Confocal optical scanner
A confocal and scanner technology, applied in the field of biomedical microscopic imaging, can solve problems such as difficulty in stabilization, and achieve the effect of improving imaging stability and avoiding the problem of focal plane drift.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
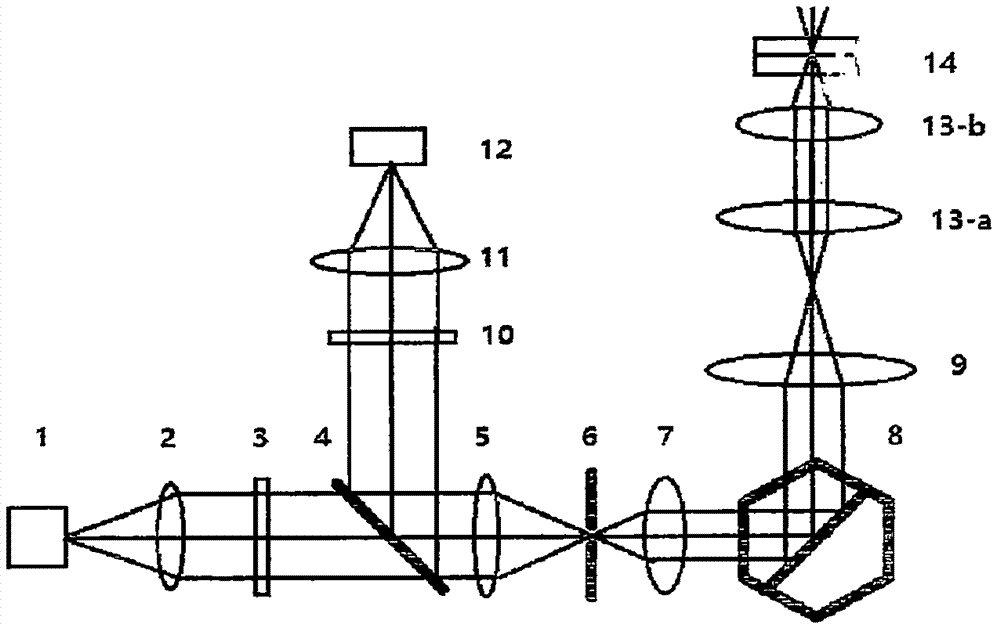
[0030] Fig. 1 is the schematic diagram of the first kind of confocal optical scanner relevant to the present invention, and the mode of operation is as follows:
[0031] Such as Figure 1-a As shown, the computer 17 controls the dynamic focusing lens 7 to turn on the light source 1 at a designated position, and the light emitted by the light source 1 is collimated into collimated light by the collimator mirror 2, and then passes through the excitation filter 3 to select a suitable wavelength band to obtain the excitation light; The excitation light passes through the dichroic beam splitter 4, converges through the converging lens 5 and passes through the pinhole 6, and then passes through the dynamic focusing lens 7, XY scanning galvanometer 8, telecentric scanning lens 9, sleeve lens 3a and objective lens 13b to excite the sample 14; the original path of fluorescence emitted by the sample 14 returns to the dichroic beam splitter 4, then reflects and passes through the emissio...
