Sensorless initial position detecting method for permanent magnet synchronous motor
A permanent magnet synchronous motor, initial position detection technology, applied in the direction of control of electromechanical transmission, control of generator, motor control, etc., can solve the problems of zero-crossing point solution, too long time for magnetic pole judgment stage, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
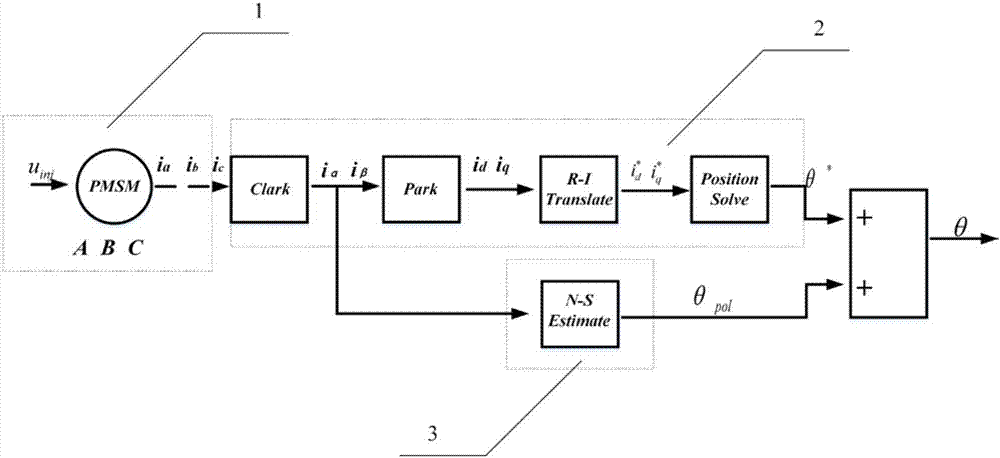
[0055] Specific implementation mode one: see figure 1 Describe this embodiment, a sensorless initial position detection method of a permanent magnet synchronous motor described in this method is a position detection method based on a virtual pulse vibration high-frequency injection method, which is characterized in that it includes a permanent magnet synchronous motor mathematical model part 1 , Position solution part 2 and magnetic pole correction part 3.
[0056] The mathematical model part 1 of the permanent magnet synchronous motor includes system voltage equations and flux linkage equations. The position calculation part 2 is a preliminary judgment of the rotor position based on the virtual pulse vibration high-frequency injection method. When the motor is at rest, assume that the rotor has a high rotational speed ω * r , to establish the corresponding virtual synchronous rotating coordinate system d * -q * , and the initial state d of the virtual coordinate system ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0057] Specific embodiment 2: This embodiment is a further limitation of the permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor position detection device based on the virtual pulse vibration high-frequency injection method described in the specific embodiment 1. The mathematical model part of the permanent magnet synchronous motor 1 , including the system voltage equation and the flux linkage equation, as shown in formula (1) and formula (2) respectively.
[0058] The voltage equation in the natural coordinate system:
[0059]
[0060] The flux linkage equation is:
[0061]
[0062] Among them, ψ 3s is the flux linkage of the three-phase winding; u 3s ,R,i 3s Respectively, the phase voltage, resistance and current of the three-phase winding; L 3s is the inductance of the three-phase winding, F 3s is a sinusoidal function matrix with a phase difference of 120°, and satisfies:
[0063] i A , i B , i C is the three-phase current, R is the phase resistance, u A , u B , ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
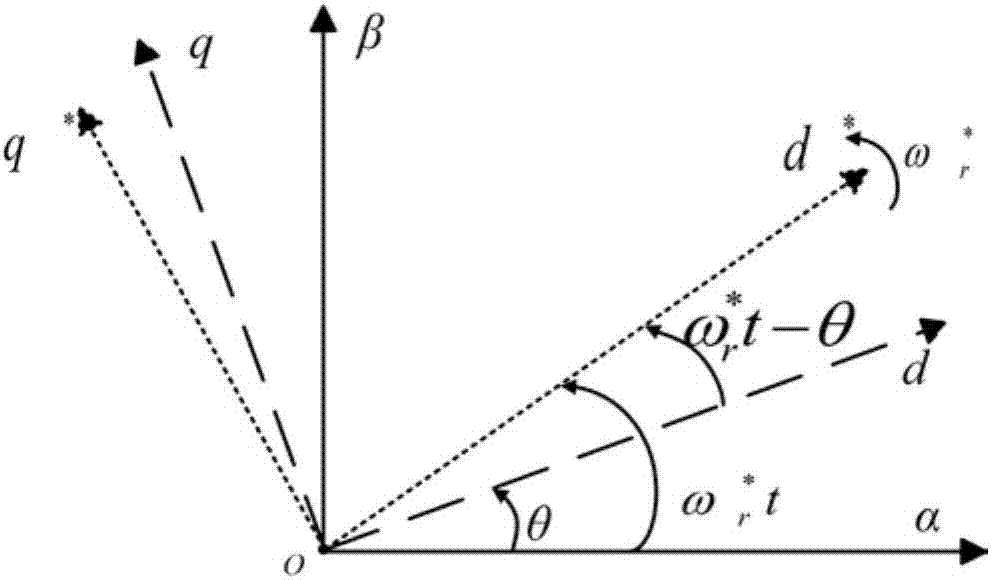
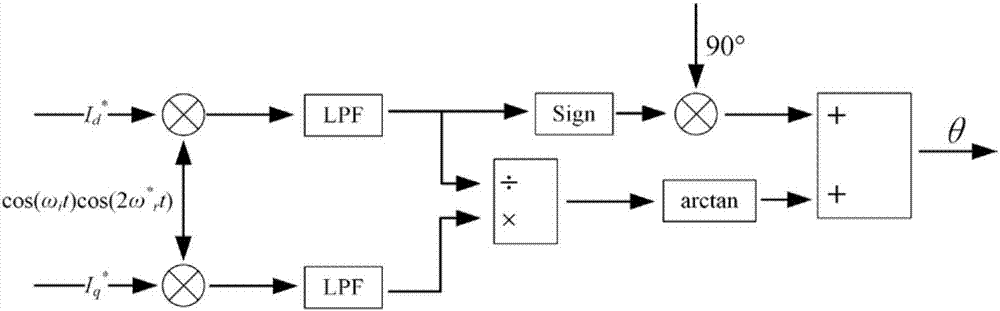
[0064] Specific implementation mode three: see figure 2 , 3 This embodiment is described. This embodiment is a further limitation of the permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor position detection device based on the virtual pulse vibration high-frequency injection method described in the first embodiment. The position calculation part 2 includes the following steps:
[0065] Step 1: Inject a high-frequency voltage signal into the virtual direct axis and solve the current response in the virtual synchronous rotating coordinate system. according to figure 2 The coordinate relationship transformation shown includes:
[0066] Clark transformation:
[0067]
[0068] PARK transformation:
[0069]
[0070] Transformation between virtual-real synchronously rotating coordinate systems:
[0071]
[0072] Among them, ω * r is the assumed motor speed;
[0073] Inject a high-frequency voltage signal U into the virtual direct axis i cos ω i t, transform it into the act...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com