Lead-free free-cutting silicon magnesium phosphorus brass alloy and preparation method thereof
A silicon-magnesium-phosphorus brass and easy-cutting technology, which is applied in the field of lead-free easy-cutting silicon-magnesium-phosphorus brass alloy and its preparation, can solve the problems of difficult control of alloy quality, high material hardness, and large amount of addition, and achieve excellent Excellent casting performance and mechanical properties, excellent corrosion resistance, and excellent cutting performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] (1) Weigh Cu, Zn, Si, Mg, P, Al, and B according to the mass percentage of the lead-free free-cutting silicon-magnesium-phosphorus brass alloy, and Mg, P, Al, and B are all added in the form of master alloys , the mass percentages of the above components are as follows: Cu 60wt%, Si0.9wt%, Mg 0.5wt%, P 0.6wt%, Al 0.3wt%, 0.003wt% B, the rest are Zn and other impurities, the content of impurities is less than 1wt %;
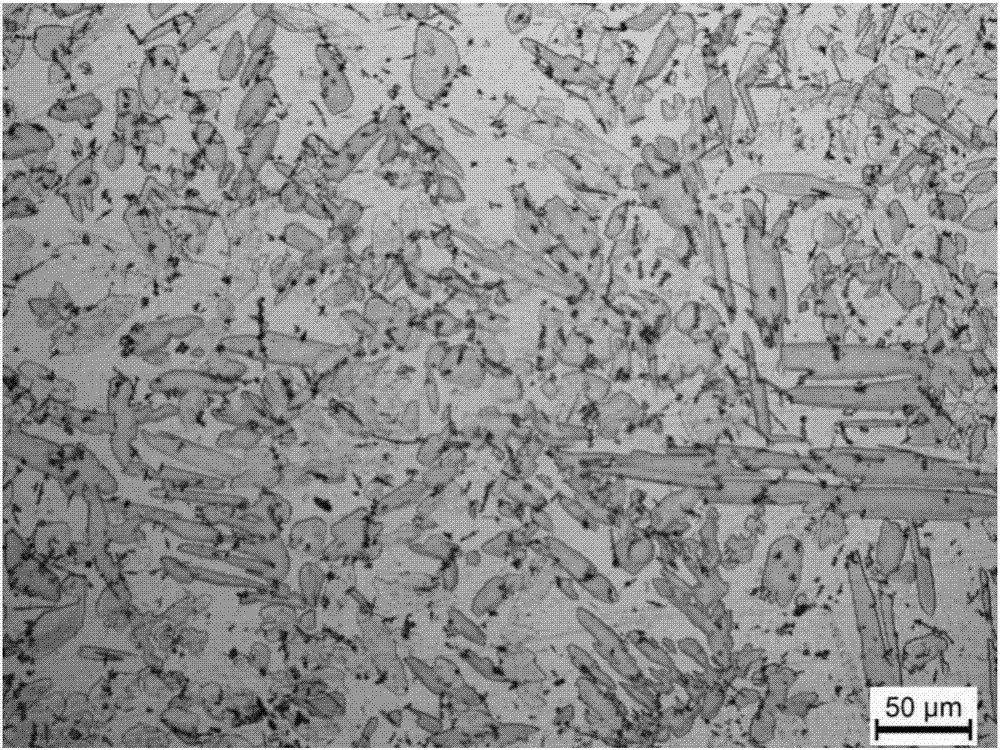
[0050] (2) Melt the alloy in a graphite crucible, first melt Cu and Si, then cool down to 700°C and add Al, Zn, Mg, P, B sequentially, after all the metals are melted, the obtained alloy melt is kept at 1050°C for 20 Minutes to achieve homogenization of the alloy melt composition, slag removal, pouring into a mold preheated to 200°C at 1050°C, cooling to room temperature, and demoulding to obtain the lead-free free-cutting silicon-magnesium-phosphorus brass alloy.
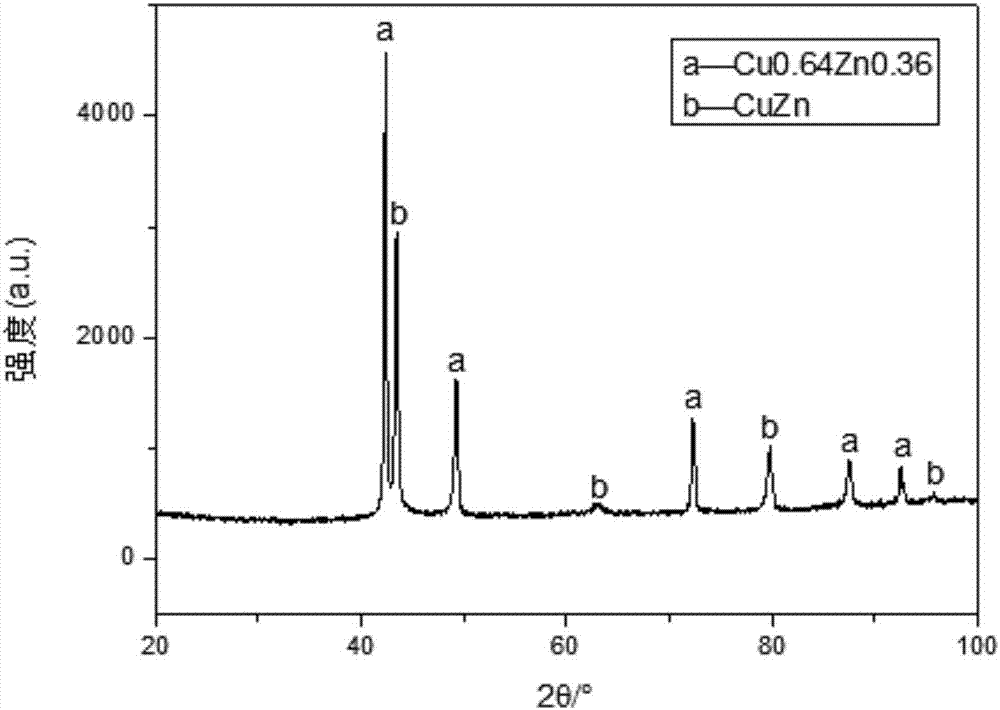
[0051] The X-ray diffraction pattern of the lead-free free-cutting silicon-magnesium-phosp...
