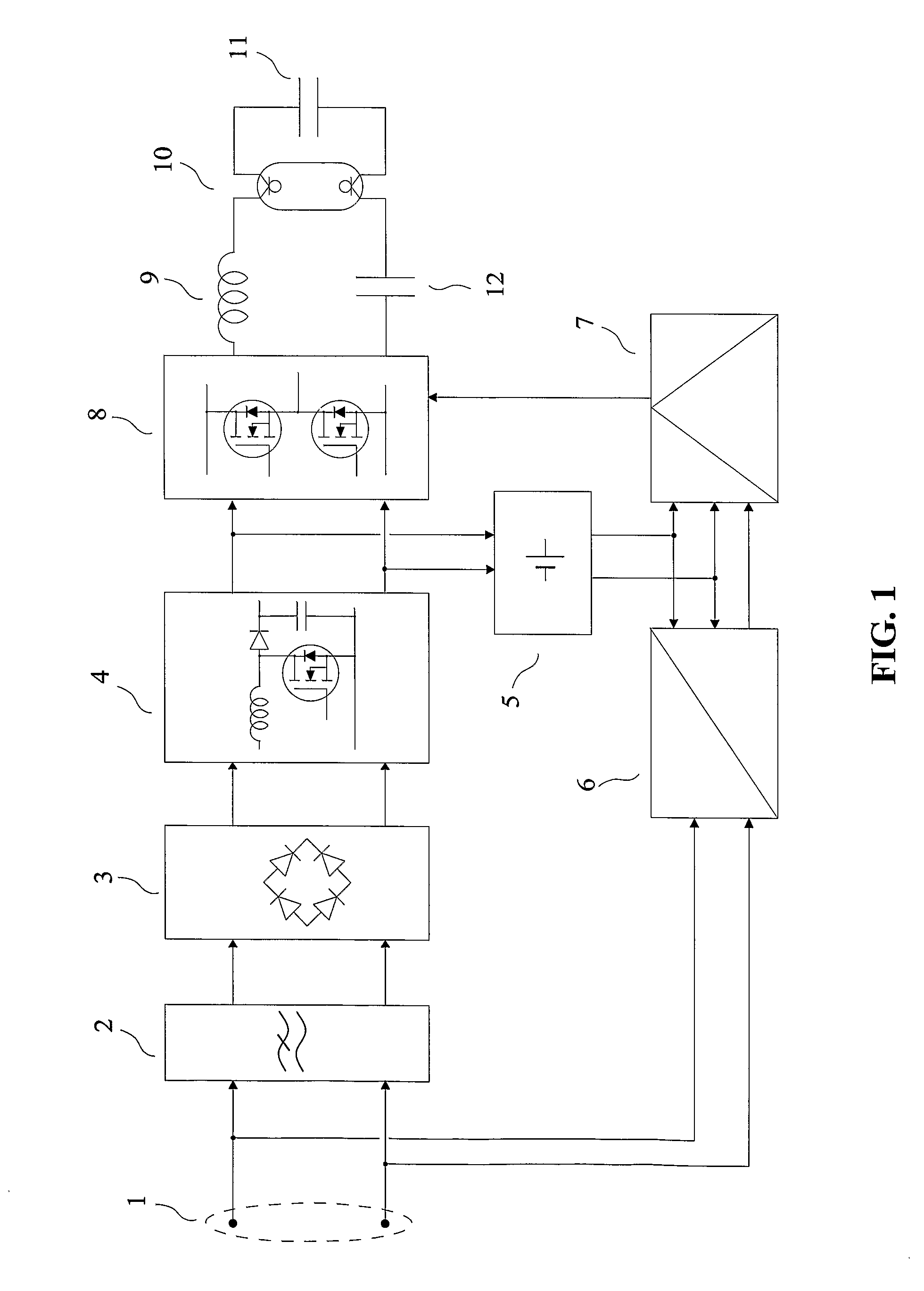
Transmitting device for free-space optical transmission. The invention relates to a transmitting device for transmission through space, using electromagnetic waves of the infrared and / or visible and / or ultraviolet bands produced by one or several discharge lamps. The device is connected by its input terminals (1) to an a.c. energy distribution system. A mains filter (2) reduces the conducted electromagnetic disturbances produced by the power circuits comprising a rectifier (3), a power-factor-correction circuit (4), a low-voltage power supply (5) and an inverter (8). The inverter (8) is connected to a series inductor (9) connected in series with a hot-cathode fluorescent lamp (10) and a capacitor (12), a parallel capacitor (11) allowing an optimal start of the lamp. A receiving set for transmission via power distribution lines (6) delivers “demodulated signals” applied to the control circuitry (7) which controls the state of the switches of the inverter (8). The light produced is modulated as a function of the “demodulated signals”.
Owner:ZXTALK ASSETAB
Ion source
ActiveUS20100051825A1Reduce in quantitySimple structureMaterial analysis by optical meansIon beam tubesIonizationAtomic physics
An ion source includes a plasma generating chamber into which an ionization gas containing fluorine is introduced, a hot cathode provided on one side in the plasma generating chamber, an opposing reflecting electrode which is provided on other side in the plasma generating chamber and reflects electrons when a negative voltage is applied from a bias power supply to the opposing reflecting electrode, and a magnet for generating a magnetic field along a line, which connects the hot cathode and the opposing reflecting electrode, in the plasma generating chamber. The opposing reflecting electrode is formed of an aluminum containing material.
Owner:NISSIN ION EQUIP CO LTD
Portable ultraviolet water purification system
InactiveUS7390417B2Easy to transportProtection from damageWater treatment parameter controlWater/sewage treatment by irradiationLow voltageUltraviolet lights
A portable water-purification system includes a container for holding a liquid and an ultraviolet light source configured for immersion in the liquid. The ultraviolet light source is a straight low-cost tube controlled by electronic circuitry for providing hot-cathode striking at a relatively low voltage using a fly-back inductor. The operation of the water purification system is controlled by a micro-controller within the electronic circuitry.
Owner:MERIDIAN DESIGN
Techniques for providing a multimode ion source
InactiveUS20090166554A1Material analysis by optical meansIon beam tubesPlasma generatorMultiple modes
Techniques for providing a multimode ion source are disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the techniques may be realized as an apparatus for ion implantation, the apparatus including an ion source having a hot cathode and a high frequency plasma generator, wherein the ion source has multiple modes of operation.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
Plasma device with double-hollow cathode and double-hollow cathode and applications
