A room temperature magnetic refrigeration alloy magnetocaloric material and its preparation method and application
A magnetocaloric material and magnetic refrigeration technology, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of high Curie temperature, prominent thermal hysteresis problem, small adjustable temperature width, etc. simple effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
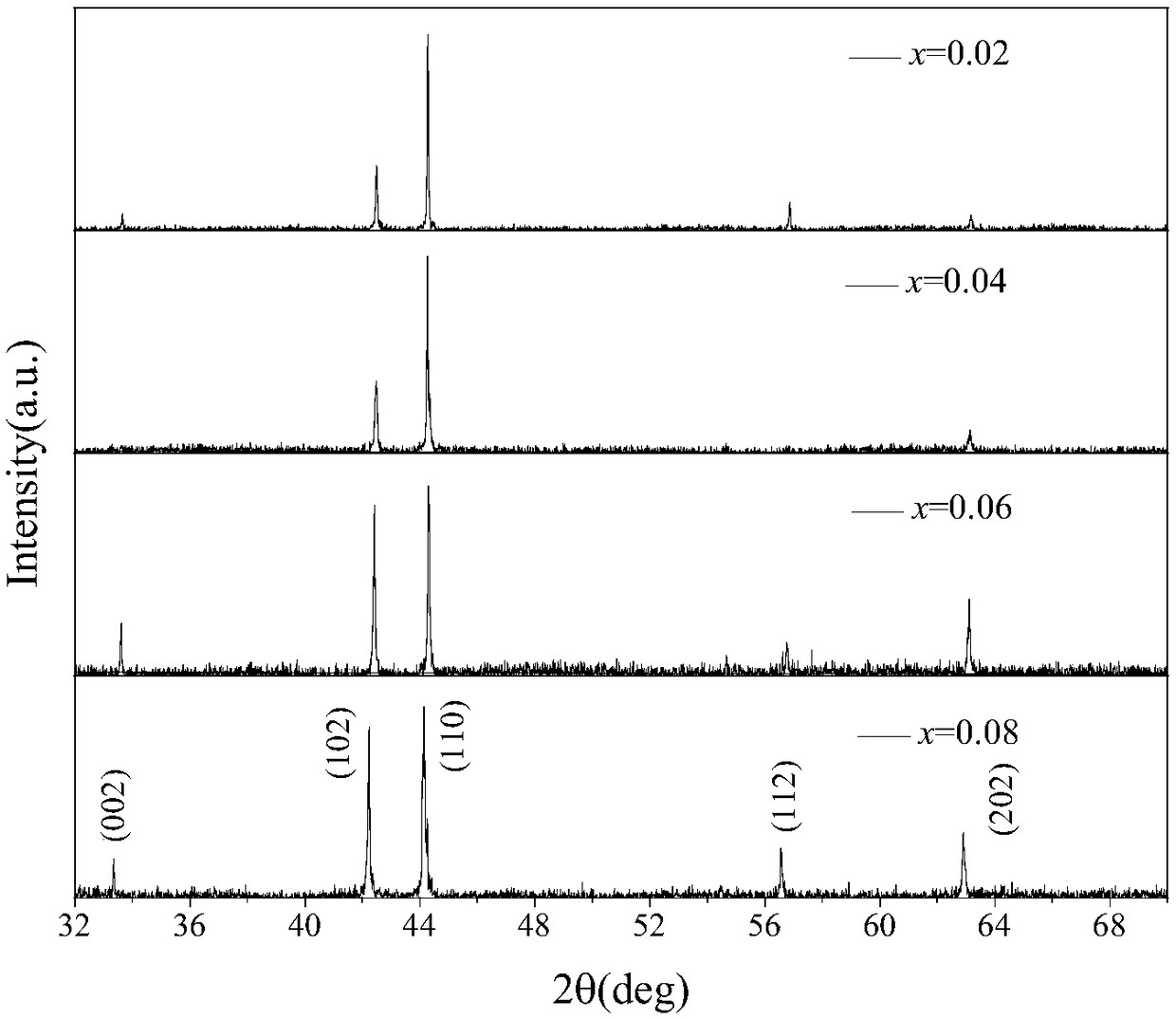
[0034] The purity of the raw materials used is 99.9% Mn, 99.9% Co, 99.99% Ti, 99.99% Ge, each powder is weighed according to the molar atomic percentage, the atomic percentage of the manganese element is 33.3-34.4%, and the atomic percentage of the cobalt element is 32.8- 33.3%, the atomic percentage of titanium element is 0.6-2.7%, and the atomic percentage of germanium element is 30.2-32.7%.