Embodiment 2
[0057] (1) Weigh Cu, Zn, Si, Mg, P, Al, B, Re according to the mass percentage of lead-free free-cutting silicon-magnesium-phosphorus brass alloy components, among which Mg, P, Al, B, and Re are all in the middle Added in the form of alloy, the mass percentage of the above components is as follows: Cu 60wt%, Si 0.7wt%, Mg 0.7wt%, P 0.7wt%, Al 0.3wt%, 0.003wt% B, 0.003wt% Re, the rest is Zn and other impurities, the content of which is less than 1wt%;
[0058] (2) Melt the alloy in a graphite crucible, first melt Cu and Si, then cool down to 700°C and add Al, Zn, Mg, P, B, Re in sequence, and after all the metals are melted, the obtained alloy melt is at 1050°C Keeping the temperature for 20 minutes to achieve homogenization of the alloy melt composition, slag breaking, pouring into a mold preheated to 200°C at 1050°C, cooling to room temperature, and demoulding to obtain the lead-free free-cutting silicon-magnesium-phosphorus Brass alloy.
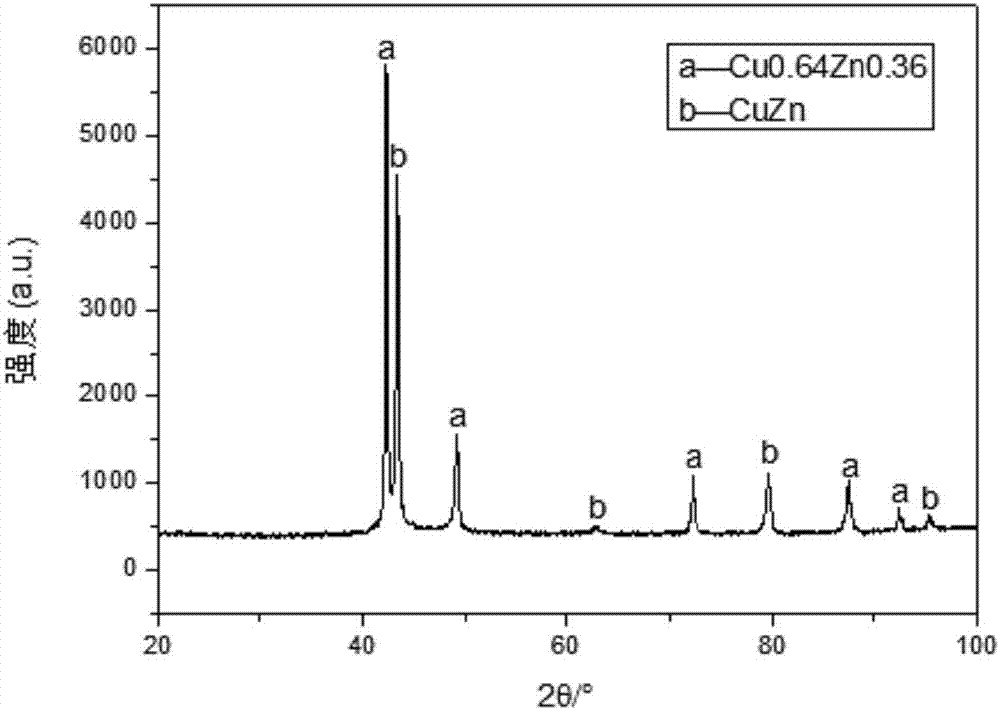
[0059] The X-ray diffraction patte...
Embodiment 3
[0065] (1) Weigh Cu, Zn, Si, Mg, P, and Al respectively according to the mass percentage of lead-free free-cutting silicon-magnesium-phosphorus brass alloy, where Mg, P, and Al are all added in the form of master alloys, and the above components The mass percentages of Al are as follows: Cu 60wt%, Si 0.7wt%, Mg 0.6wt%, P 0.5wt%, Al 0.3wt%, the rest are Zn and other impurities, and the content of impurities is less than 1wt%;
[0066] (2) Melt the alloy in a graphite crucible, first melt Cu and Si, then cool down to 700°C and add Al, Zn, Mg, P sequentially, after all the metals are melted, the obtained alloy melt is kept at 1050°C for 20 minutes, After homogenizing the composition of the alloy melt, slag breaking is carried out, pouring into a mold preheated to 200°C at 1050°C, cooling to room temperature, and demoulding to obtain the lead-free free-cutting silicon-magnesium-phosphorus brass alloy.
[0067] The X-ray diffraction pattern of the lead-free free-cutting silicon-mag...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com