InactiveCN102497721AEasy to replaceSatisfaction yields a singlePlasma techniqueMode controlPlasma flow
The invention discloses a plasma device with a double-hollow cathode and a double-hollow cathode and applications. The device comprises filaments, a hot cathode, an anode, a double-hollow cathode, a cold cathode, a vacuum chamber and a magnet, wherein the double-hollow cathode comprises an outer wall and a lining layer and is of a double-layer structure. Due to the double-layer hollow cathode structure, the lining layer is easy to disassemble and change, so that the lining layer can be observed and analyzed properly, and simultaneously, the demand that single or multiple types of metal plasma is / are generated by a sputtering cathode in an arc chamber. On one hand, according to the plasma device, a double-hollow cathode plasma sputtering mode controlled by a magnetic mirror field is adopted for generating high-density plasma with the single or multi-element metal and plasma flow with high efficiency, and the plasma device is used for the modification on the surface of irradiation material of the metal plasma and research on the high-purity high-flow metal ion beam; and on the other hand, the plasma device is combined with various surface analyzing technologies to observe and analyze the inner surface of the double-hollow cathode, and used for researching the mutual action between the plasma and a machine wall in magnetic confinement fusion.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Ionization gauge with a cold electron source
ActiveUS7768267B2Thermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsElectron sourceIonization
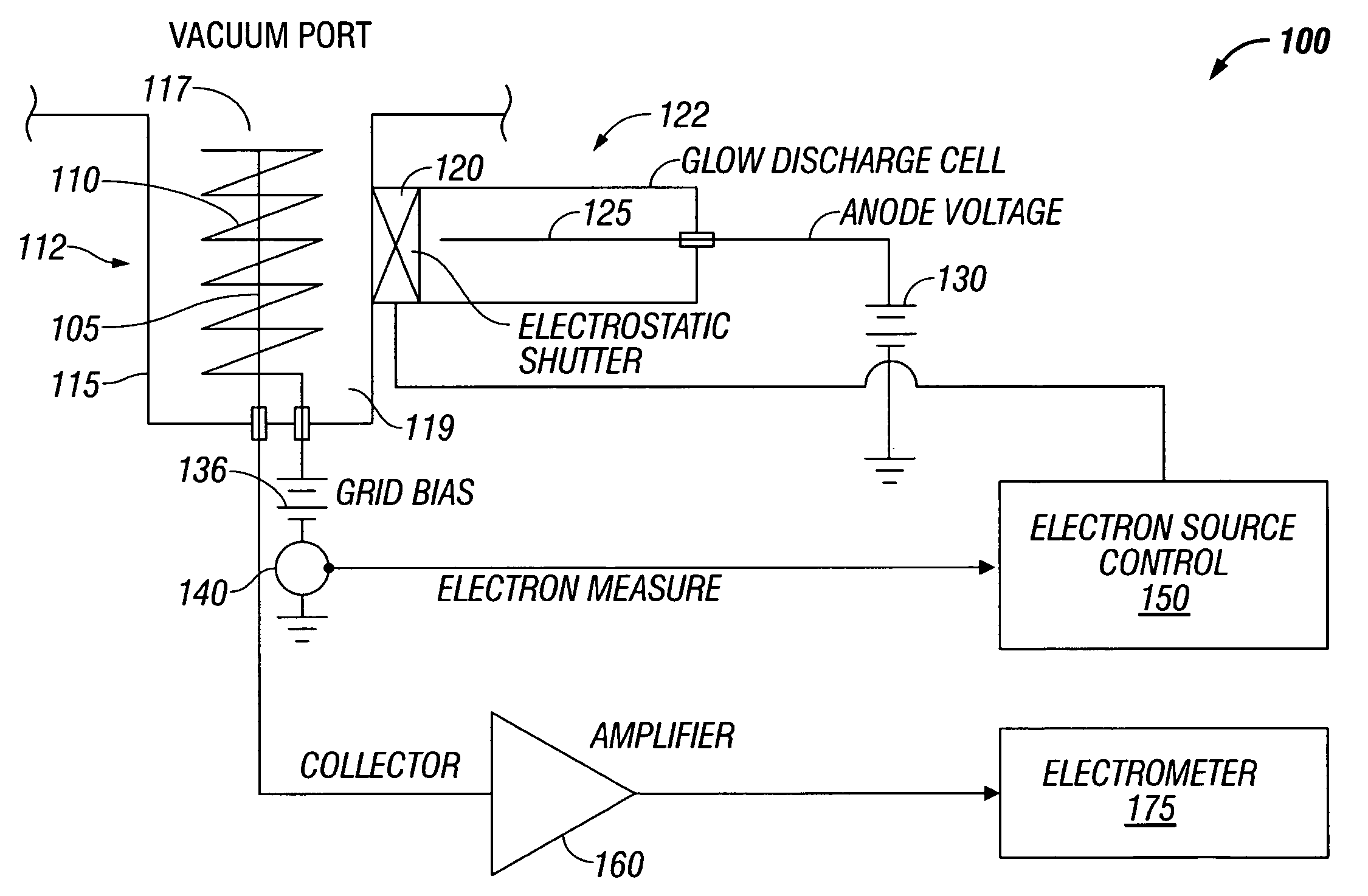
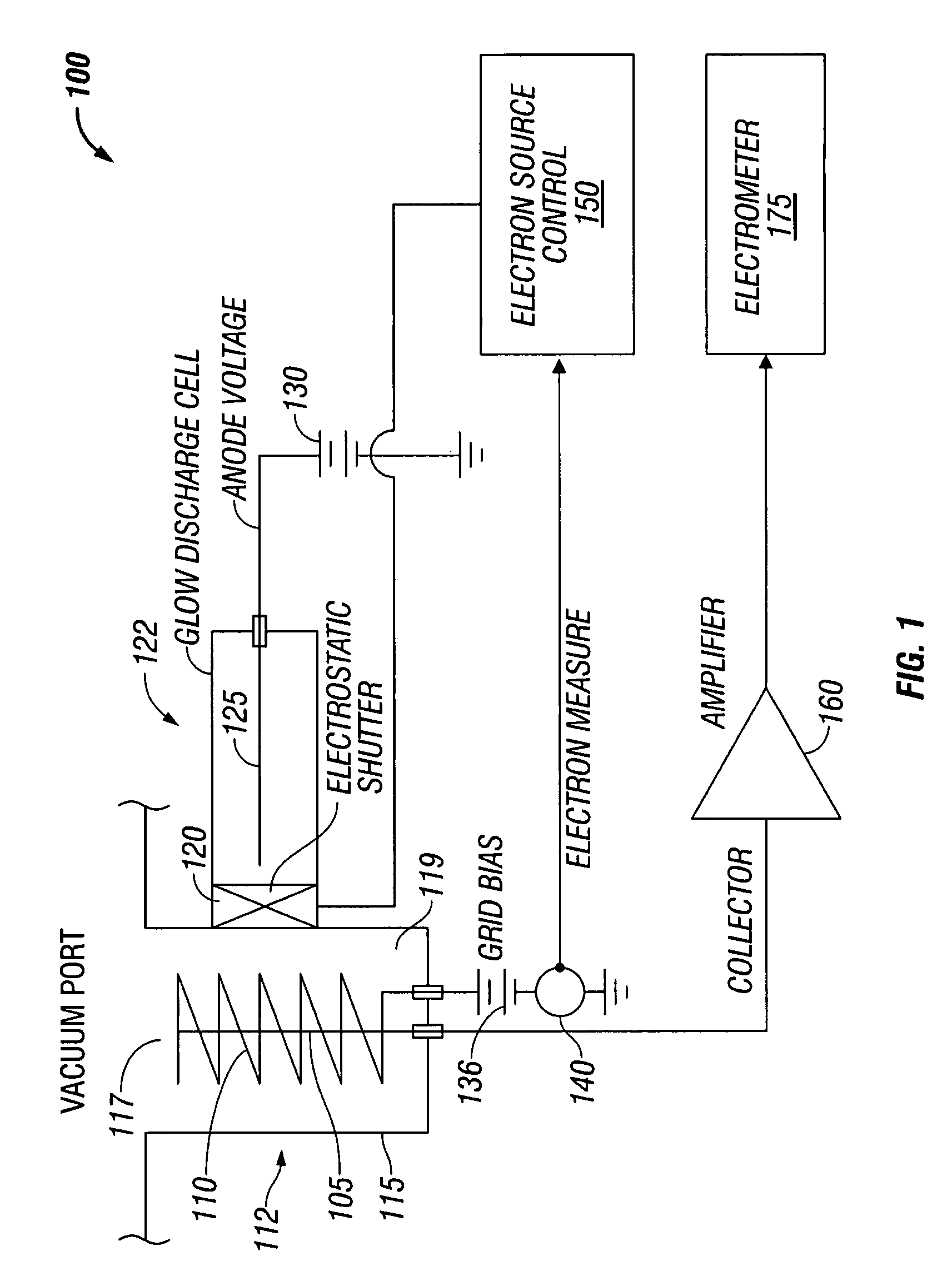
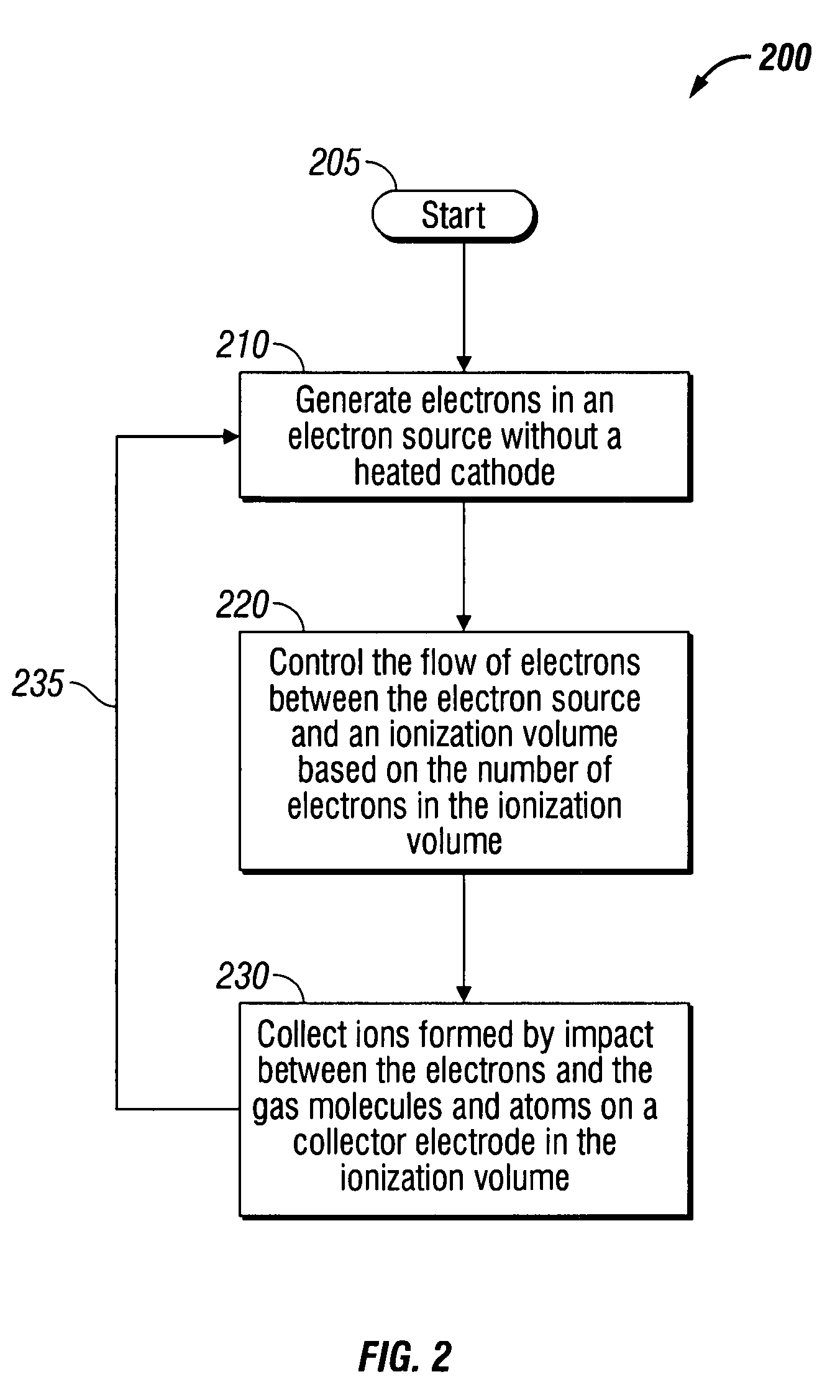
An ionization gauge that eliminates a hot cathode or filament, but maintains a level of precision of gas density measurements approaching that of a hot cathode ionization gauge. The ionization gauge includes a collector electrode disposed in an ionization volume, an electron source without a heated cathode, and an electrostatic shutter that regulates the flow of electrons between the electron source and the ionization volume. The electrostatic shutter controls the flow of electrons based on feedback from an anode defining the ionization volume. The electron source can be a Penning or glow discharge ionization gauge.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Regenerable method and system for desulfurizing reformate
ActiveUS20060240296A1Reduce the amount requiredImprove reformer regenerationCombination devicesFuel cells groupingFuel cellsFour-way valve
A system for removing sulfur from a continuous reformate stream feeding a fuel cell stack. First and second sulfur traps are disposed in parallel between a hydrocarbon reformer and the fuel cell stack. The ends of the sulfur traps are connected to conventional four-way valves such that either trap may be selected for trapping sulfur from the reformate stream, while the other trap is undergoing regeneration by backflushing the accumulated adsorbed sulfur deposits. Thus, the sulfur traps may be used and stripped alternately, permitting continuous supply of desulfurized reformate to the fuel cell assembly. In a currently preferred embodiment, the hot cathode air exhaust is used to assist in stripping the out-of-service trap. In an alternative embodiment, two reformers are provided and the reformers are alternately regenerated along with their respective traps.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Method to operate GEF4 gas in hot cathode discharge ion sources
