Position sensorless control method for permanent magnet synchronous motor based on low frequency voltage injection method
A permanent magnet synchronous motor, low-frequency voltage technology, applied in the direction of motor generator control, electronic commutation motor control, motor control, etc., can solve the problems of high-frequency noise pollution, reduce noise pollution, improve practicability, and relieve ear-piercing noise effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
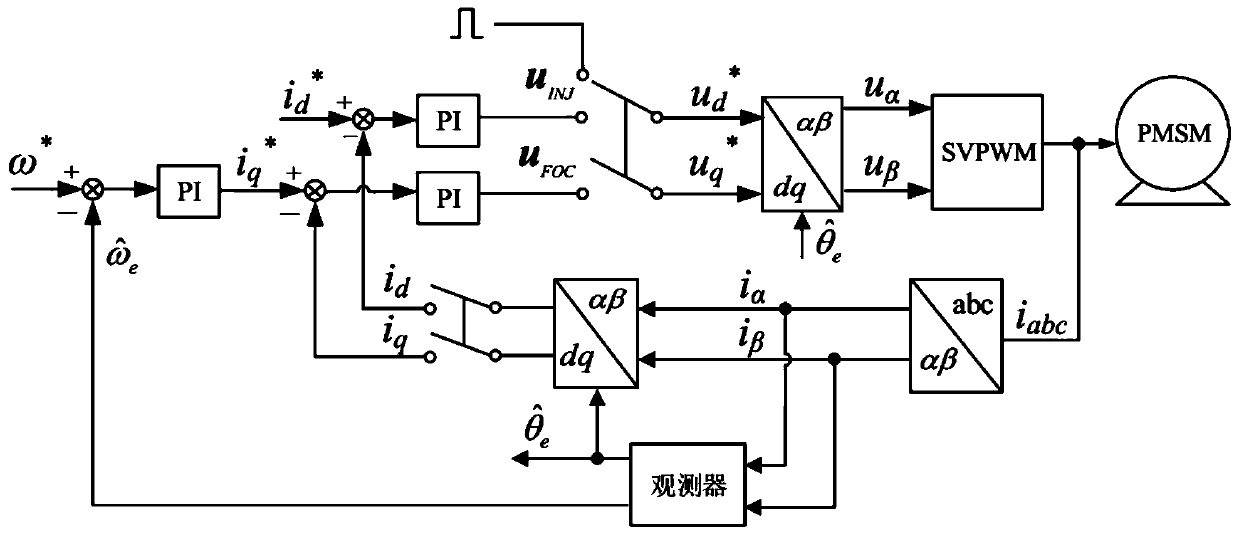
[0024] Embodiment 1: The control method of the permanent magnet synchronous motor without position sensor based on the low-frequency voltage injection method includes the following steps:
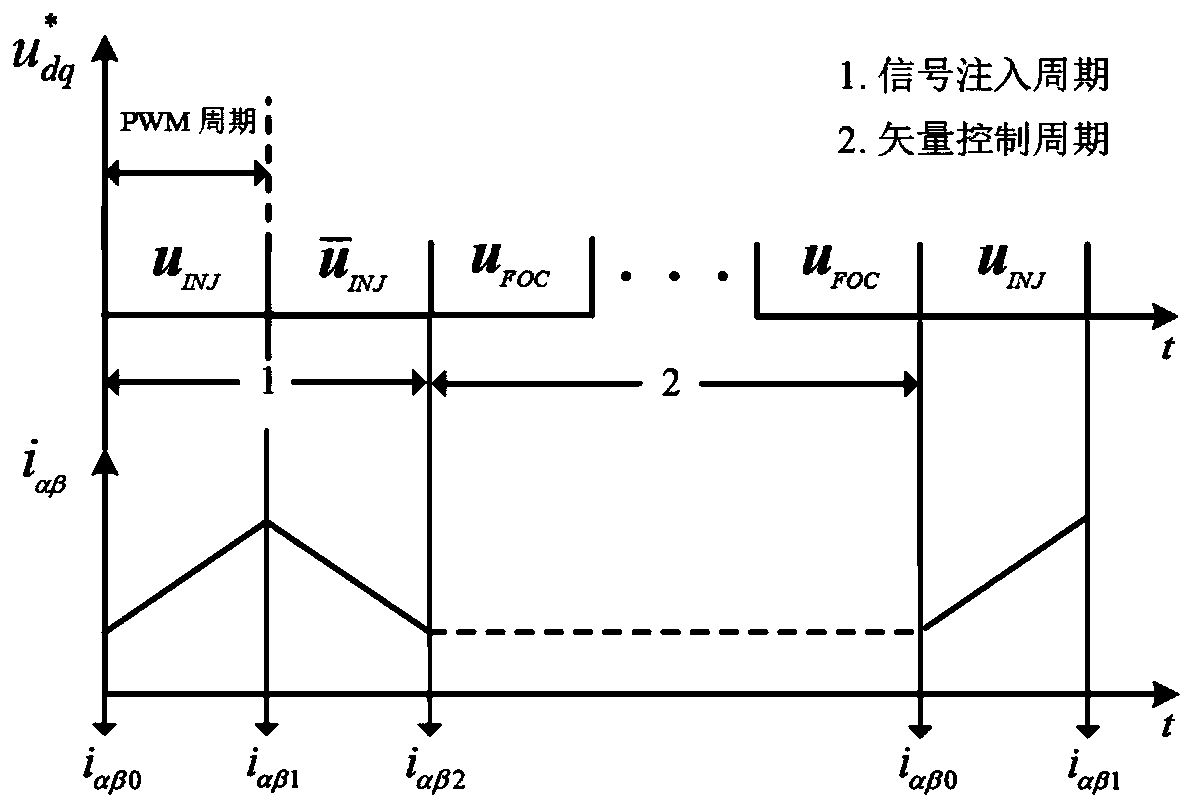
[0025] Step 1: During the operation of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, inject low-frequency pulse voltage into the dq shafting of the permanent magnet synchronous motor through the control of the microprocessor; in order to avoid the interference of the filter on the low-frequency voltage, the control sequence of the motor is divided into injection Period and control period are beneficial to the injection and extraction of low-frequency pulse voltage; the dq axis system refers to the rotating coordinate system of the motor. When the low-frequency pulse voltage is injected, it is the injection period, and when the motor is controlled, it is the control period; the dq axis system includes d-axis and q axis, the d-axis points to the N-pole direction of the rotor magnetic field, and the ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0029]Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that in the step 1, during the operation of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, a low-frequency pulse voltage is injected into the dq shafting of the permanent magnet synchronous motor through the control of the microprocessor Specifically:
