Vertical Deep Trough Bottom Unloading Mining Method for Huge Thick Potash Deposit
A mining method and bottom unloading technology, which is applied in ground mining, mining equipment, earth square drilling, etc., can solve the problems of leaving too many protective pillars, increasing the cost of relocation, and reducing the degree of safety and reliability. The effect of tailings accumulation on ecological and environmental protection, reducing the cost of moving and reversing, and improving safety and reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
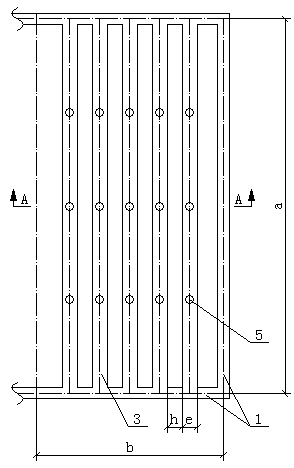
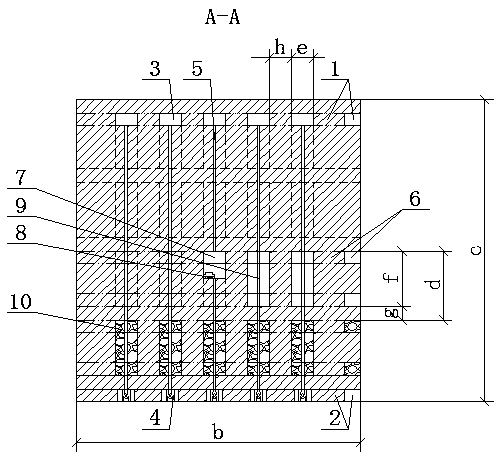
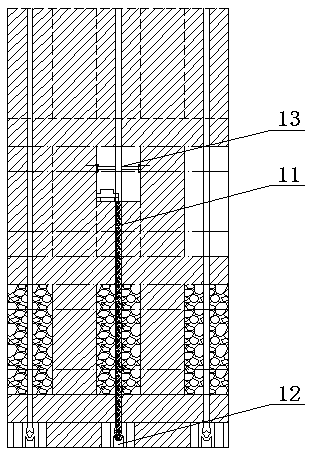
[0033] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 6 Shown, the huge thick potassium salt ore deposit vertical deep groove bottom unloading type mining method of the present invention, carry out according to the following steps:
[0034] The first step is to analyze and calculate the mechanical structure of the ore body and surrounding rock according to the thickness, burial depth, shape, stratum and other occurrence conditions of the huge potassium salt deposit with a thickness of more than 30m, and reasonably determine the mining technical parameters of the working face. The technical parameters are the length, width and thickness of the mining block, the thickness of the layer, the length, width and height of the deep groove, the thickness of the interlayer and the width of the protective pillar, and the layout of the roadway for ore mining.
[0035] In the second step, according to the length of 500-2000m, the width of 70-200m, and the thickness of the ore body, the mining block of the wo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com