InactiveUS6215125B1Material analysis by optical meansSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenOperating life
The present invention provides a method of extending, i.e. prolonging, the operating lifetime of hot cathode discharge ion source by utilizing and introducing a nitrogen-containing co-bleed gas into an ion implantation apparatus which contains at least a hot cathode discharge ion source and an ion implantation gas such as GeF4.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for shielding feedthrough pin insulators in an ionization gauge operating in harsh environments
InactiveUS20080100301A1Easy to operateDamage to materialVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsDischarge tube/lamp detailsEngineeringIonization
Shields for feedthrough pin insulators of a hot cathode ionization gauge are provided to increase the operational lifetime of the ionization gauge in harmful process environments. Various shield materials, designs, and configurations may be employed depending on the gauge design and other factors. In one embodiment, the shields may include apertures through which to insert feedthrough pins and spacers to provide an optimal distance between the shields and the feedthrough pin insulators before the shields are attached to the gauge. The shields may further include tabs used to attach the shields to components of the gauge, such as the gauge's feedthrough pins. Through use of example embodiments of the insulator shields, the life of the ionization gauge is extended by preventing gaseous products from a process in a vacuum chamber or material sputtered from the ionization gauge from depositing on the feedthrough pin insulators and causing electrical leakage from the gauge's electrodes.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
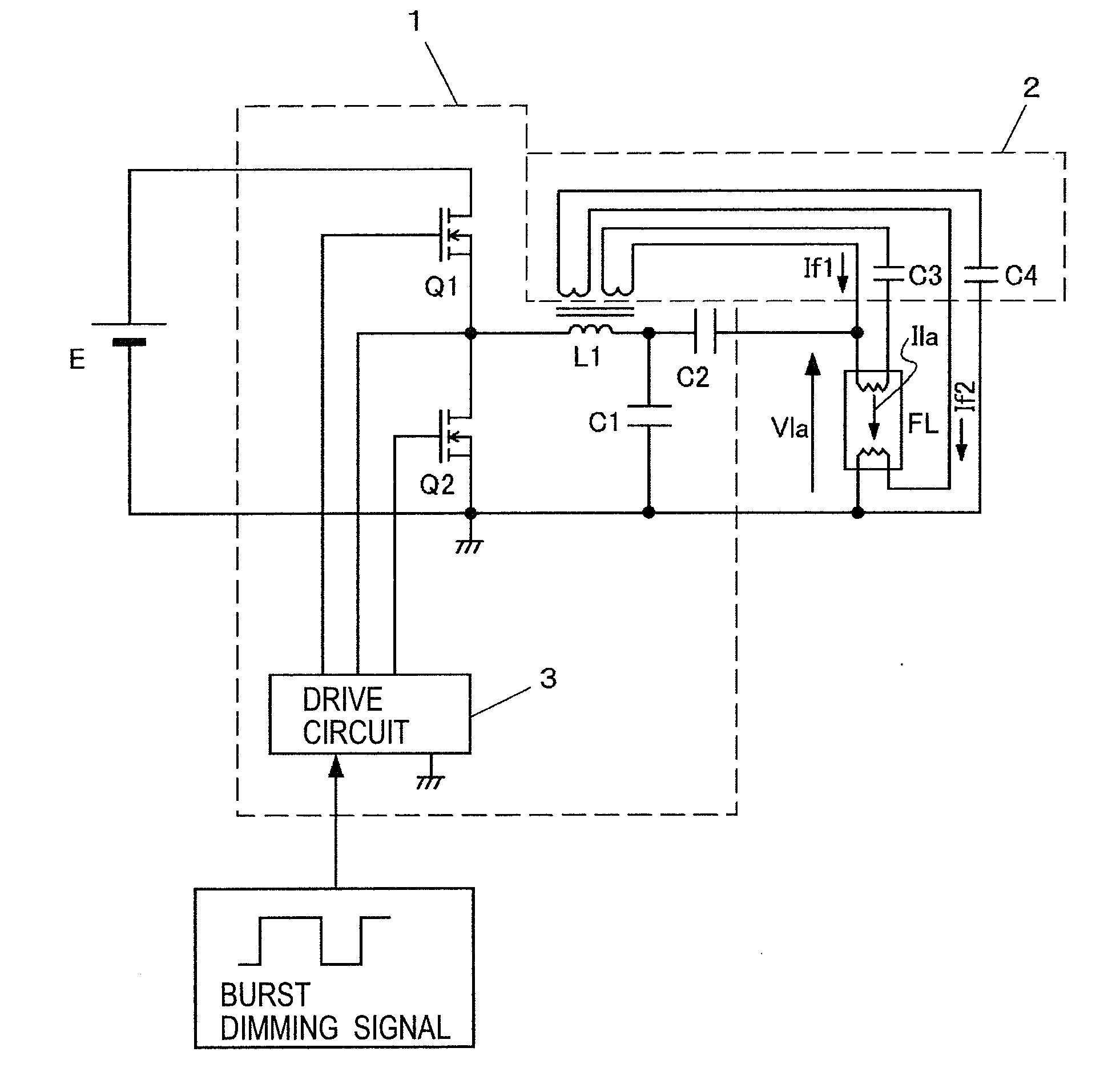
Discharge lamp lighting device, illumination device, and liquid crystal display device
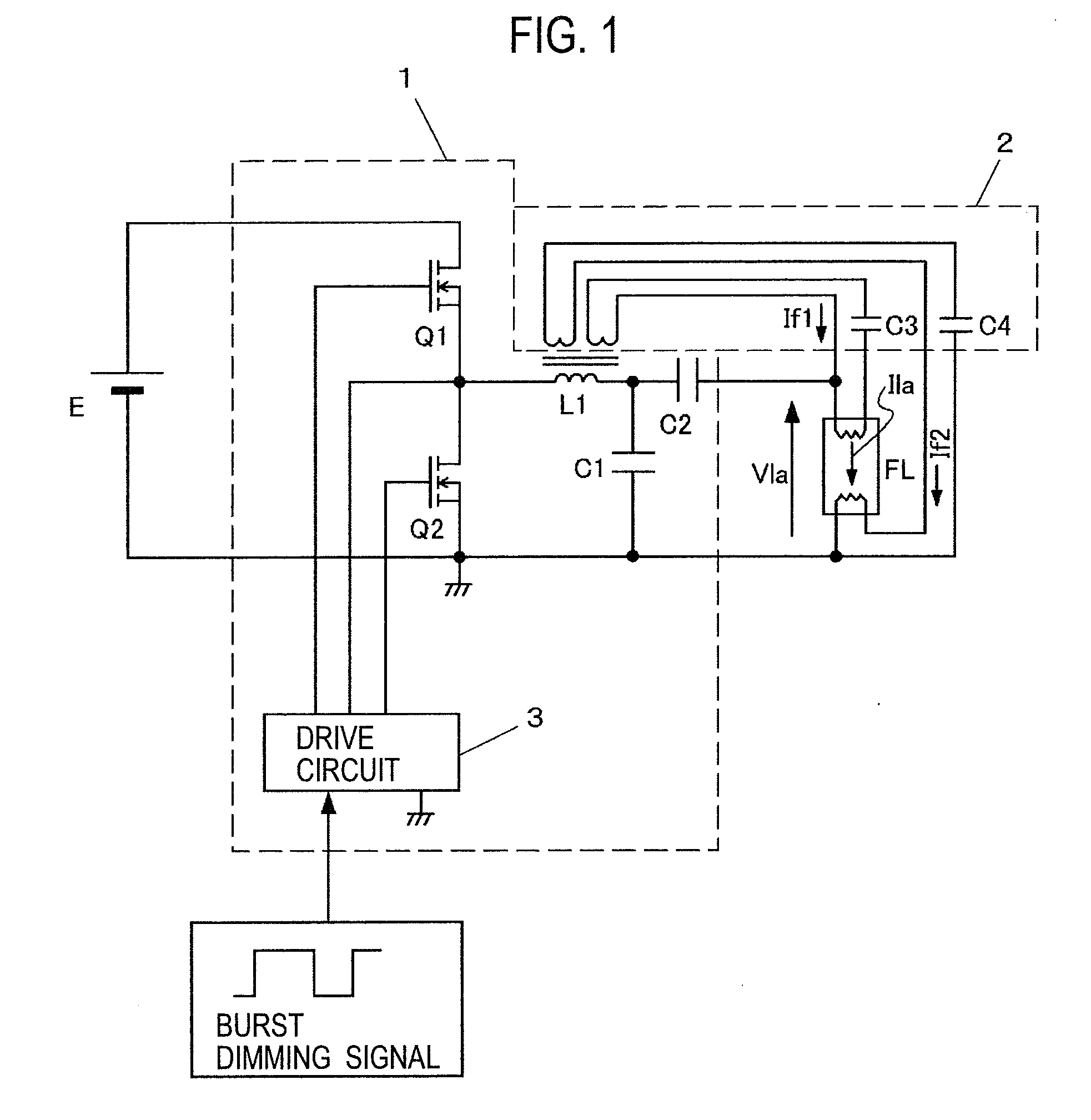
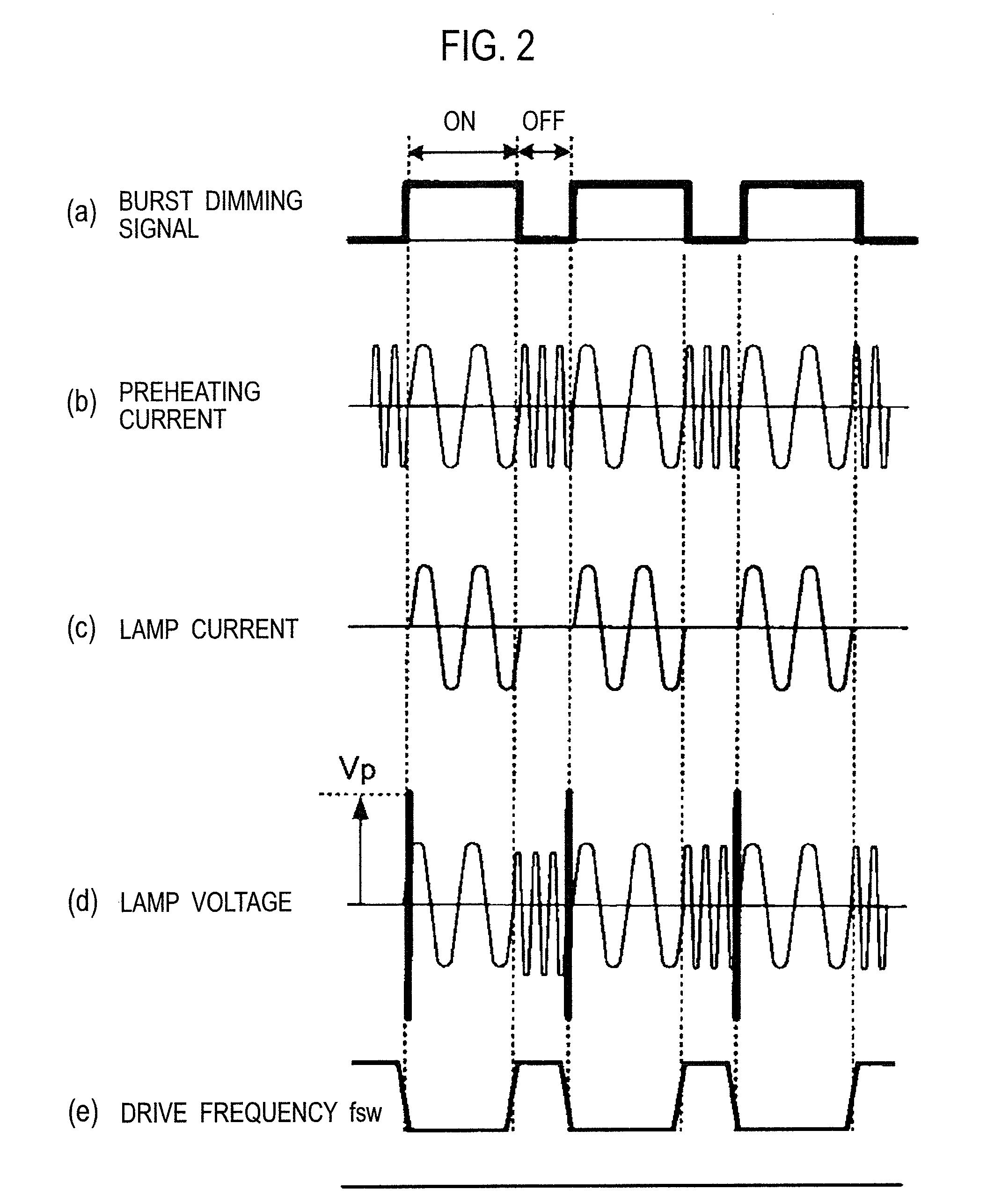
InactiveUS20100039581A1Electrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementBurst dimmingElectricity
A burst dimming signal to determine a ratio between an ON period and an OFF period is inputted. In the OFF period of the burst dimming signal, a lamp current Ila is stopped from flowing to a discharge lamp FL, while a lamp voltage Vla is applied to both ends of the discharge lamp FL, and preheating currents If1 and If2 are supplied to hot cathodes of the discharge lamp FL. In the ON period of the burst dimming signal, the discharge lamp FL is electrically broken down and is supplied with the lamp current Ila.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Method for growing high quality nano-diamond membrane with low cost
InactiveCN101294274AReduce surface roughnessImprove physicsChemical vapor deposition coatingSuperhard materialMaterials science