[0030] Inject a low-frequency pulse voltage into the dq axis of the vector control system:
[0031]
[0032] where u dqi is the low-frequency pulse voltage injected into the dq axis system, k is the control sequence, and k=1,2,3,...,V i is the magnitude of the injected voltage;
[0033] A method is employed in which the injection period and the control period are separated from each other. Such as figure 1 shown. The way of pulse voltage injection is equivalent to a switch, which is located at the output position of the current loop. When performing motor control, the given voltage under the dq axis system is the output voltage of...
specific Embodiment approach 3
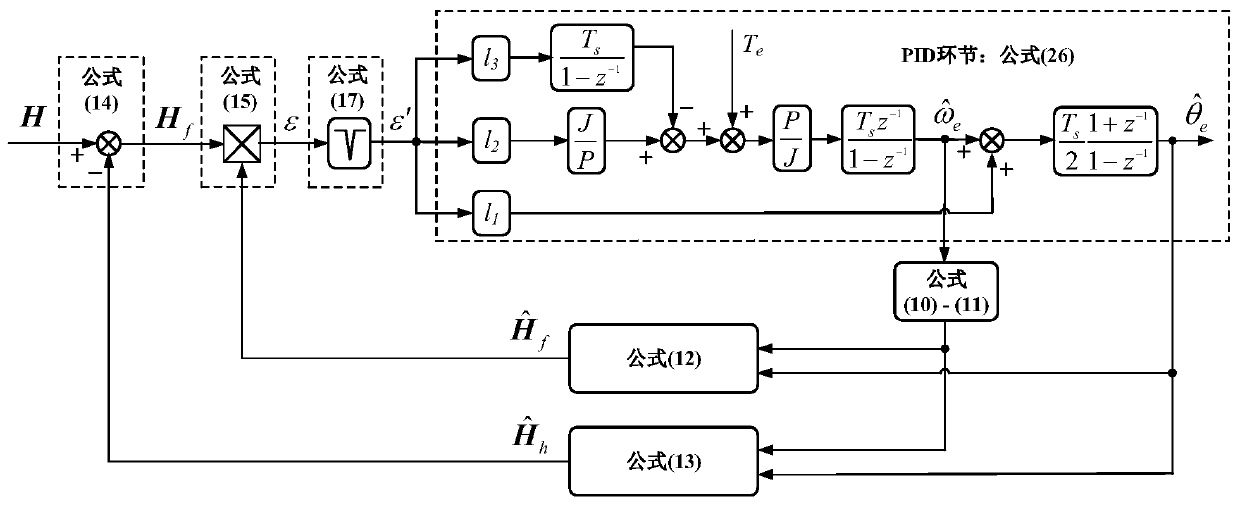
[0037] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that in the second step, the pulse current information is extracted from the αβ shafting of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, and the quadrature signal of the rotor position is obtained through current differential calculation. The specific process is:
[0038] The dq shaft system equation of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is:
[0039]
[0040] where u d and u q are the stator voltages of d-axis and q-axis respectively, where i d and i q are the stator currents of d-axis and q-axis respectively, R s is the stator resistance, L d and L q are the stator inductances of d-axis and q-axis respectively, ω e is the electrical speed of the motor, ψ f is the rotor flux linkage;
[0041] Transform the formula (2) into the αβ axis through the coordinate transformation. Assuming that the injected voltage amplitude is large enough, the voltage drop on the resistor and the influenc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com