[0035] The alloy is smelted in a vacuum electric arc furnace, and the weighed high-purity powder mixture is added to the vacuum electric arc furnace. Before the alloy is smelted, firstly use a mechanical pump to evacuate the vacuum below 5Pa, and turn on the molecular pump to evacuate again to below 10 Pa. -4 Pa, inject high-purity argon gas (99.999%) with a pressure of 10Pa, repeat the above vacuum pumping and gas washing operation steps twice, use a current of about 30A to start a fire, move the electrode to the top of the sample and about 0.5cm away from the sample, and slowly The c...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The room temperature magnetic refrigeration alloy magnetocaloric material of this embodiment, the chemical general formula of this material is MnCo 1-x Ti x Ge, where x is 0.02, the atomic percentage of manganese element in the material is 33.3%, the atomic percentage of cobalt element is 32.8%, the atomic percentage of titanium element is 1.2%, and the atomic percentage of germanium element is 32.7%.
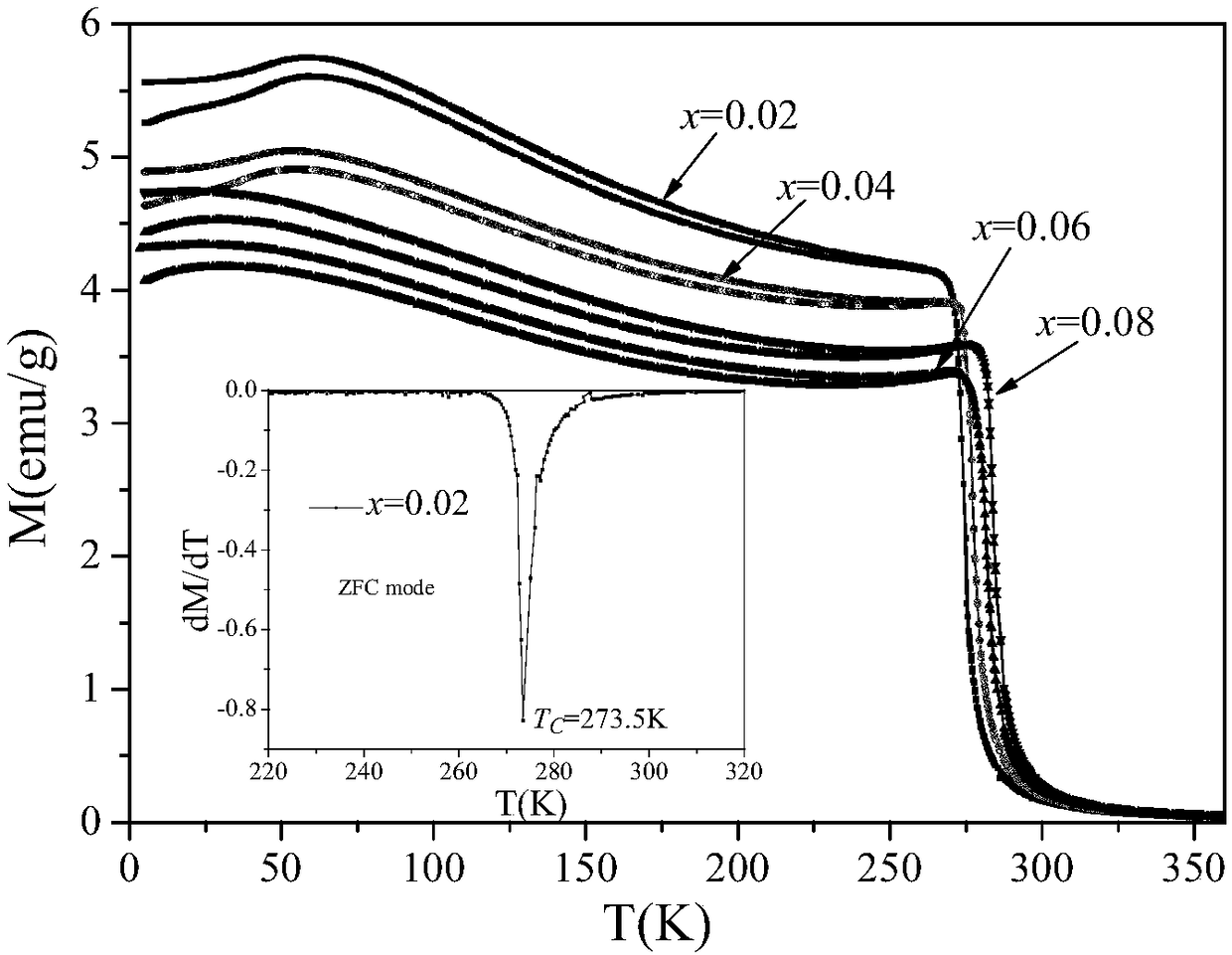
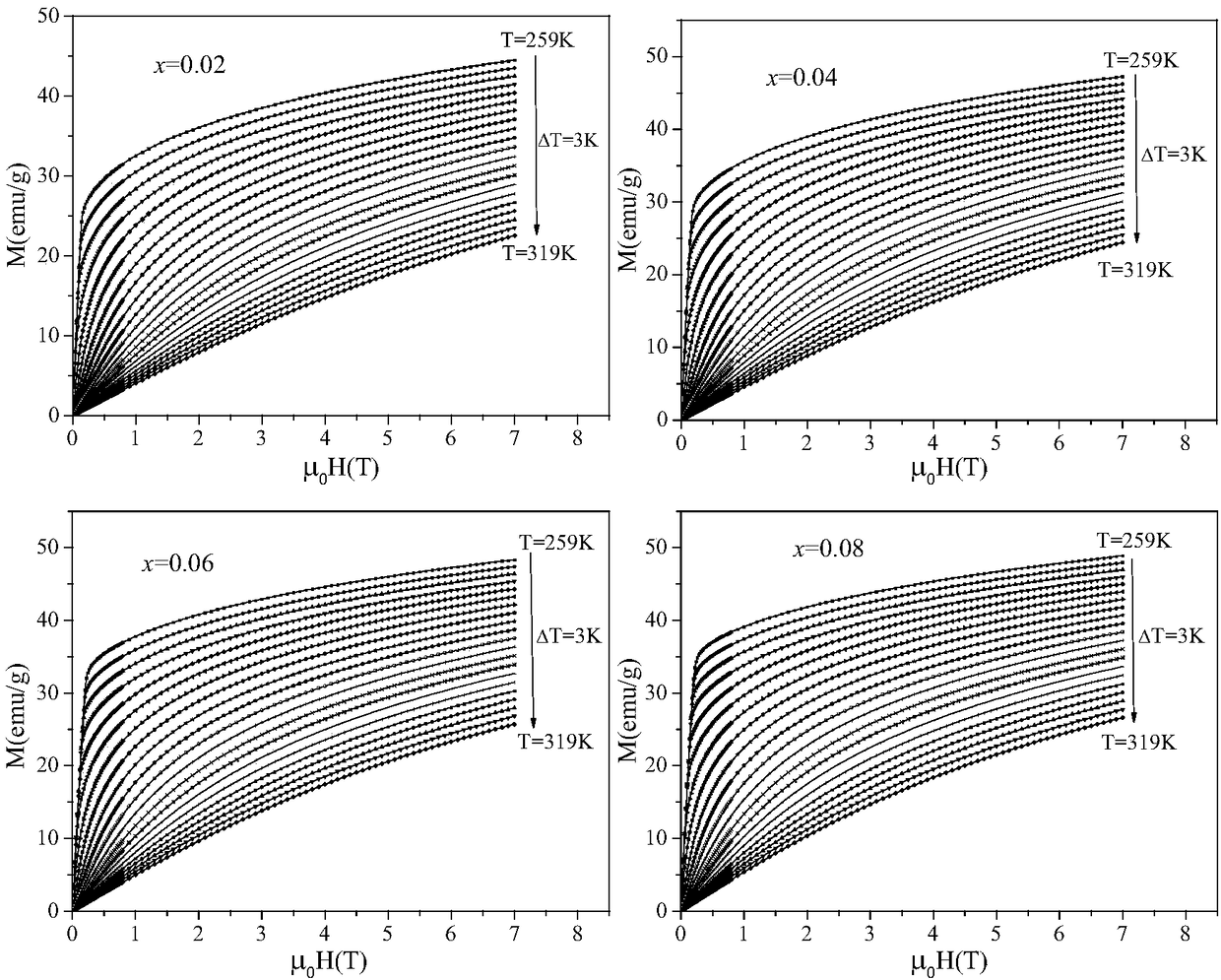
[0049] The Curie temperature of the material in this example is raised from 273.5K to 284K, and under a magnetic field change of 5T, the maximum magnetic entropy becomes 3.16J kg -1 K -1 ,3.30J·kg -1 K -1 ,3.28J·kg -1 K -1 ,3.25J·kg -1 K -1 .
[0050] The preparation method of the room temperature magnetic refrigeration alloy magnetocaloric material in this embodiment specifically includes the following steps:
[0051] Step (1): Weighing manganese powder, cobalt powder, titanium powder and germanium powder according to molar atomic percentage, and mixing them un...
Embodiment 3
[0062] The room temperature magnetic refrigeration alloy magnetocaloric material of this embodiment, the chemical general formula of this material is MnCo 1-x Ti x Ge, where x is 0.05, the atomic percentage of manganese element in the material is 34.4%, the atomic percentage of cobalt element is 33.3%, the atomic percentage of titanium element is 2.1%, and the atomic percentage of germanium element is 30.2%.
[0063] The Curie temperature of the material in this example is raised from 273.5K to 284K, and under a magnetic field change of 5T, the maximum magnetic entropy becomes 3.16J kg -1 K -1 ,3.30J·kg -1 K -1 ,3.28J·kg -1 K -1 ,3.25J·kg -1 K -1 .
[0064] The preparation method of the room temperature magnetic refrigeration alloy magnetocaloric material in this embodiment specifically includes the following steps:
[0065] Step (1): Weighing manganese powder, cobalt powder, titanium powder and germanium powder according to molar atomic percentage, and mixing them un...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com