The invention relates to a method for producing high-quality nano-diamond film with low cost, which belongs to the superhard material growth field. The method takes hydrogen, argon and carbonaceous gas as the precursor gas, plasma is formed by utilizing hot cathode glow discharge excitation, the diamond film nucleation and growth can be alternately performed through controlling the gas supply proportion, the diamond crystal particles are controlled within the nanometer range, and high-quality nano-diamond film is deposited after mainly going through the process of nucleation, nano-diamond film deposition and removal of the non-diamond phase carbon on the surface of the film. The method for producing the high-quality nano-diamond film with low cost has the advantages of high excitation current, quick growth speed, high film forming quality and low preparation cost; the prepared nano-diamond film also has the advantages of low surface roughness, small friction coefficient and low electrical resistivity besides excellent physical and chemical properties of the conventional diamond; the surface grain size is 10 to 100 nm.
Owner:MUDANJIANG NORMAL UNIV
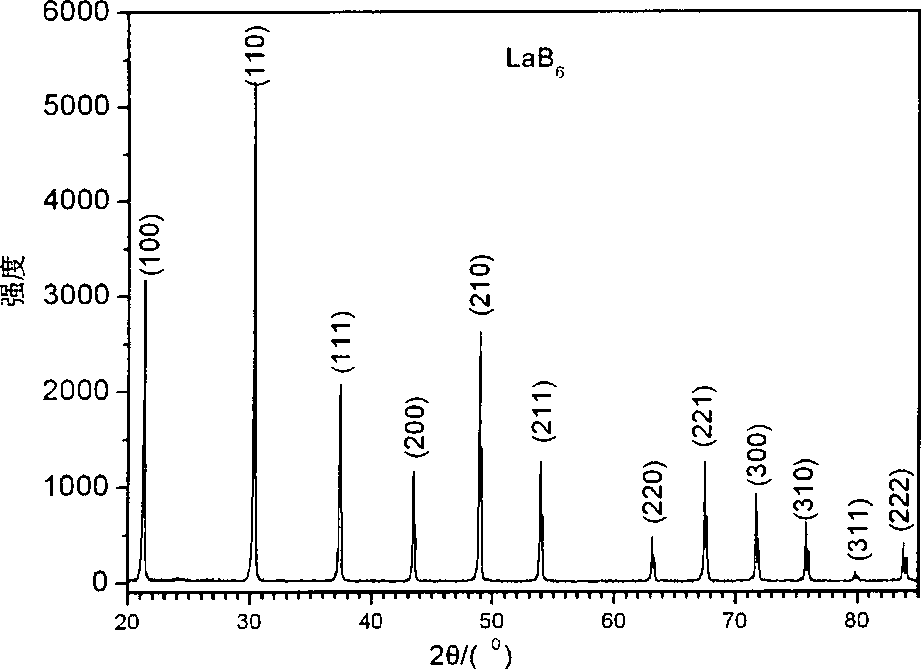
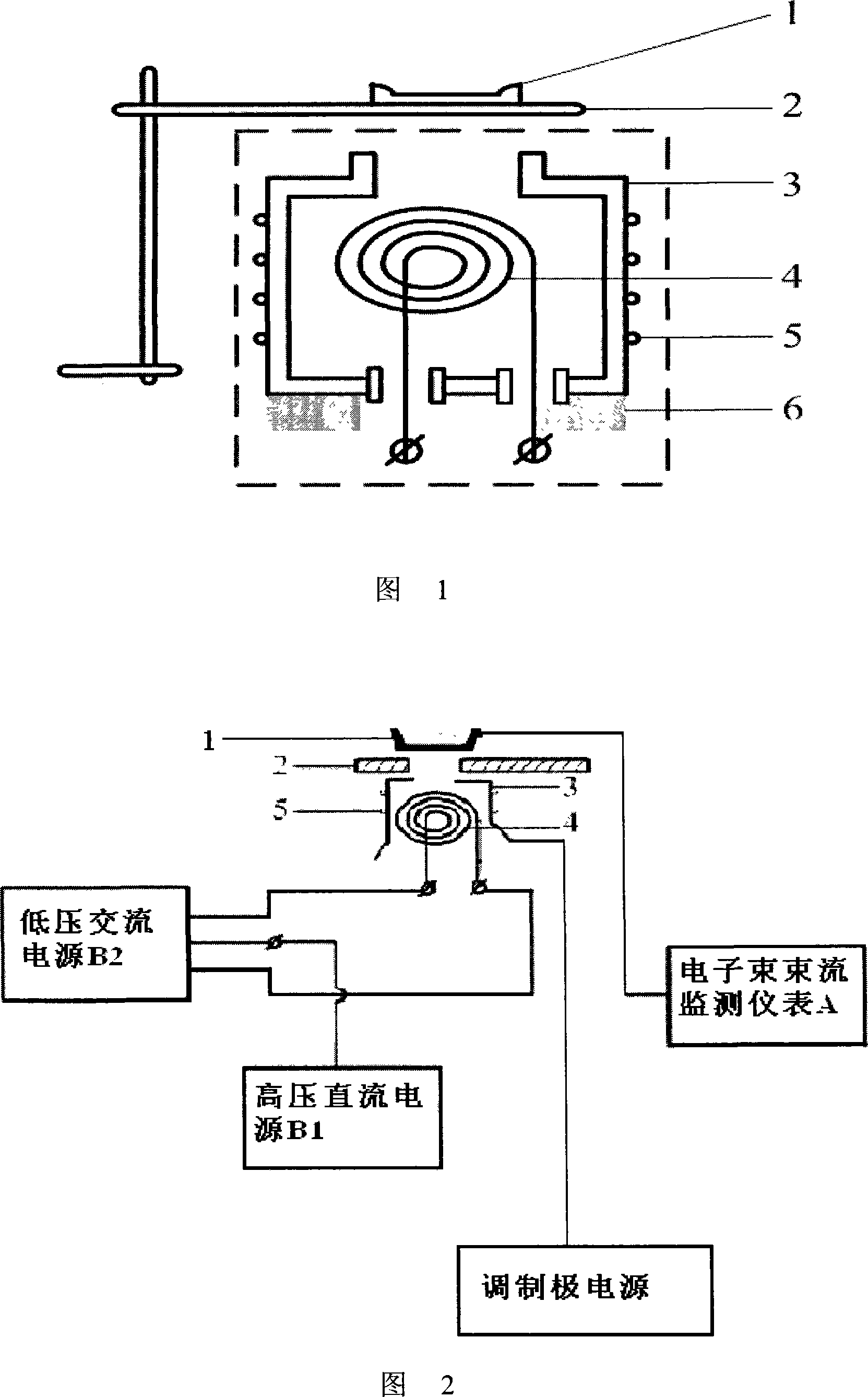
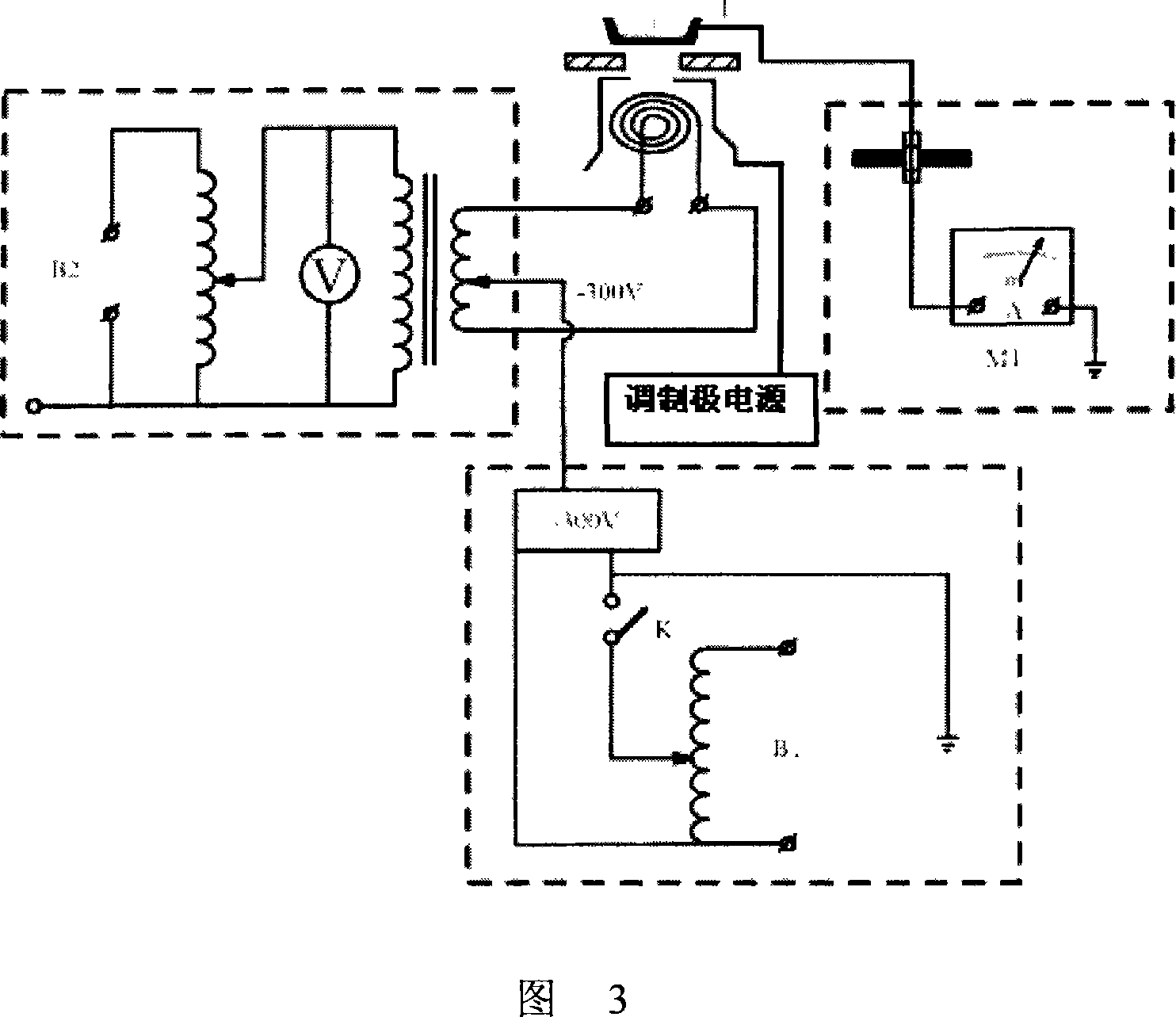
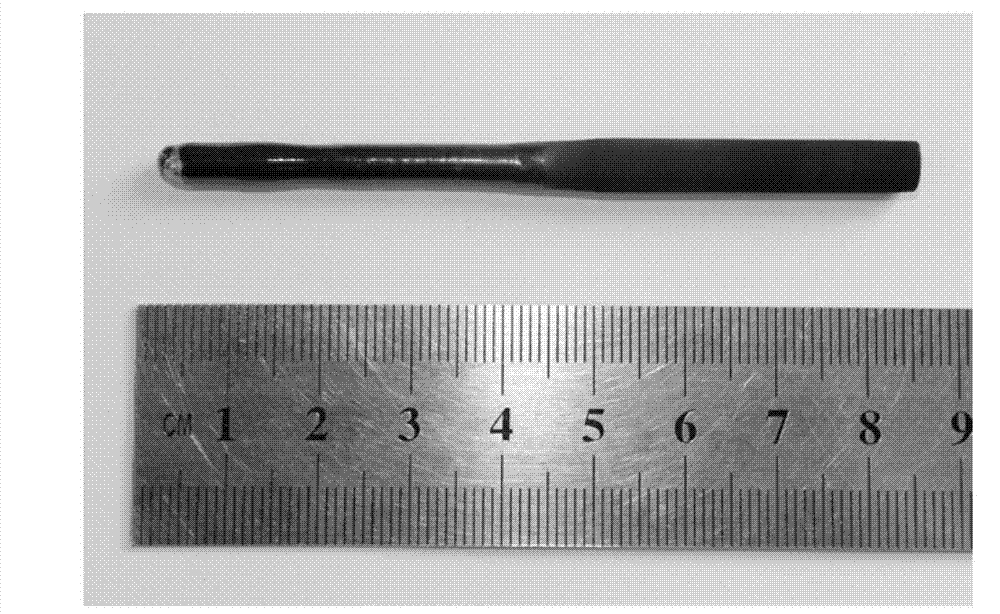
Rapid preparation method of LaB6 polycrystalline bulk cathode material
The invention discloses a method for quickly preparing bulk LaB6 polycrystal cathode material, and belongs to the technical field of rare earth boride hot cathode material. The prior preparation technology of LaB6 cathode material has the problems of high sintering temperature, long sintering time, and complicated process and so on. The method is as follows: LaB6 powder is placed in a mould, compacted and placed in a SPS sintering furnace to be sintered under the conditions of an applied pressure of from 30 to 50 Mpa, an atmosphere of high-purity argon gas or vacuum with a vacuum degrees more than 5Pa, temperature raise at a speed of from 90 to 200 DEG C / min, a sintering temperature of between 1400 and 1700 DEG C, and a temperature holding period of from 5 to 20 minutes, and then the bulk LaB6 polycrystal cathode material is obtained as the furnace cools down. The method of the invention lowers the sintering temperature, reduces sintering time and simplifies process while improving the mechanical property and emission property of LaB6 cathode material.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
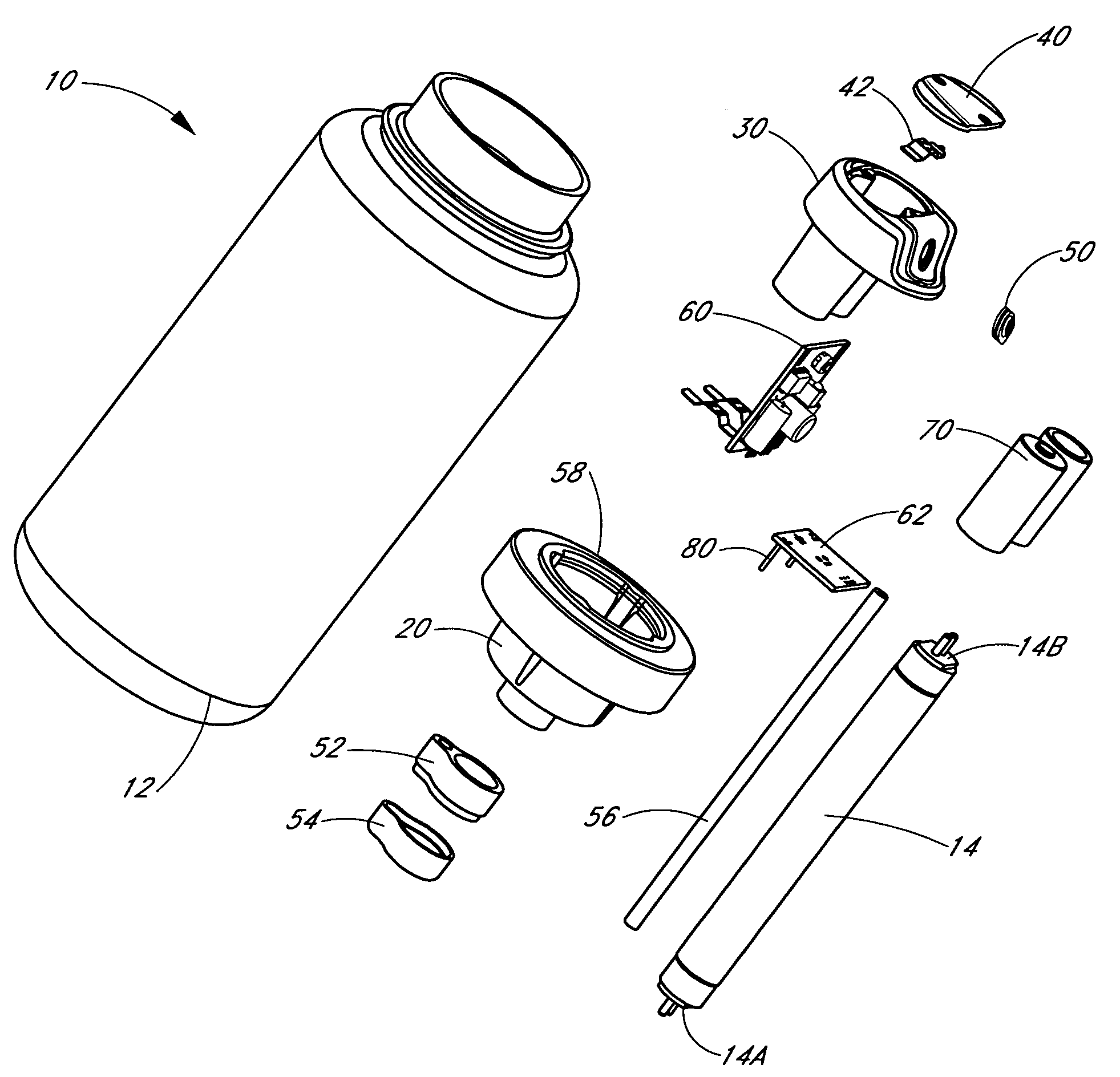
High Power Cold Cathode Tubular Fluorescent Lamp
InactiveUS20060273731A1Increase the lengthLong processSolid cathode detailsStructural circuit elementsEffect lightEngineering
