Application of physical foaming agent and chemical foaming agent in skylight sealing strip non-porous rubber microcellular foaming
A technology of chemical foaming agent and physical foaming agent, which is applied in the field of microcellular foaming of compact glue for skylight sealing strips, and achieves the effects of simple operation, easy production, and reduced production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
3.5
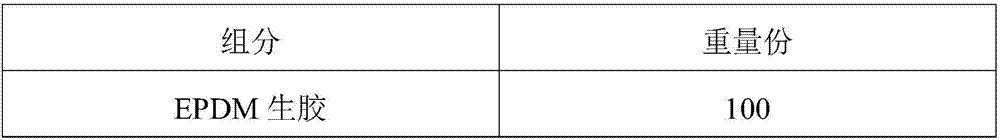
[0037] In the first step, each component is weighed according to the ratio.
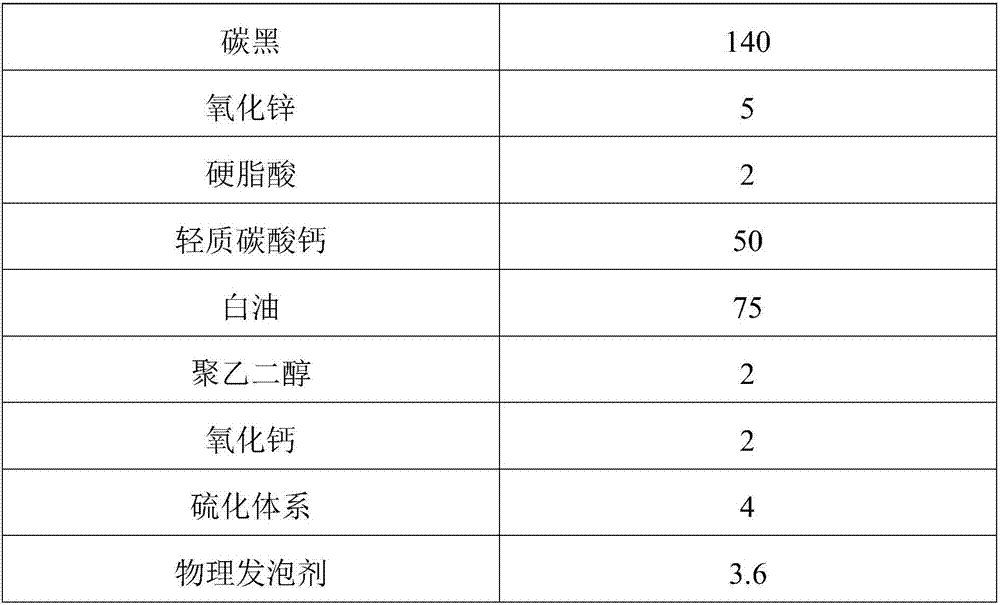
[0038] The second step is the rubber compounding process. One-stage mixing: first press and mix EPDM raw rubber, then add zinc oxide, stearic acid, polyethylene glycol, carbon black, light calcium carbonate, white oil and mix evenly, and then discharge the rubber. At 145°C, the film is discharged, cooled and parked. Two-stage mixing: first mix the first rubber after being parked for 24 hours, then add calcium oxide, vulcanization system, physical foaming agent, chemical foaming agent for mixing, and control the glue discharge temperature below 100℃. The distance is 1-1.5mm to prevent damage to the molecular structure of the blowing agent.
[0039] The third step is the extrusion vulcanization process. First pass the product through the extruder, the temperature of the extruder is controlled at 60°C, and the temperature of the rubber at the exit of the extruder is controlled at 70-90°C. Then throu...
Embodiment 2
3
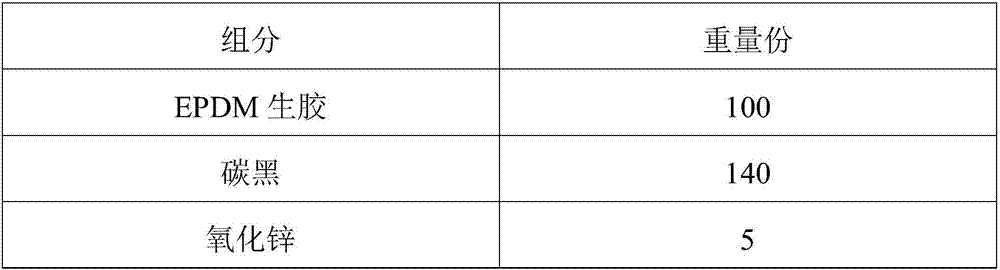
[0042] In the first step, each component is weighed according to the ratio.
[0043] The second step is the rubber compounding process. One-stage mixing: first press and mix EPDM raw rubber, then add zinc oxide, stearic acid, polyethylene glycol, carbon black, light calcium carbonate, white oil and mix evenly, and then discharge the rubber. At 155°C, the film is discharged, cooled, and parked. Two-stage mixing: first mix the first rubber after being parked for 24 hours, then add calcium oxide, vulcanization system, physical foaming agent, chemical foaming agent for mixing, and control the glue discharge temperature below 100℃. The distance is 1-1.5mm to prevent damage to the molecular structure of the blowing agent.
[0044] The third step is the extrusion vulcanization process. First pass the product through the extruder, the temperature of the extruder is controlled at 75°C, and the temperature of the rubber at the exit of the extruder is controlled at 70-90°C. Then throug...
Embodiment 3
3.6
[0047] In the first step, each component is weighed according to the ratio.
[0048] The second step is the rubber compounding process. One-stage mixing: first press and mix EPDM raw rubber, then add zinc oxide, stearic acid, polyethylene glycol, carbon black, light calcium carbonate, white oil and mix evenly, and then discharge the rubber. At 150°C, the film is discharged, cooled, and parked. Two-stage mixing: first mix the first rubber after being parked for 24 hours, then add calcium oxide, vulcanization system, physical foaming agent, chemical foaming agent for mixing, and control the glue discharge temperature below 100℃. The distance is 1-1.5mm to prevent damage to the molecular structure of the blowing agent.
[0049] The third step is the extrusion vulcanization process. First pass the product through the extruder, the temperature of the extruder is controlled at 75°C, and the temperature of the rubber at the exit of the extruder is controlled at 70-90°C. Then thro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com