Embodiment 2
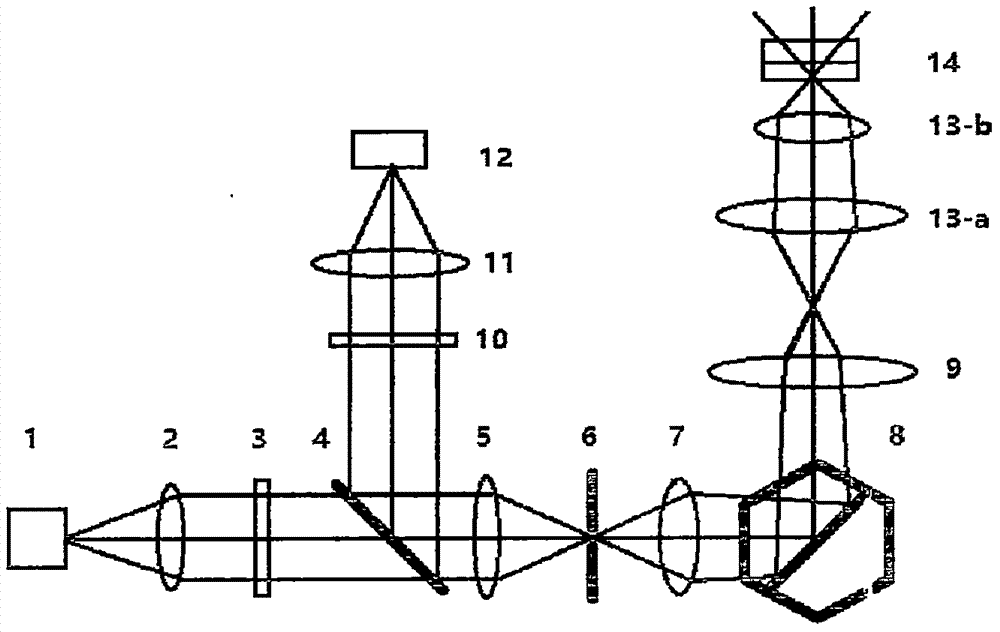
[0037] figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the second confocal optical scanner related to the present invention. The difference between it and Embodiment 1 is as follows: the pinhole 6 moves back and forth along the optical axis, and the position of the dynamic focus lens 7 is fixed, so that through The illumination light of the pinhole 6 is converted into excitation light in any form of converging, collimating or diverging, so as to realize scanning imaging at different focal planes.
Embodiment 3
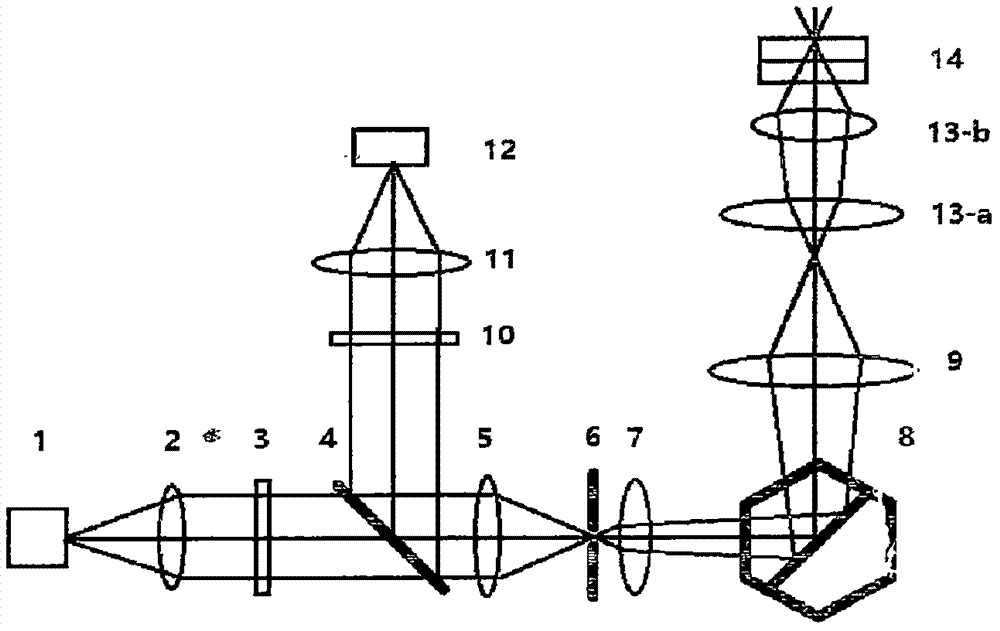
[0039] image 3 It is a schematic diagram of the third confocal optical scanner related to the present invention, and its difference with Embodiment 1 is as follows: through a total reflection mirror 15 and a beam combining mirror 16, two groups of the same, with light source 1, collimator Optical path of straight mirror 2, excitation filter 3, dichroic beam splitter 4, converging lens 5, pinhole 6, dynamic focusing lens 7, XY scanning galvanometer 8, emission filter 10, imaging lens 11 and detector 12 The optical paths of the structures coincide, and then are simultaneously introduced into the microscope (including the tube lens 13a and the objective lens 13b) through the telecentric scanning galvanometer 9, and simultaneously scan samples 14 of different or the same focal plane under different or the same field of view.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com