A high power tubular CCFL device comprises at least one CCFL; and a light transmission tube having two ends, where the at least one CCFL is at a fixed location inside the light transmission tube. At least two fixtures are used, one fixture at each of the two ends of the light transmission tube. At least two connectors are used, one connector at each of the two ends of the light transmission tube for connection to input electric power. Preferably a portion of a driver (which preferably includes at least one high voltage transformer) is employed in the fixture. The fixture connects the light transmission tube, the CCFL(s) and the connector. When input electric power is supplied to the connector, the portion of the driver (e.g. at least one high voltage transformer) will cause suitable voltage to be supplied to cause the CCFL to supply light. The above described CCFL device is suitable for replacing the hot cathode. To design a CCFL device that generates multi-color lighting for various purposes such as entertainment, two or more CCFLs may be used. A driver circuit converts input electric power to an AC output in the range of about 5-400 volts and at a frequency in the range of about 1 kc-800 kc. At least one high voltage transformer responds to said AC output to cause suitable voltage(s) to be supplied to each of the CCFLs to cause the CCFLs to supply light. In one embodiment, a plurality of CCFL lamp units are used, each equipped with its own driver control circuit that supplies a suitable voltage to the CCFL of such unit. Hence, the driver circuits applying AC outputs to the two or more CCFL lamp units may apply AC outputs that are different from one another, so that the two or more CCFL units are individually controlled to emit light of the same or different intensities.
Owner:TBT ASSET MANAGEMENT INT
Inkjet recording method, inkjet recording system, and printed material
InactiveUS20100026771A1Quality improvementHigh film strengthDuplicating/marking methodsOther printing apparatusVinyl etherUltraviolet
An inkjet recording method is provided that includes a step of discharging onto a recording medium an ink composition containing a vinyl ether compound, an oxirane compound and / or oxetane compound, a cationic photopolymerization initiator, and a colorant, and a step of curing the discharged ink composition by irradiation with UV rays by UV irradiation means having an aperture type hot cathode fluorescent tube having a getter in the interior thereof. There are also provided an inkjet recording system that includes recording medium transport means, an inkjet head for discharging an ink composition containing a vinyl ether compound, an oxirane compound and / or oxetane compound, a cationic photopolymerization initiator, and a colorant to thus form an image on a recording medium, and UV irradiation means for curing the ink composition discharged onto the recording medium by irradiation with UV rays, the UV irradiation means having as a UV light source an aperture type hot cathode fluorescent tube having a getter in the interior thereof, a printed material obtained by the inkjet recording method, and a printed material obtained using the inkjet recording system.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Techniques for providing a multimode ion source
Techniques for providing a multimode ion source are disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the techniques may be realized as an apparatus for ion implantation, the apparatus including an ion source having a hot cathode and a high frequency plasma generator, wherein the ion source has multiple modes of operation.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
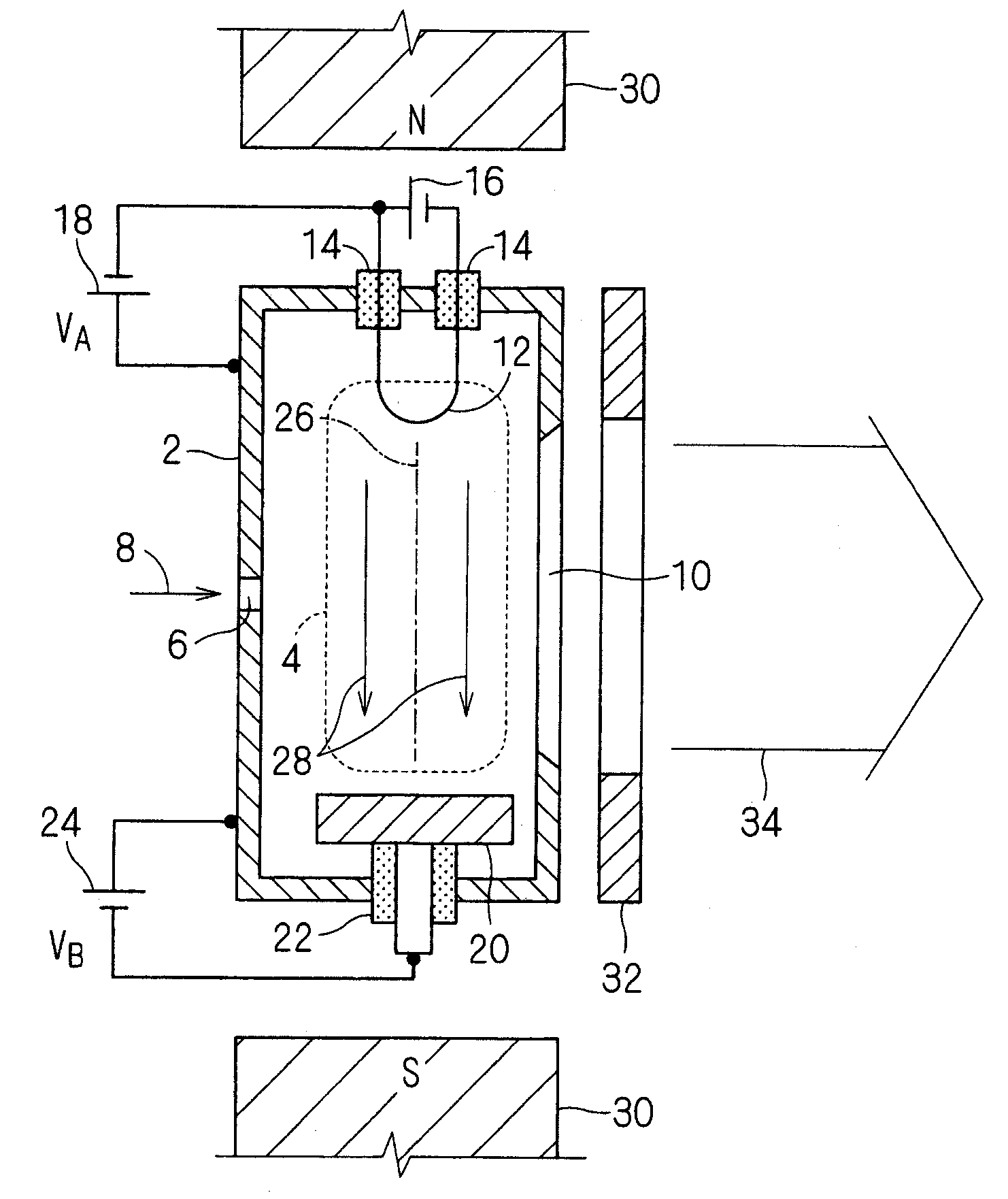
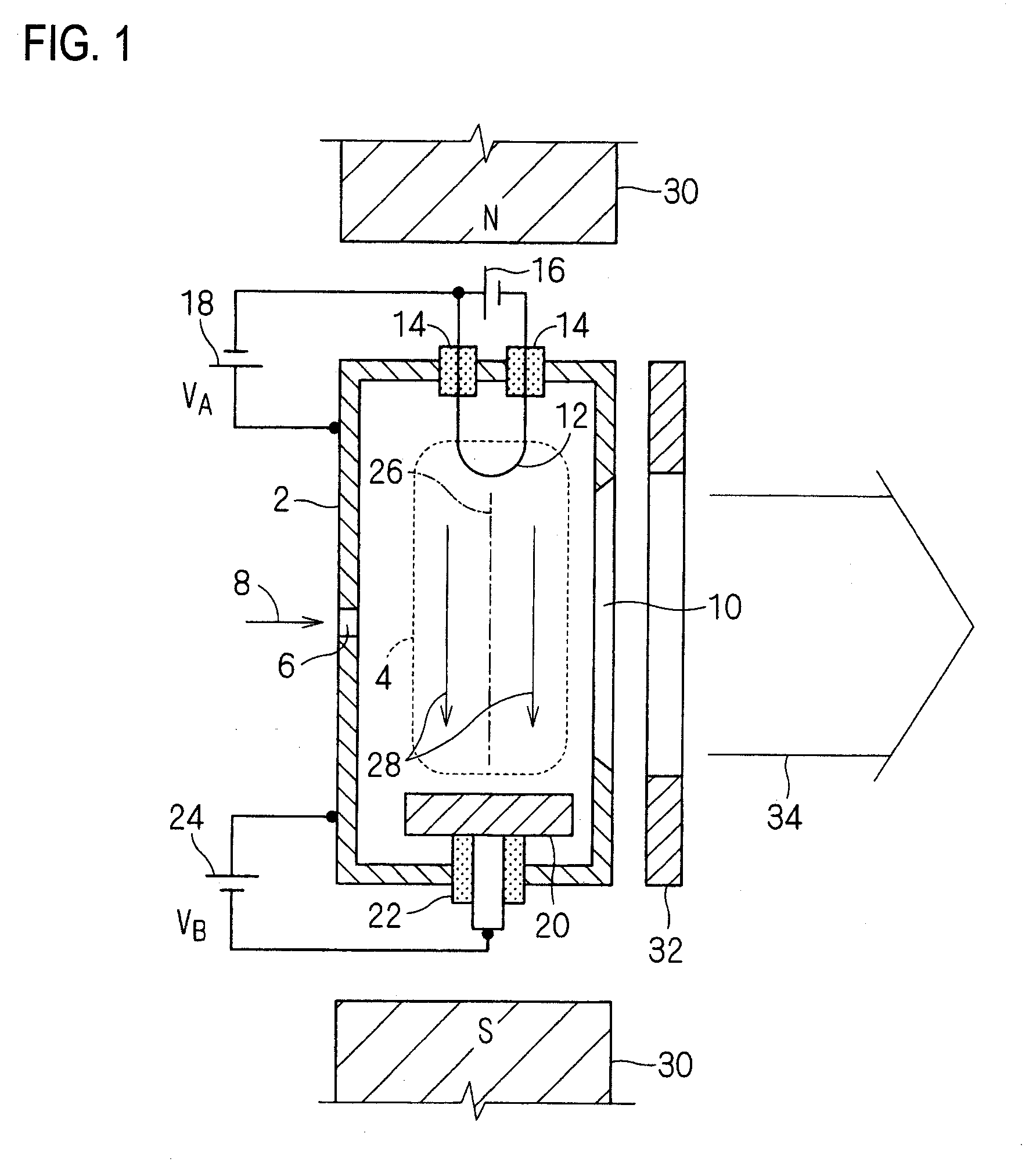
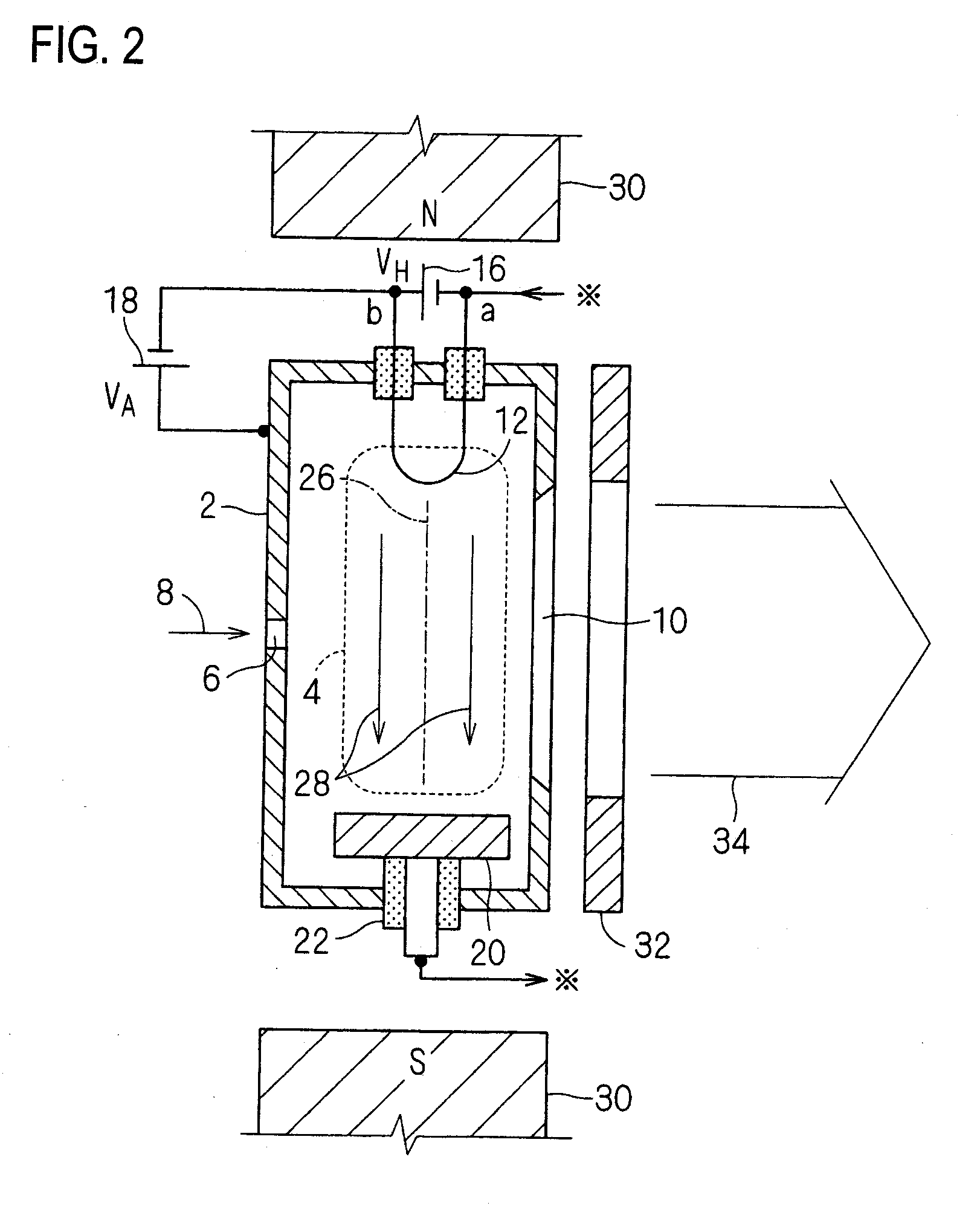
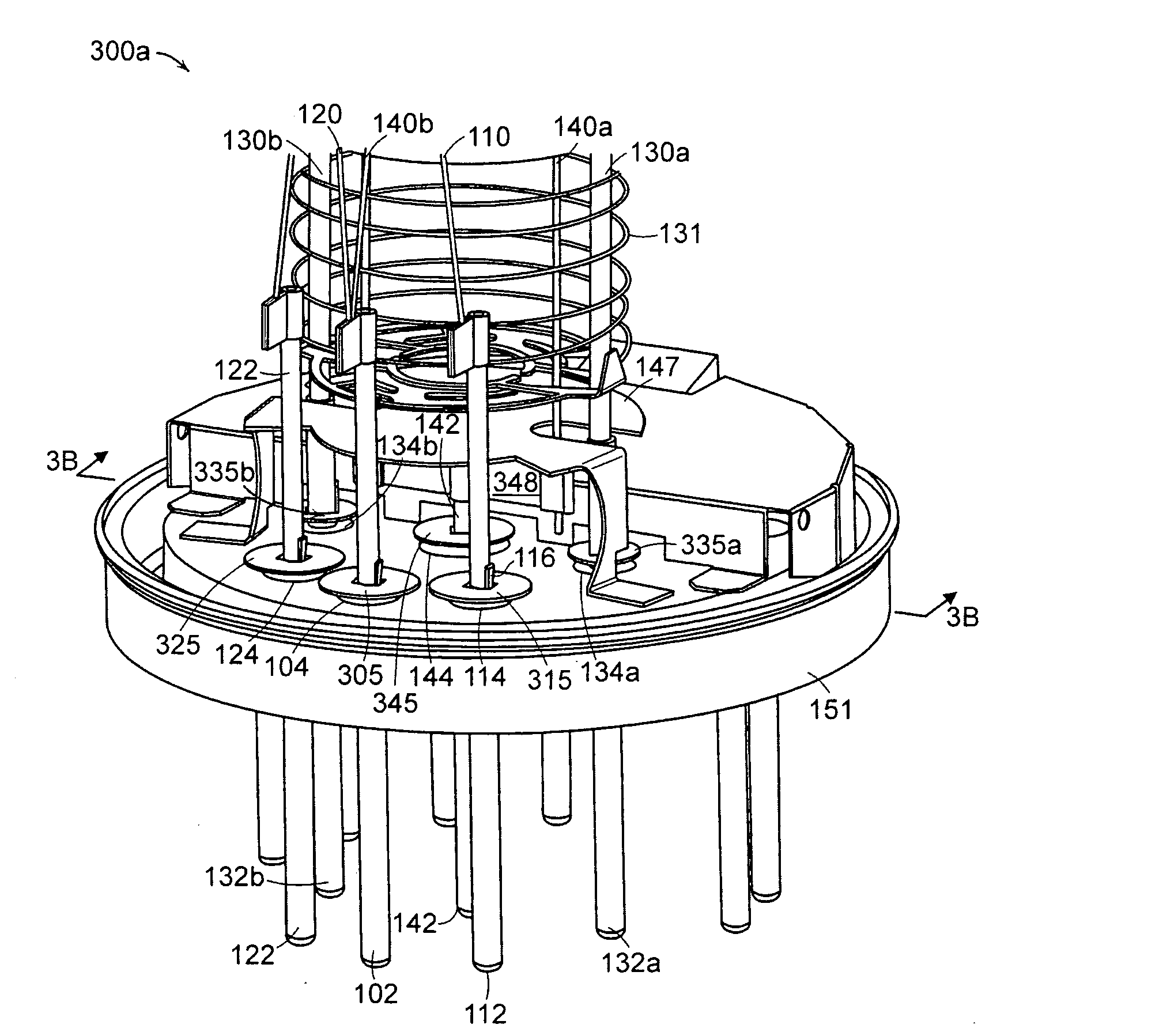
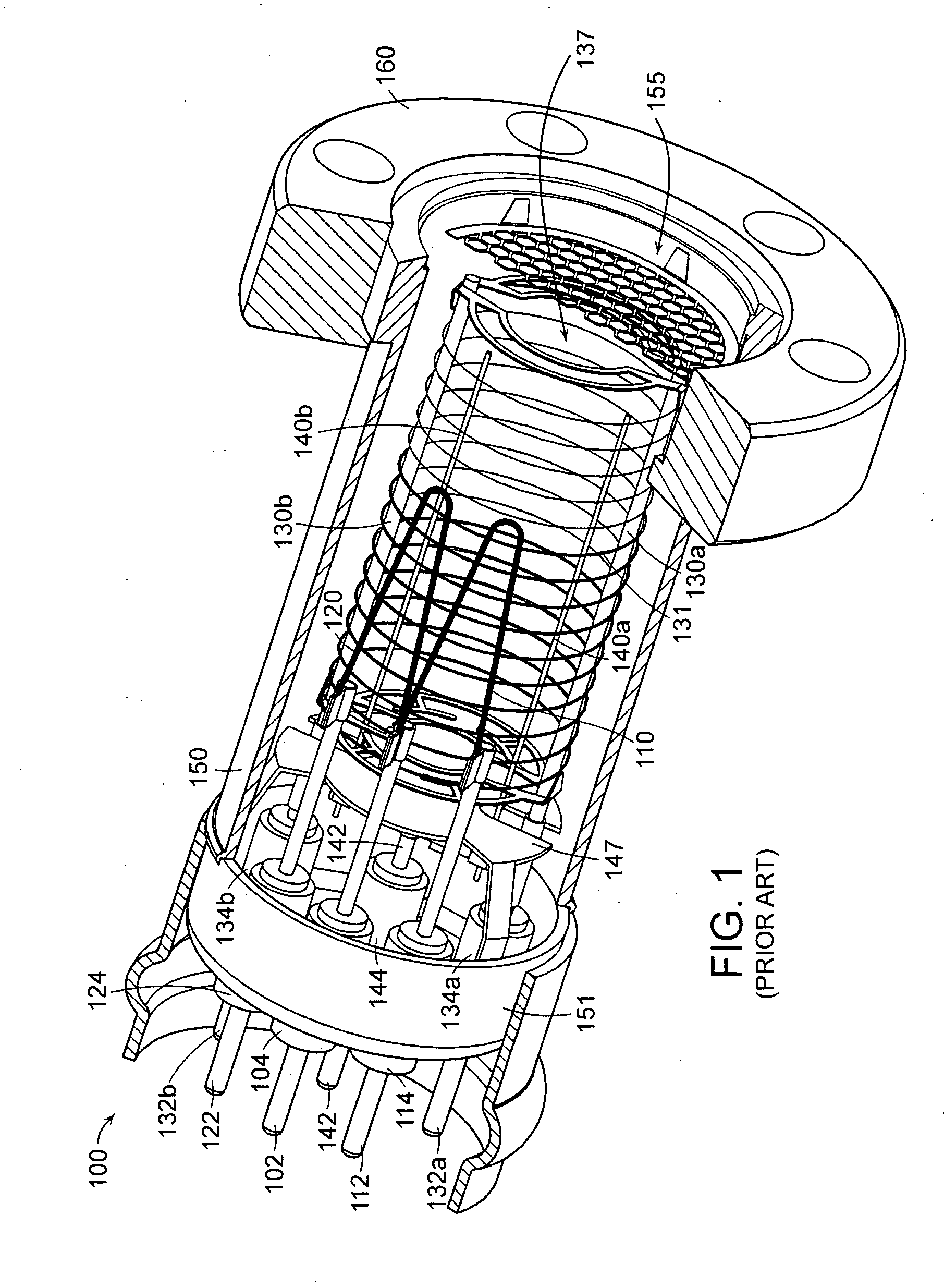
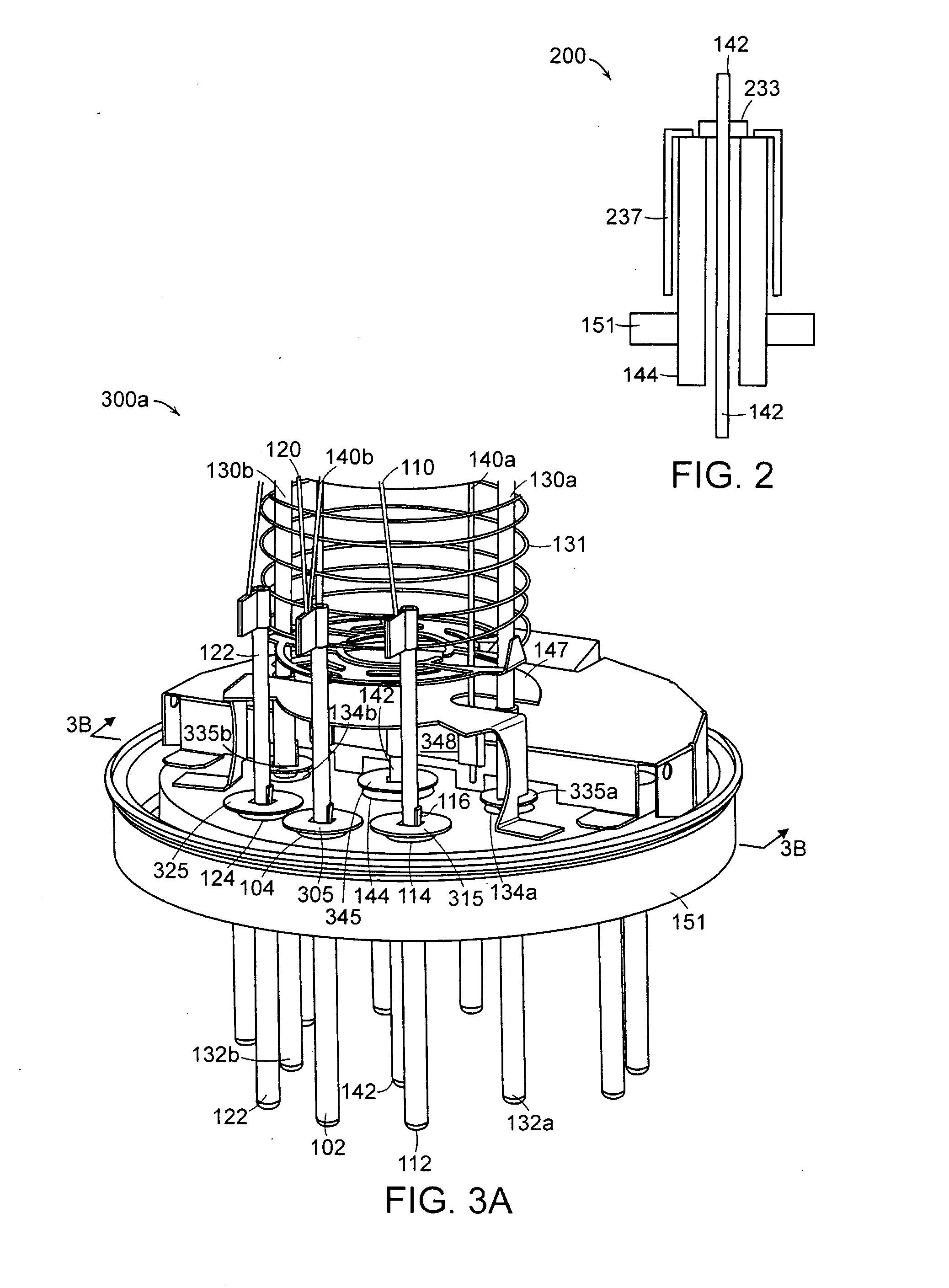
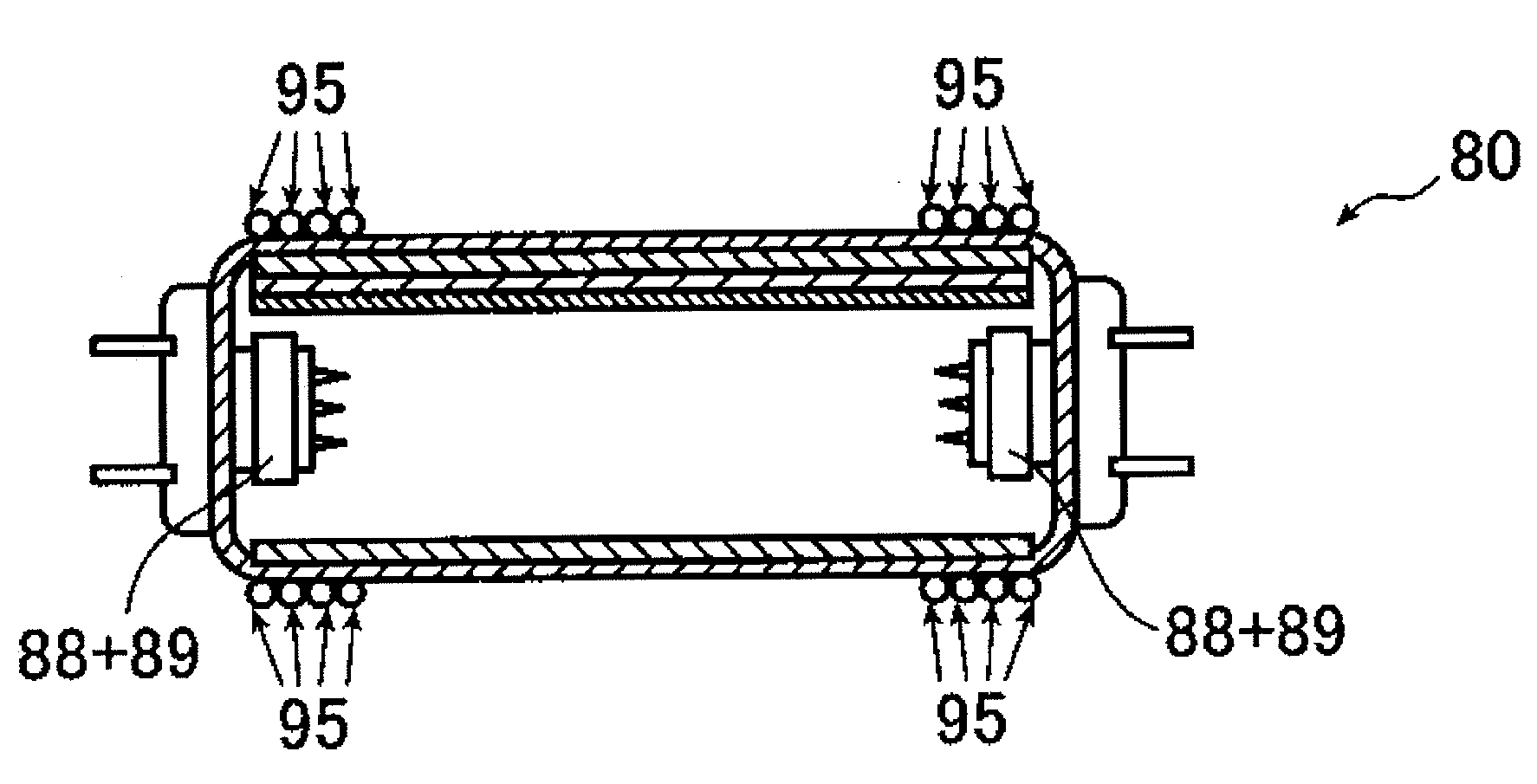
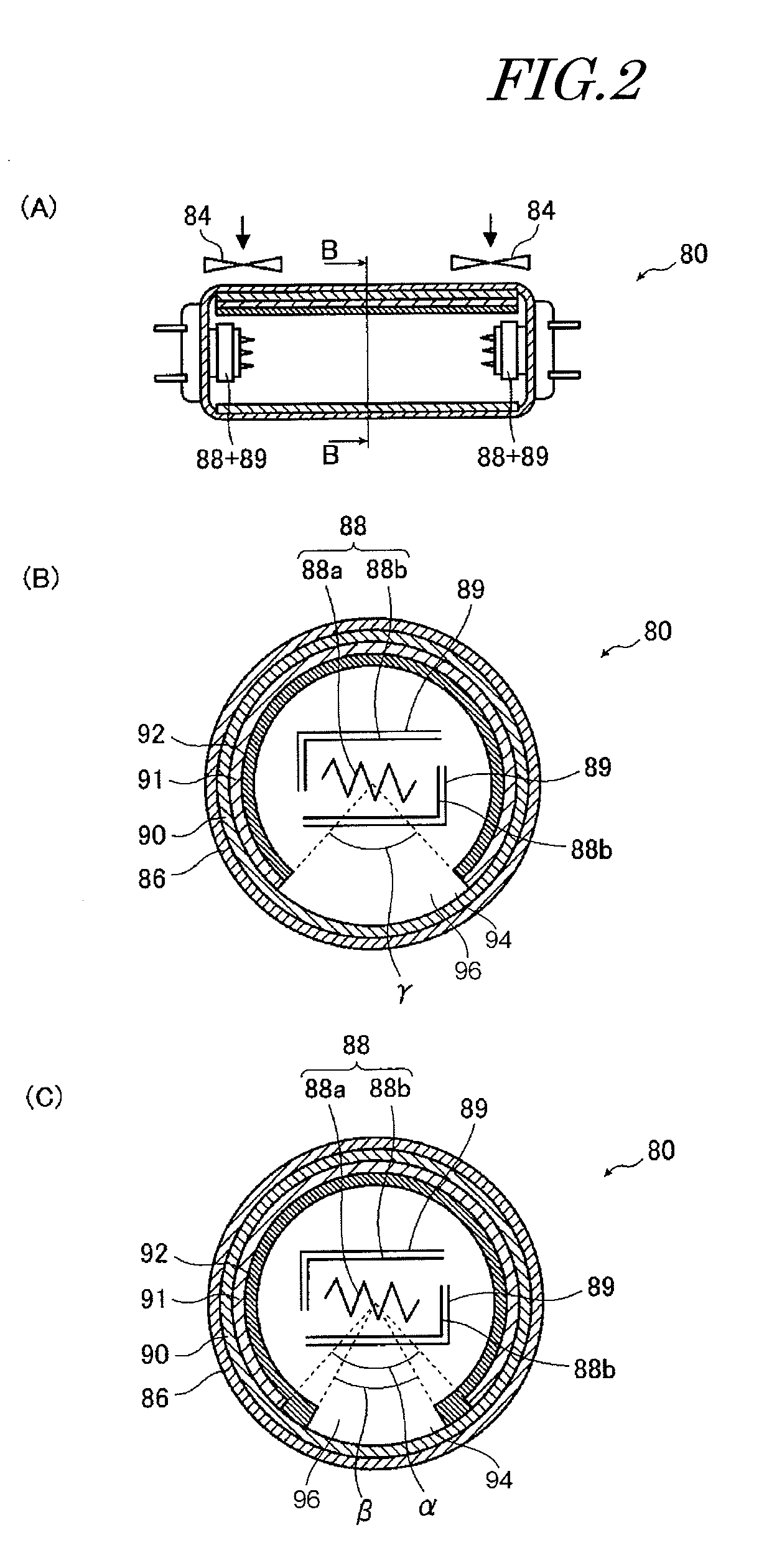
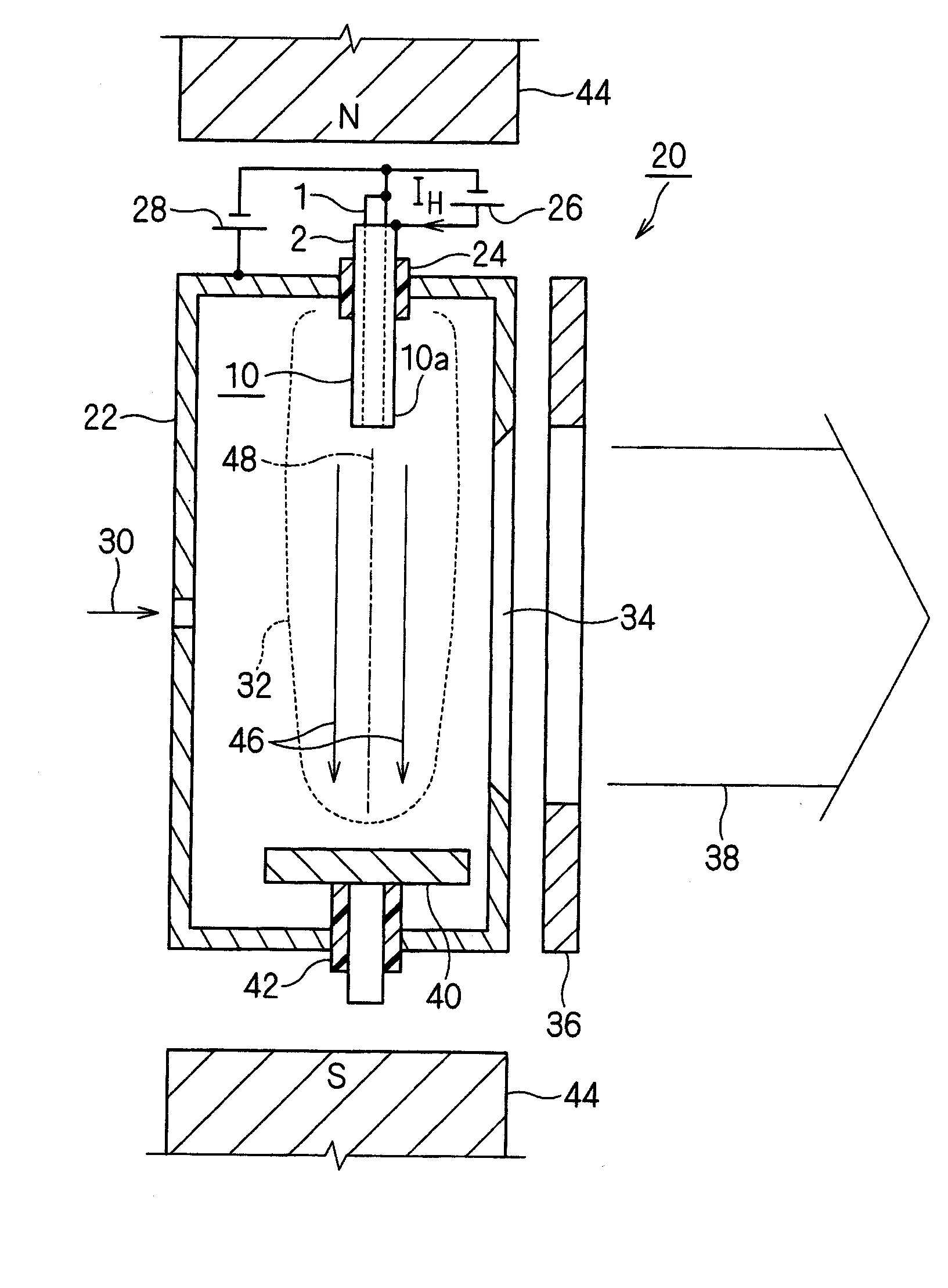
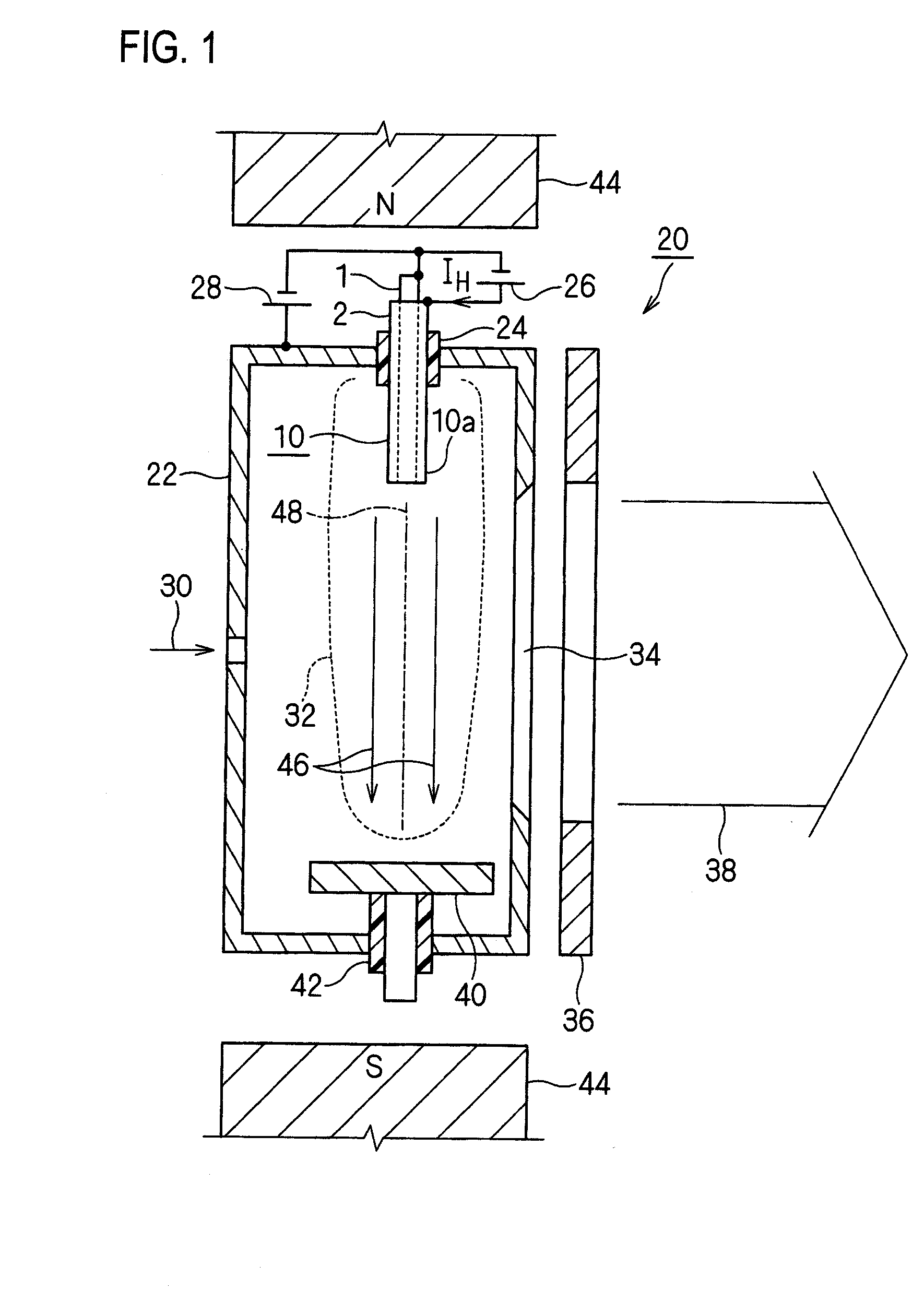
Hot cathode and ion source including the same
InactiveUS20100038556A1Inhibit temperature riseExtended service lifeMaterial analysis by optical meansIon beam tubesElectrical conductorEngineering
A hot cathode includes: a hollow external conductor; a hollow internal conductor which is placed coaxially inside the external conductor; and a connection conductor which electrically connects tip end portions of the conductors. A heating current is folded back through the connection conductor to flow in opposite directions in the external conductor and the internal conductor.
Owner:NISSIN ION EQUIP CO LTD
Method and apparatus for shielding feedthrough pin insulators in an ionization gauge operating in harsh environments
InactiveUS7456634B2Easy to operateDamage to materialVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsDischarge tube/lamp detailsEngineeringIonization
Shields for feedthrough pin insulators of a hot cathode ionization gauge are provided to increase the operational lifetime of the ionization gauge in harmful process environments. Various shield materials, designs, and configurations may be employed depending on the gauge design and other factors. In one embodiment, the shields may include apertures through which to insert feedthrough pins and spacers to provide an optimal distance between the shields and the feedthrough pin insulators before the shields are attached to the gauge. The shields may further include tabs used to attach the shields to components of the gauge, such as the gauge's feedthrough pins. Through use of example embodiments of the insulator shields, the life of the ionization gauge is extended by preventing gaseous products from a process in a vacuum chamber or material sputtered from the ionization gauge from depositing on the feedthrough pin insulators and causing electrical leakage from the gauge's electrodes.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
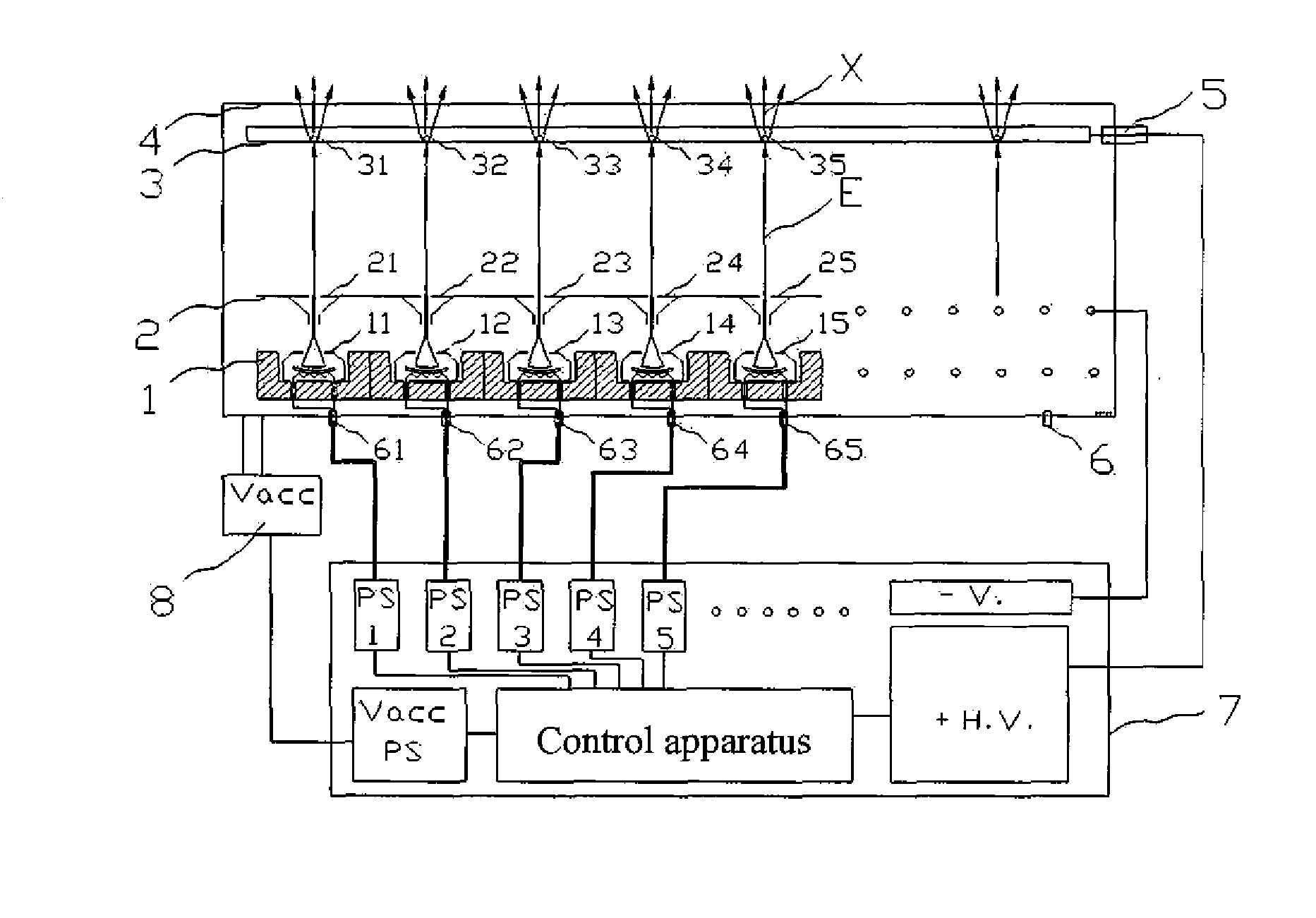
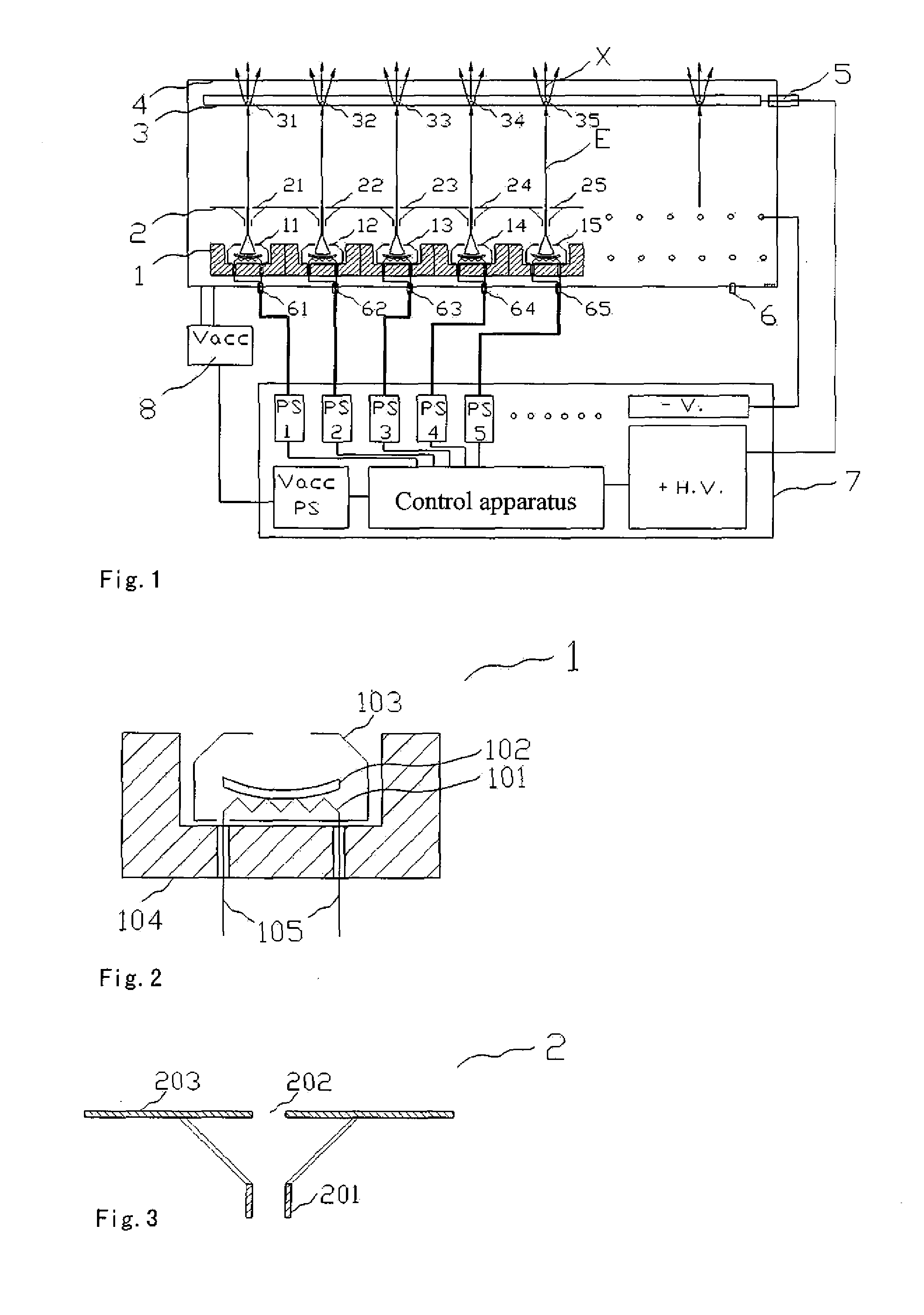
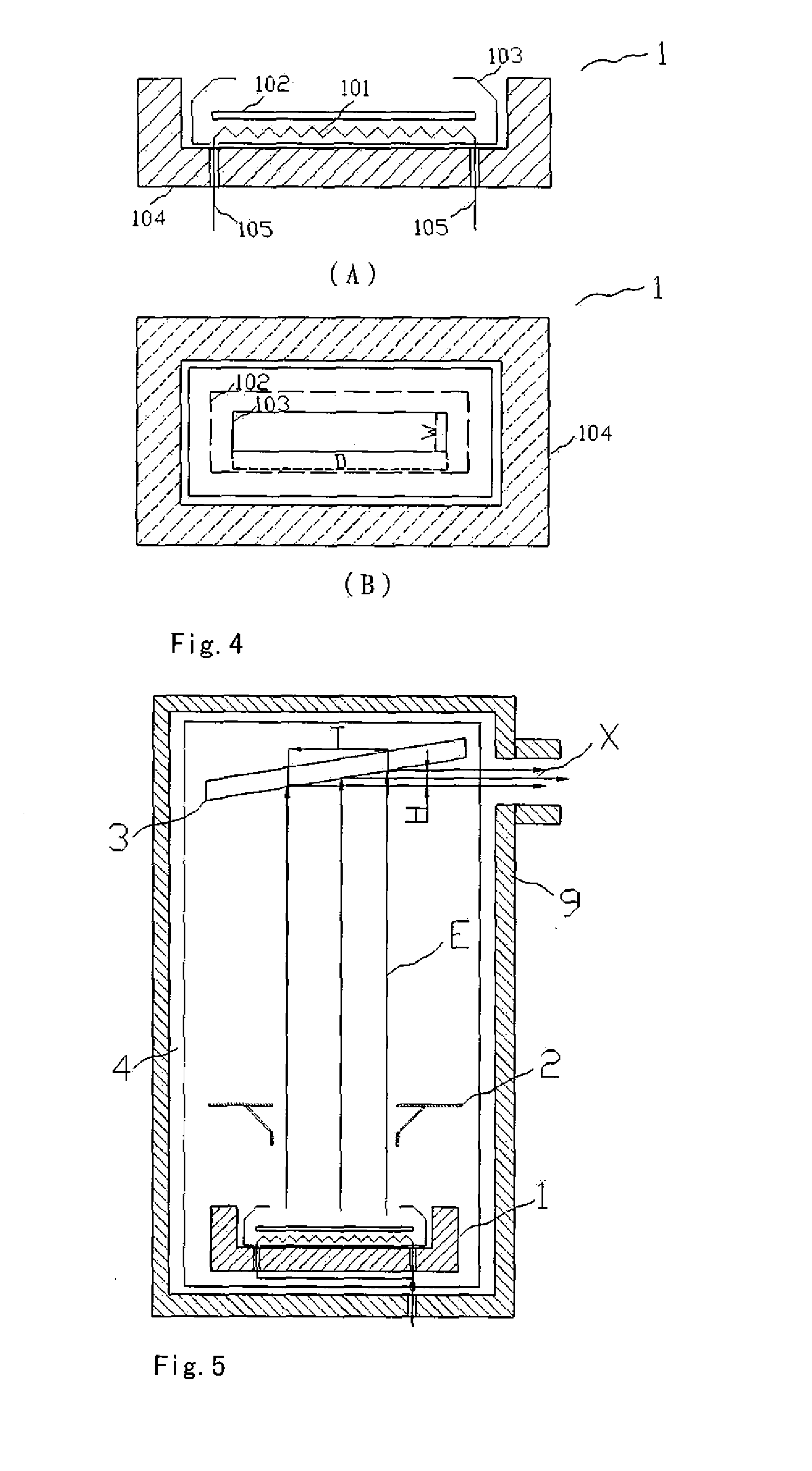
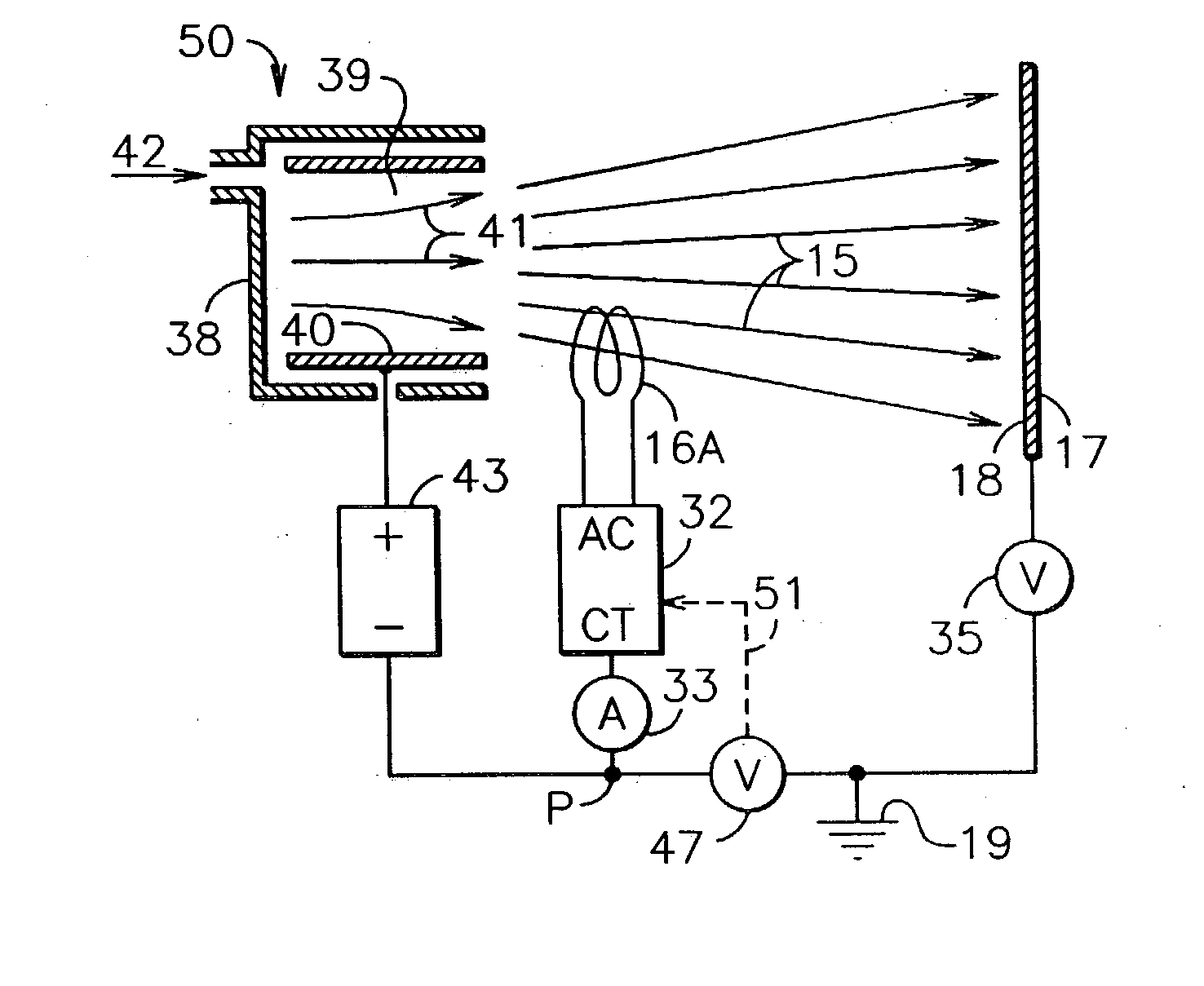
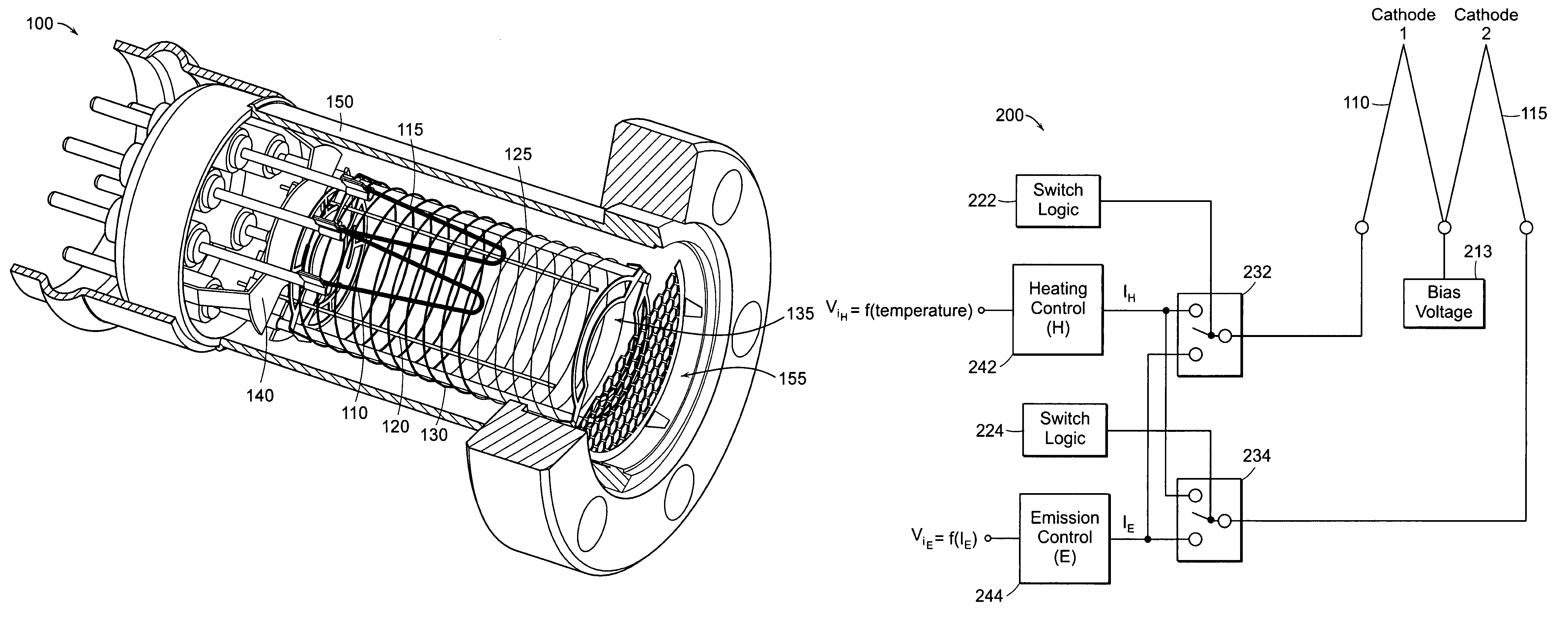
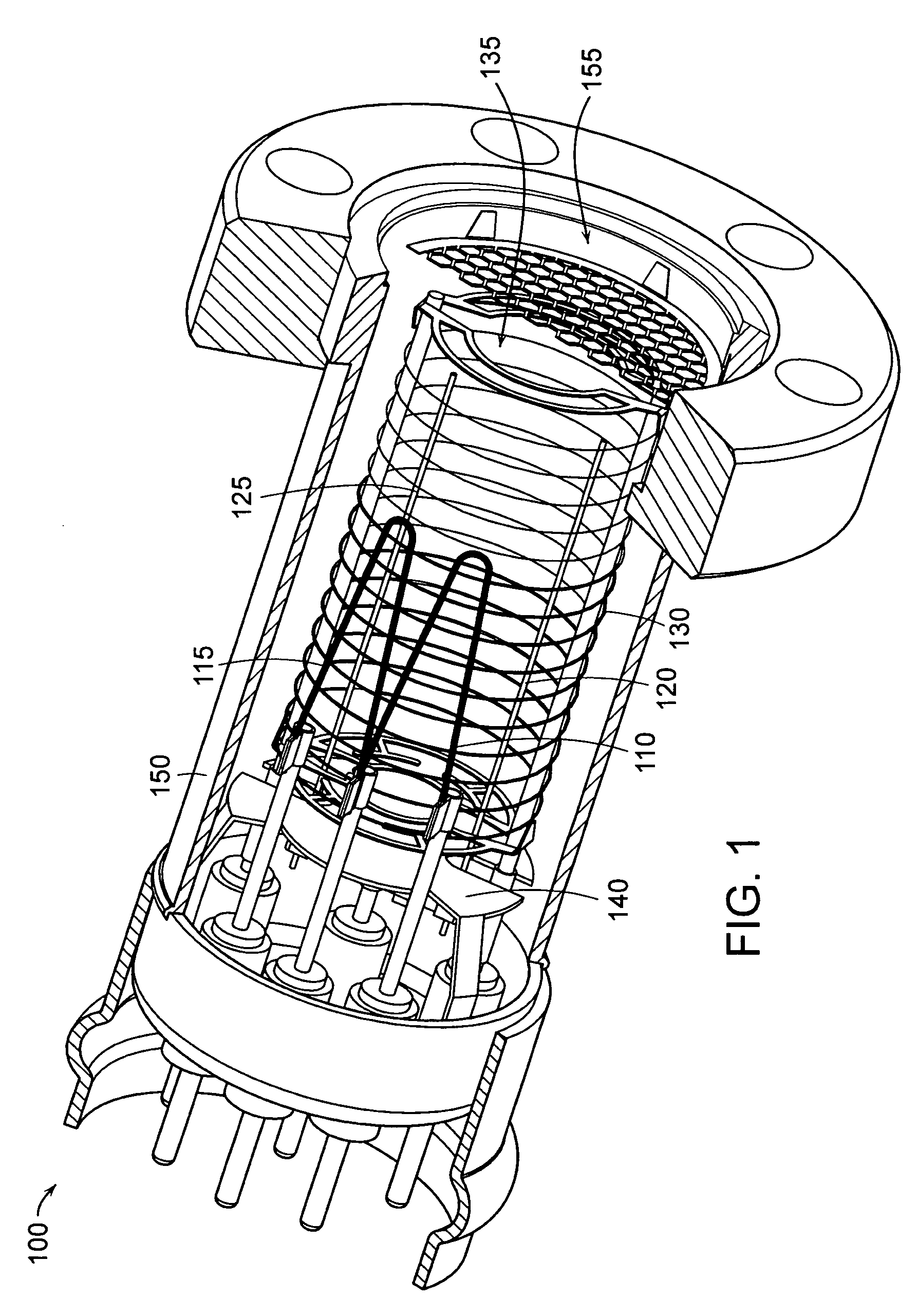
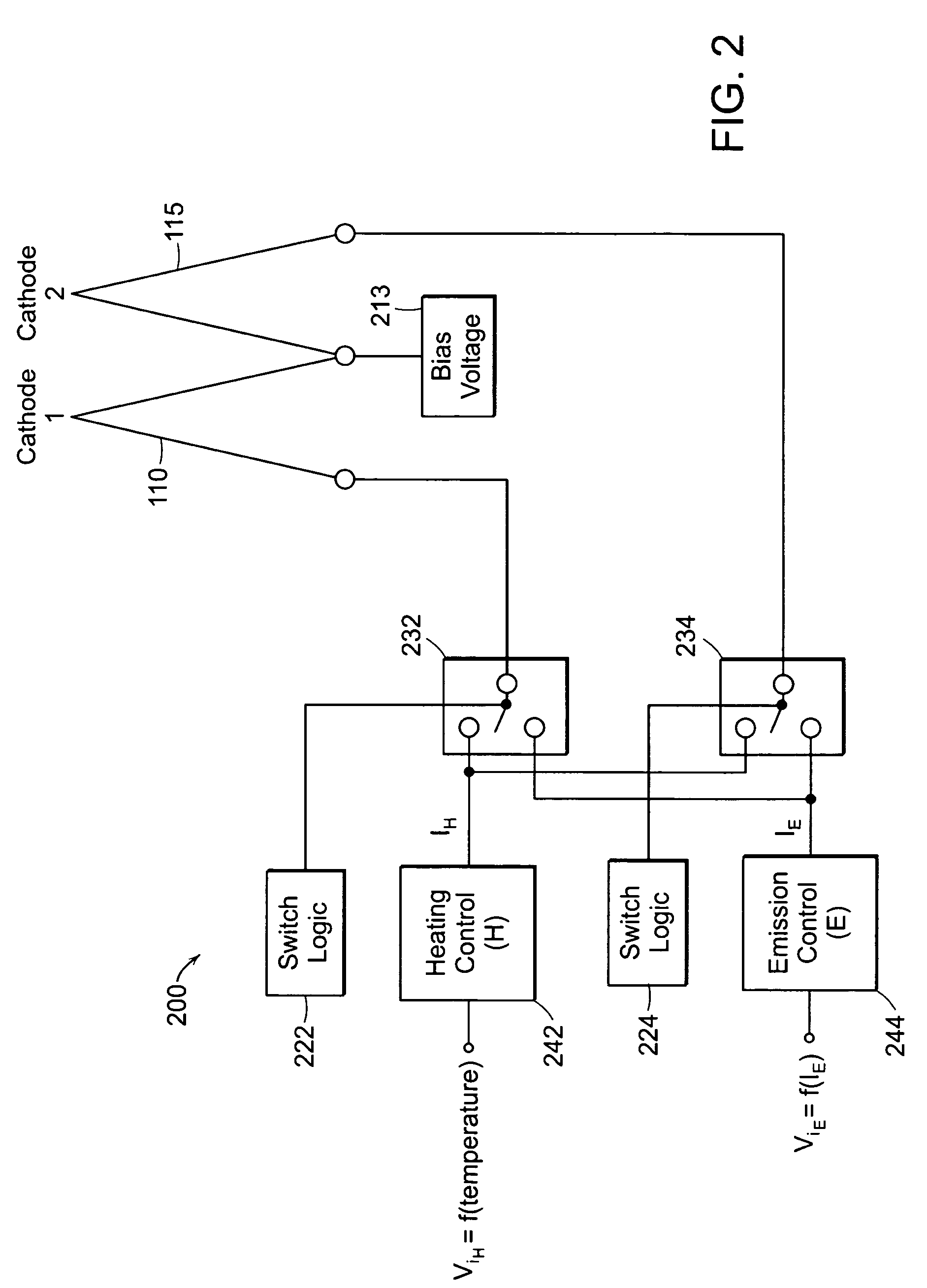
Cathode control multi-cathode distributed x-ray apparatus and ct device having said apparatus
ActiveUS20140185739A1Easy to controlHigh currentMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayFocal position
This invention relates to an apparatus producing distributed X-ray, and in particular to a cathode control multi-cathode distributed X-ray apparatus, which produces X-ray that changes focal position in a predetermined order by arranging multiple independent hot cathodes and controlling cathodes in an X-ray source device, and a CT device having said X-ray apparatus.
Owner:NUCTECH CO LTD +1
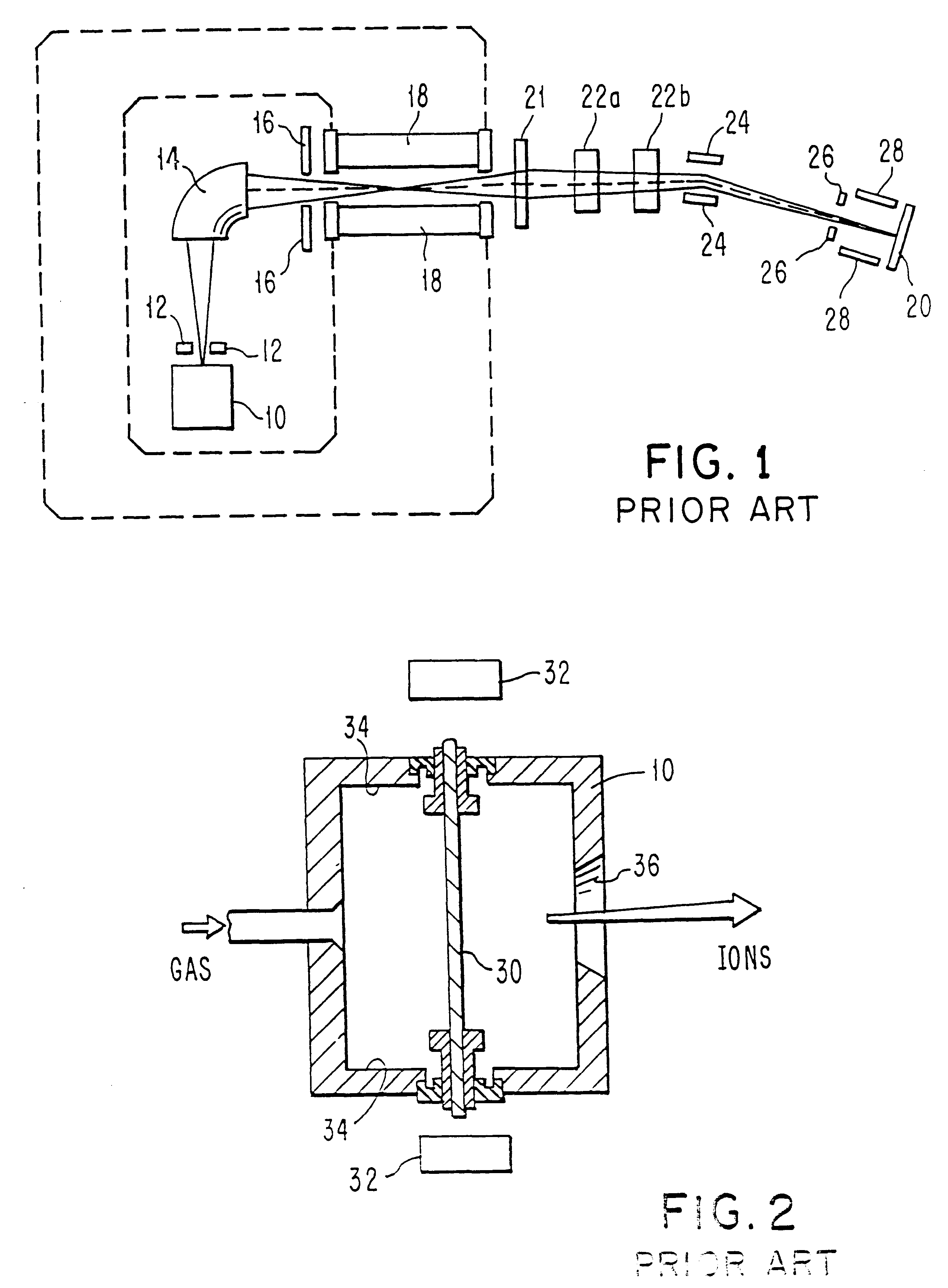
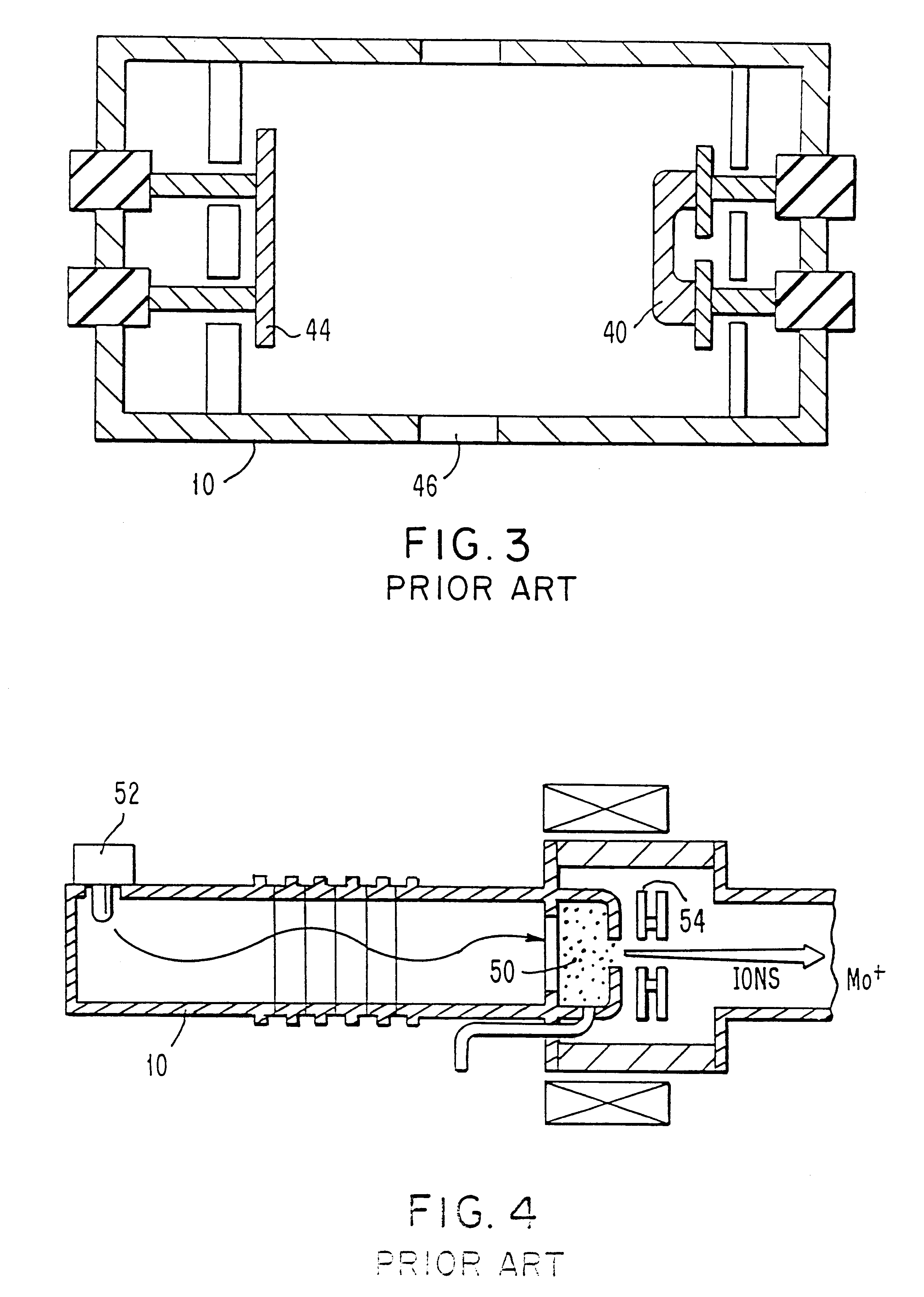
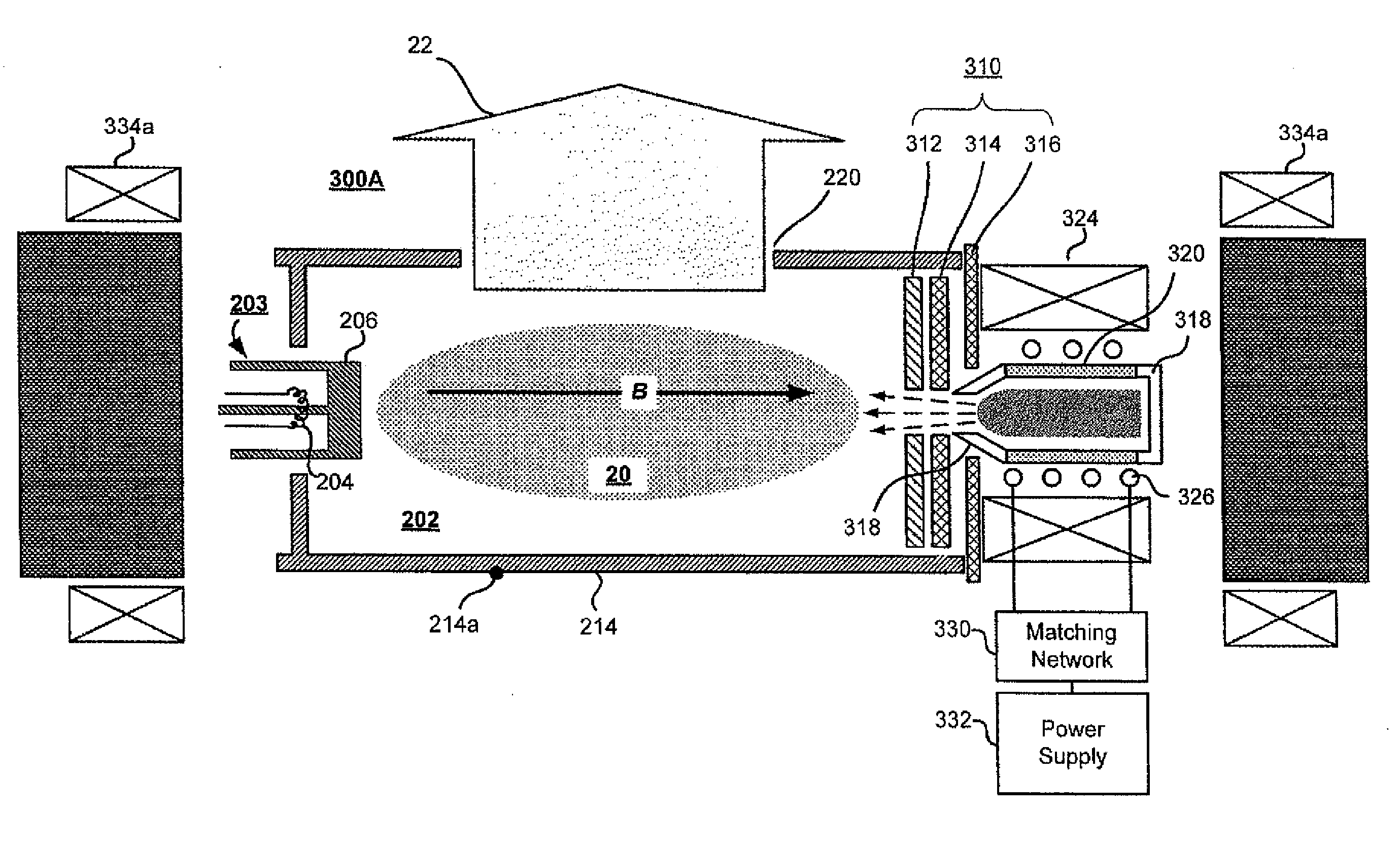
Ion-source neutralization with a hot-filament cathode-neutralizer
InactiveUS20030193295A1Current providedSimple and economical and reliableElectric arc lampsTransit-time tubesIon beamEngineering
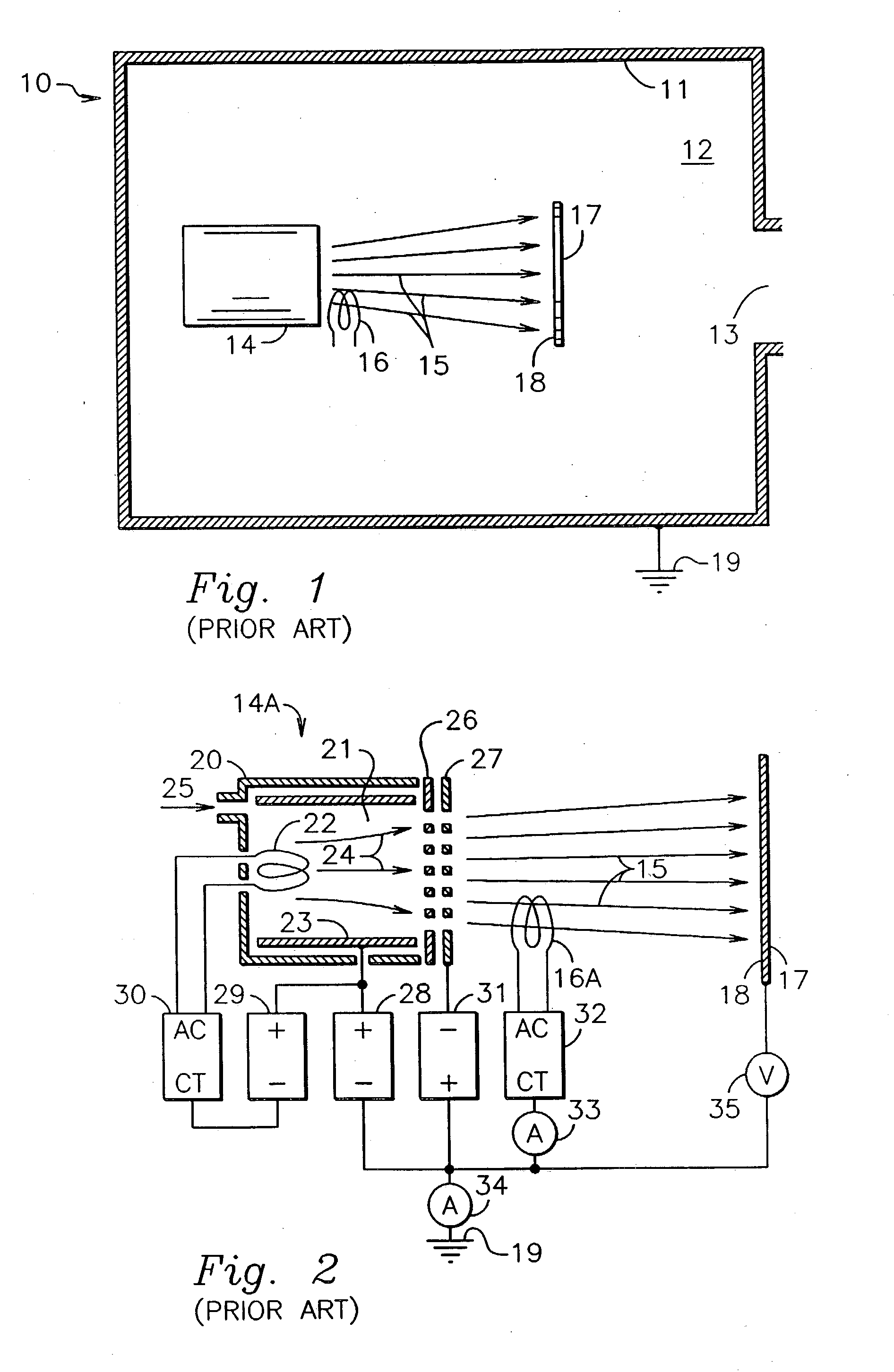
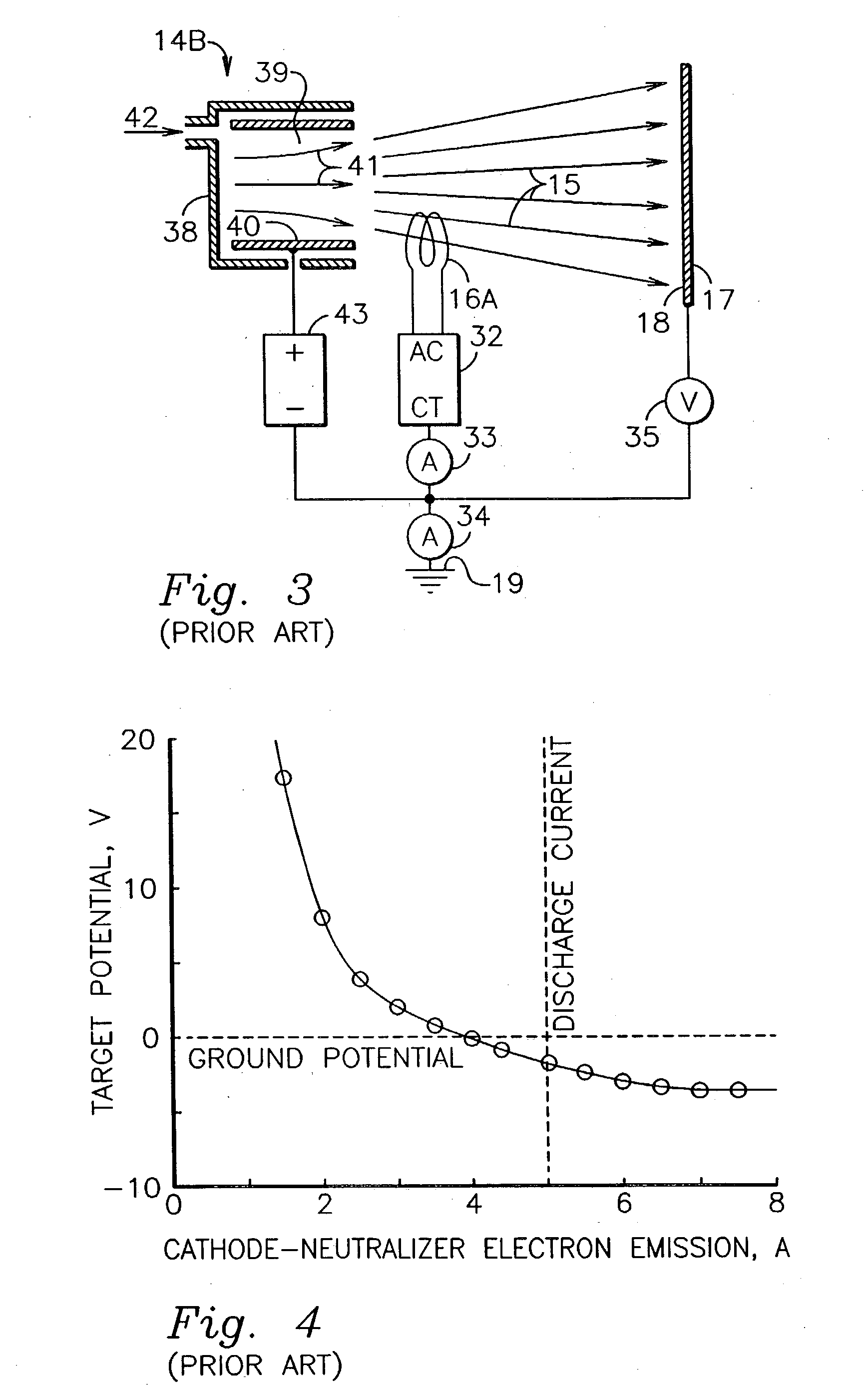
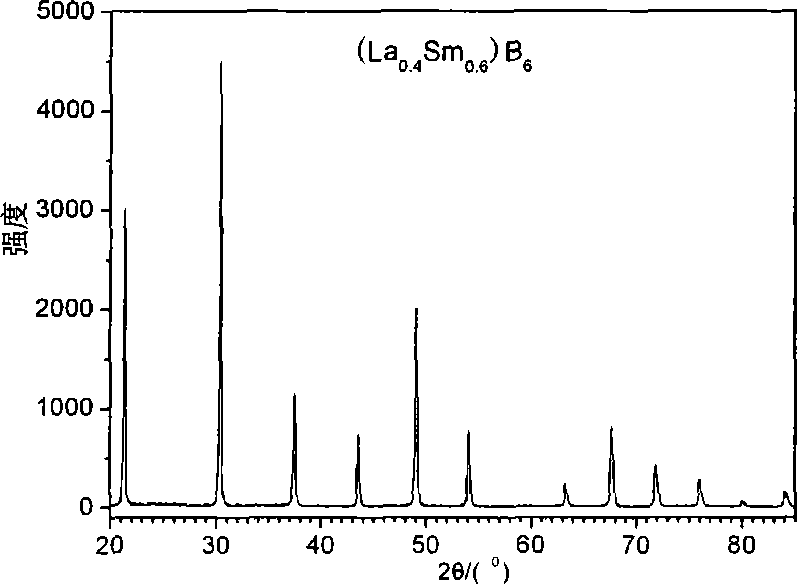
In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, the ion-beam apparatus takes the form of a gridless ion source with a hot-filament cathode-neutralizer, in which the hot filament is heated with a current from the cathode-neutralizer heater. The cathode-neutralizer is connected to the negative terminal of the discharge supply for the gridless ion source. This connection is substantially isolated from ground (the potential of the surrounding vacuum chamber, which is usually at earth ground) and its potential is measured relative to ground. The heater current to the cathode-neutralizer is controlled by adjusting it so as to maintain this potential in a narrow operating range. This control can be manual or automatic.
Owner:KAUFMAN & ROBINSON
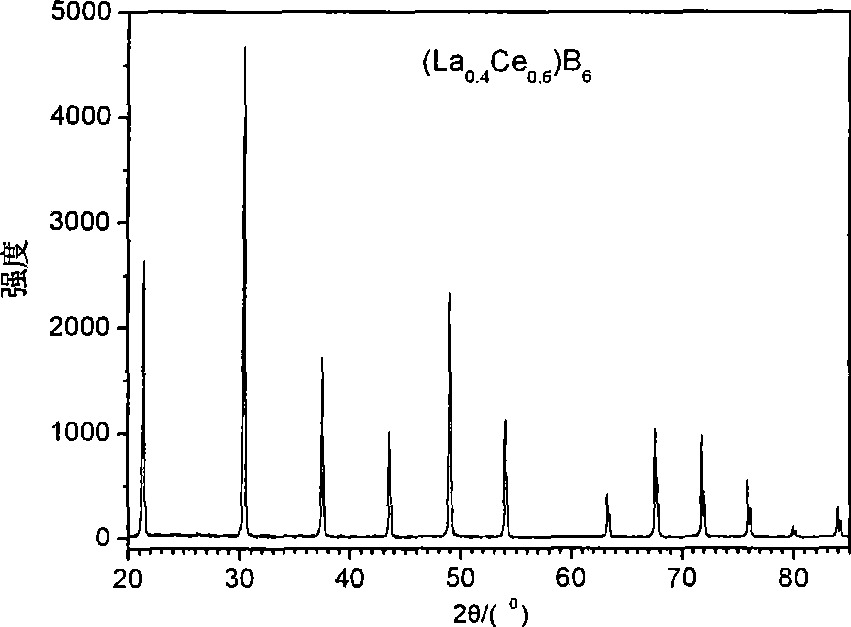
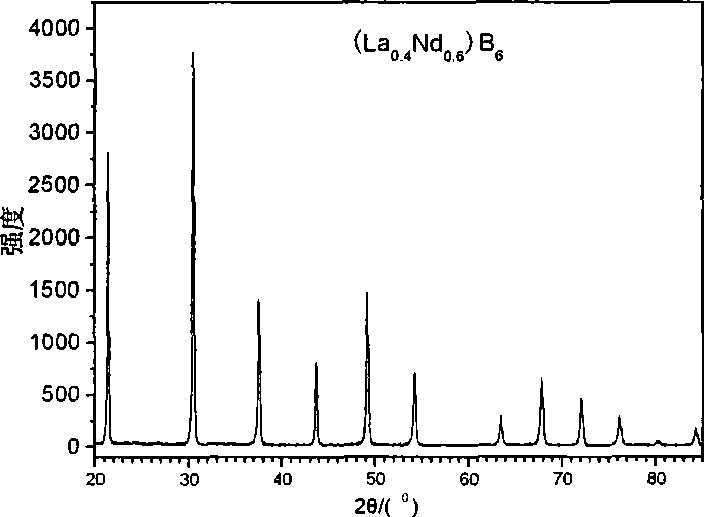
Multicomponent rare earth boride (LaxRE1-x)B6 cathode material and preparation thereof
A multi-component rare earth boride (LaxRE1-x)B6 cathode material and a preparation method thereof pertain to the technical field of rare earth boride hot cathode materials. At present, the research on the multi-component rare earth boride has the problems of few component systems, complicated process, etc. The component of the cathode material is (LaxRE1-x)B6, wherein, RE is one of Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu or Gd, and x is equal to or smaller than 0.2 and is equal to or larger than 0.8. The method comprises the following steps: LaH2 nano-powder and REH2 nano-powder are prepared by a DC arc evaporation method, mixed with the raw material B powder in a hypoxia environment, and sintered by spark plasma sintering (SPS) to obtain the (LaxRE1-x)B6, wherein, the sintering pressure is 30-50MPa, the heating rate is 100-200 DEG C per minute, the sintering temperature is 1,300-170 DEG C, and heat preservation lasts for 5-15min. The method has the advantages of low sintering temperature and simple process; and that the prepared cathode material has high purity, high density, excellent mechanical properties and emission performance.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Electron beam heating evaporation method as well as device and uses thereof
InactiveCN101177777APrecise thickness controlExcellent charge transportVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingLow voltageHigh-voltage direct current
The invention relates to a heating and evaporating method of a novel electron beam provided with powdered material with comparatively high melting point and a device thereof. The method combines an electron beam heating evaporating method and a resistance heating evaporating method to provide a filamentose cathode with a negative bias by a high voltage dc power, thus a highfield is formed between the negative bias and an earthing crucible; furthermore, a filamentose hot cathode is provided with an adjustable working current by a low voltage ac power to lead an electron beam current to be emitted by the filamentose hot cathode; the electron beam current bombards and heats the crucible at a high speed under the action of a strong electric field. An electrochromic layer tungsten trioxide WO3 film and an electrolyte layer lithium fluoride LiF film applied to electrochromic equipment can be prepared by using the electron beam heating and evaporating method of the invention; the film material prepared is dense and the charge transport performance is excellent; the film thickness can be precisely controlled when the method is applied to the evaporating preparation of polyimide substrate flexible film and solar cell nickel barrier film, and the device is characterized by simple operation.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Preparation method of large-dimension multi-element rare earth boride (Ce0.9Pr0.1)B6 single crystal
InactiveCN102808215ALarge growth sizeQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsBorideDiffractometer
The invention discloses a preparation method of a multi-element rare earth boride (Ce0.9Pr0.1)B6 single crystal, and belongs to the technical field of rare earth boride hot cathode materials. At present, the research about the multi-element rare earth boride single crystal is little; further, the prepared single crystal is small in dimension and low in purity; and the requirement of actual application cannot be met. By using the preparation method, the high-quality and large-dimension multi-element rare earth boride (Ce0.9Pr0.1)B6 single crystal is prepared by adopting a method for combining discharge plasma sintering with floating zone melting. The (Ce0.9Pr0.1)B6 single crystal prepared by using CeB6 and PrB6 powder as raw materials is a phi4.5 mm*40 mm cylinder, and the test result of a single-crystal diffractometer shows that the single crystal is favorable in quality and a twin crystal phenomenon does not occur.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method and apparatus for maintaining emission capabilities of hot cathodes in harsh environments
ActiveUS7429863B2Easy to operateReduce material usageVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsElectric lighting sourcesEngineeringIonization
A method and apparatus for operating a multi-hot-cathode ionization gauge is provided to increase the operational lifetime of the ionization gauge in gaseous process environments. In example embodiments, the life of a spare cathode is extended by heating the spare cathode to a temperature that is insufficient to emit electrons but that is sufficient to decrease the amount of material that deposits on its surface or is optimized to decrease the chemical interaction between a process gas and a material of the at least one spare cathode. The spare cathode may be constantly or periodically heated. In other embodiments, after a process pressure passes a given pressure threshold, plural cathodes may be heated to a non-emitting temperature, plural cathodes may be heated to a lower emitting temperature, or an emitting cathode may be heated to a temperature that decreases the electron emission current.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
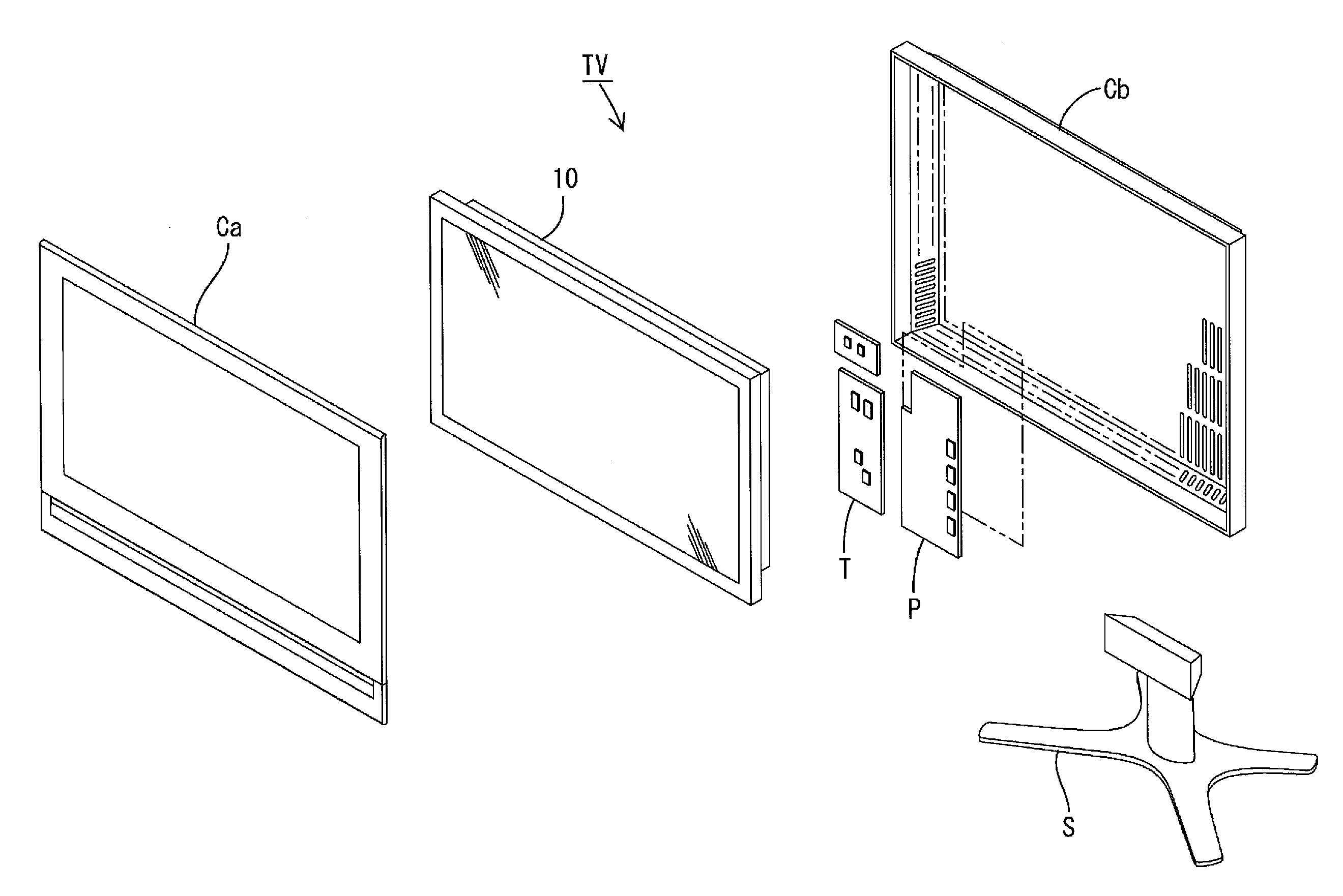
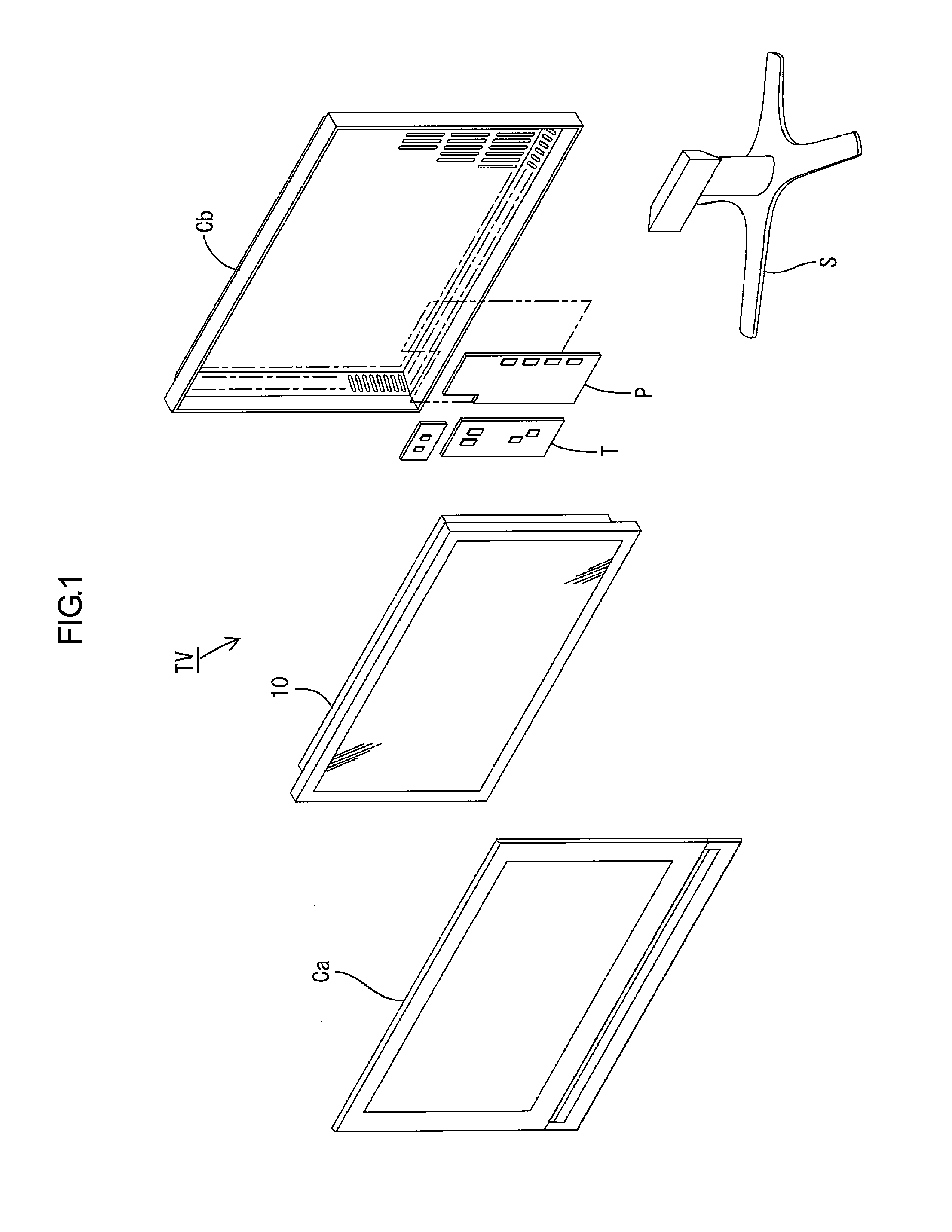
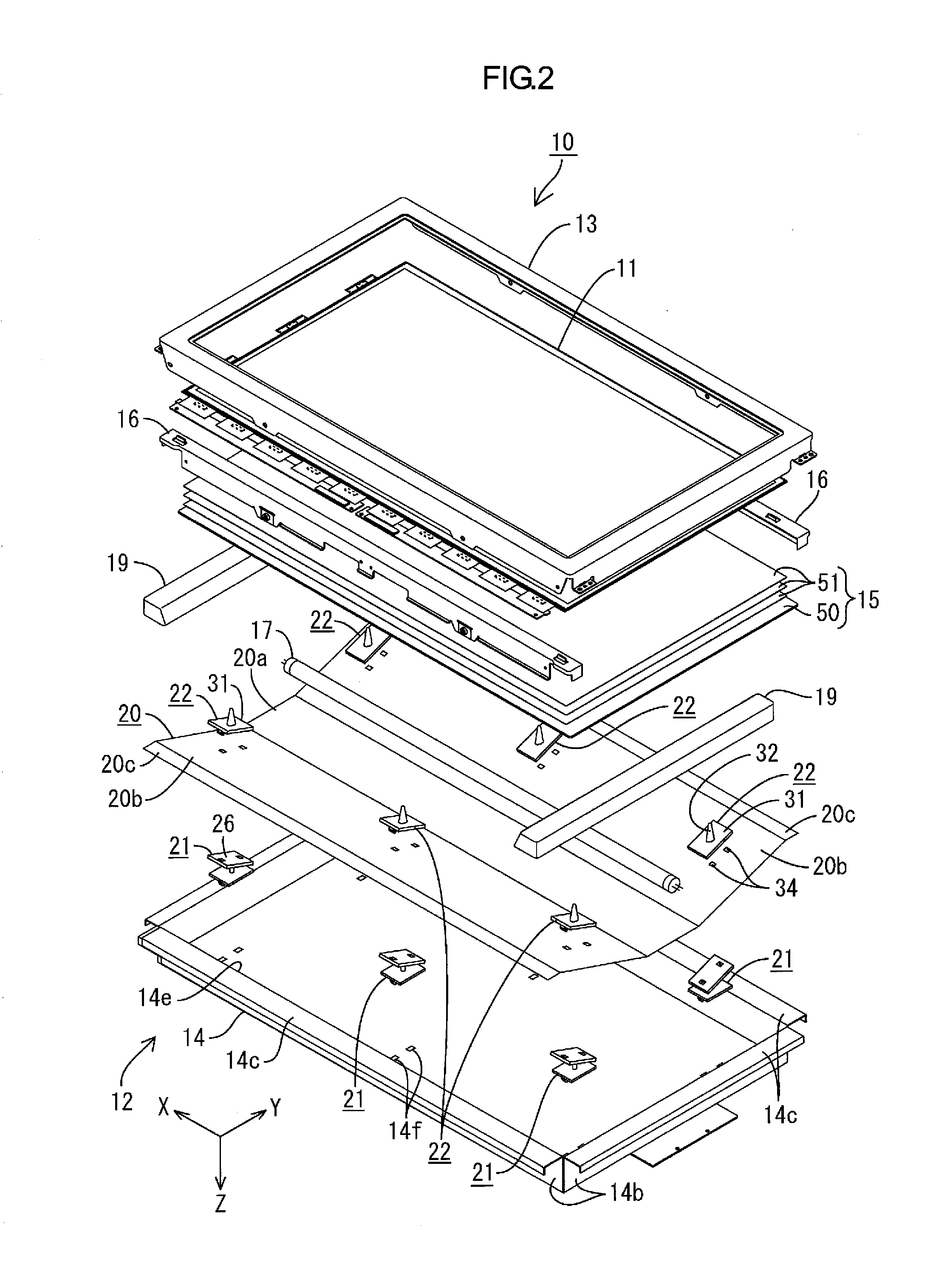
Lighting device, display device, and television receiver
InactiveUS20120176557A1Avoid changeInhibitionTelevision system scanning detailsIlluminated signsLight equipmentTelevision receivers
Occurrence of uneven brightness in a backlight unit is suppressed. A backlight unit 12 includes a hot cathode tube 17 as a light source; a chassis 14 including a bottom plate 14a arranged on a side opposite to a light exit side with respect to the hot cathode tube 17 and housing the hot cathode tube 17; a reflection sheet 20 including a bottom portion 20a extending along the bottom plate 14a and a rising portion 20b rising from a bottom portion 20a to the light exit side and reflecting light; a first holding member 21 arranged on a side opposite to the light exit side with respect to each rising portion 20b and fixed to the chassis 14; and a second holding member 22 arranged on the light exit side of each rising portion 20b and configured to sandwich each rising portion 20b with the first holding member 21.
Owner:SHARP KK
Portable ultraviolet water purification system
InactiveUS20050205480A1Easy to transportProtection from damageWater treatment parameter controlWater/sewage treatment by irradiationLow voltageUltraviolet lights
A portable water-purification system includes a container for holding a liquid and an ultraviolet light source configured for immersion in the liquid. The ultraviolet light source is a straight low-cost tube controlled by electronic circuitry for providing hot-cathode striking at a relatively low voltage using a fly-back inductor. The operation of the water purification system is controlled by a micro-controller within the electronic circuitry.
Owner:MERIDIAN DESIGN
Technique for improving performance and extending lifetime of indirectly heated cathode ion source
ActiveUS7491947B2Improving performance and lifetimeImprove lifetimeMaterial analysis by optical meansIon beam tubesIon implantationIon source
A technique improving performance and lifetime of indirectly heated cathode ion sources is disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the technique may be realized as a method for improving performance and lifetime of an indirectly heated cathode (IHC) ion source in an ion implanter. The method may comprise maintaining an arc chamber of the IHC ion source under vacuum during a maintenance of the ion implanter, wherein no gas is supplied to the arc chamber. The method may also comprise heating a cathode of the IHC ion source by supplying a filament with a current. The method may further comprise biasing the cathode with respect to the filament at a current level of 0.5-5 A without biasing the arc chamber with respect to the cathode. The method additionally comprise keeping a source magnet from producing a magnetic field inside the arc chamber.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
Preparation method for anti-oxidation composite hard coating
InactiveCN103774096AVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingOxidation resistantPulse power supply
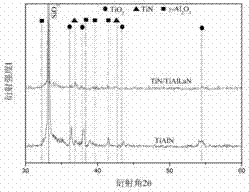
The invention discloses a preparation method for an anti-oxidation composite hard coating on a cutting tool, which comprises the steps of workpiece heating, plasma cleaning of the workpiece, transition layer preparation, coating preparation and cooling; a Ti cast ingot in a crucible is used as a Ti source of a TiN transition layer, and the evaporation rate of the Ti cast ingot is controlled through the supply current of an arc column in hot-cathode ion plating; a plane TiAlLa target is used as a source of the corresponding element of a (TiAlLa)N coating, and the sputtering rate of a target is controlled through regulating the power of a medium frequency pulsed power supply; high-purity Ar is used as ionization gas. N2 is used as reaction gas. The thickness of the (TiAlLa)N coating prepared through the method is about 2 microns, nano-hardness of the coating is more than 40 Gpa, the anti-oxidation temperature of the coating can reach over 900 DEGC, and the indentation experiment level of the coating is HF1 (VDI3198 in German standard); compared with the TiAlN coating, the (TAlLa)N coating has better resistance to oxidation and mechanical properties, and is longer in service life.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Techniques for providing a multimode ion source
Techniques for providing a multimode ion source are disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the techniques may be realized as an apparatus for ion implantation, the apparatus including an ion source having a hot cathode and a high frequency plasma generator, wherein the ion source has multiple modes of operation.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com