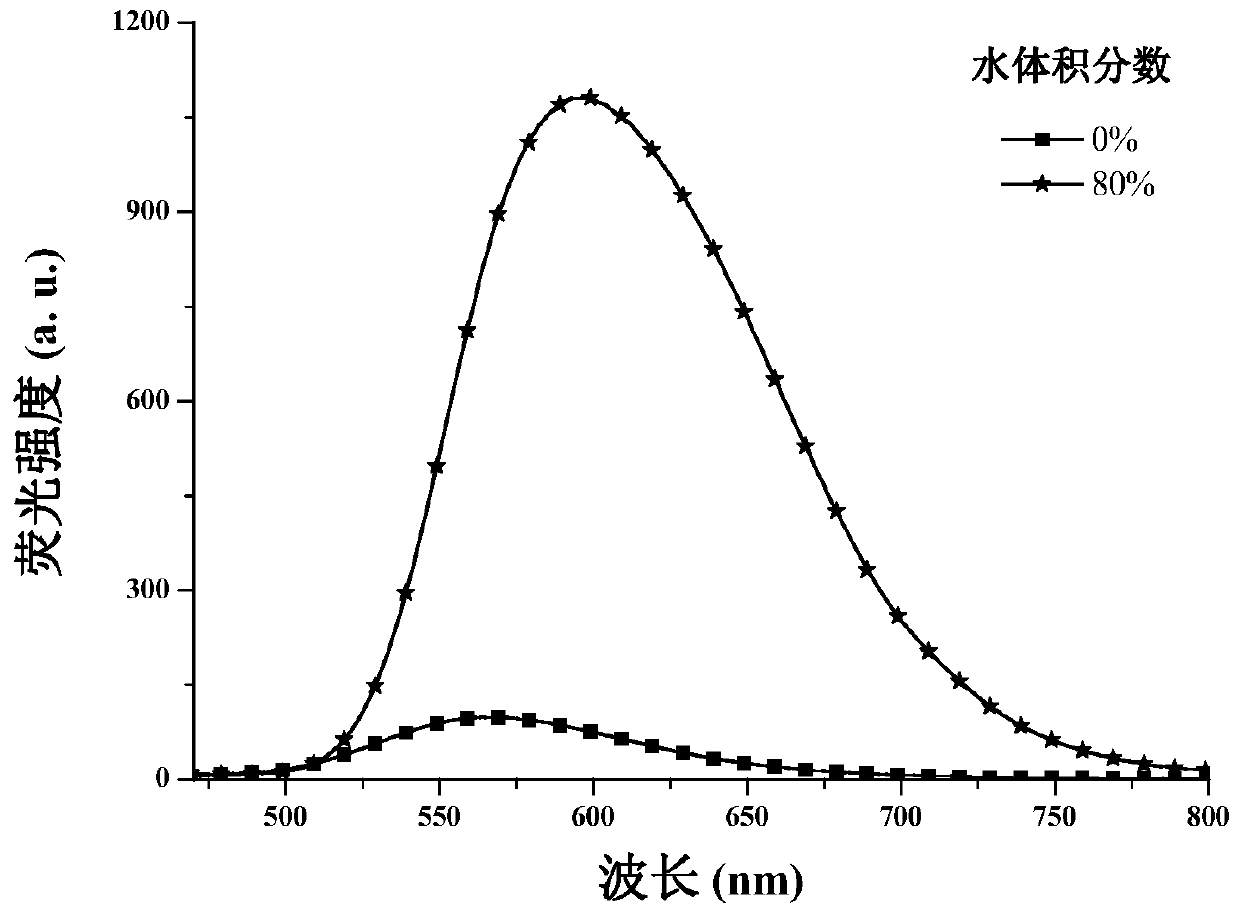
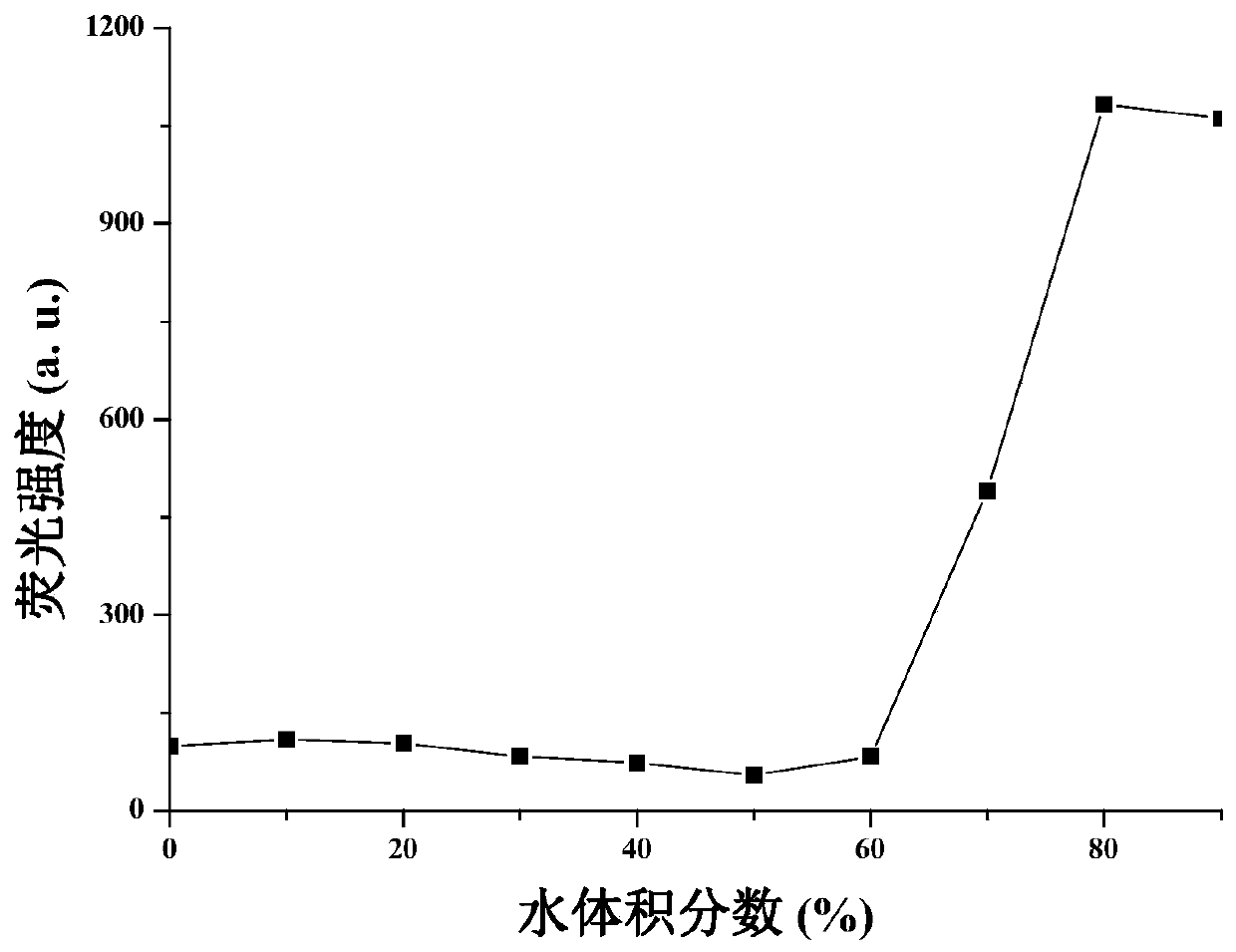
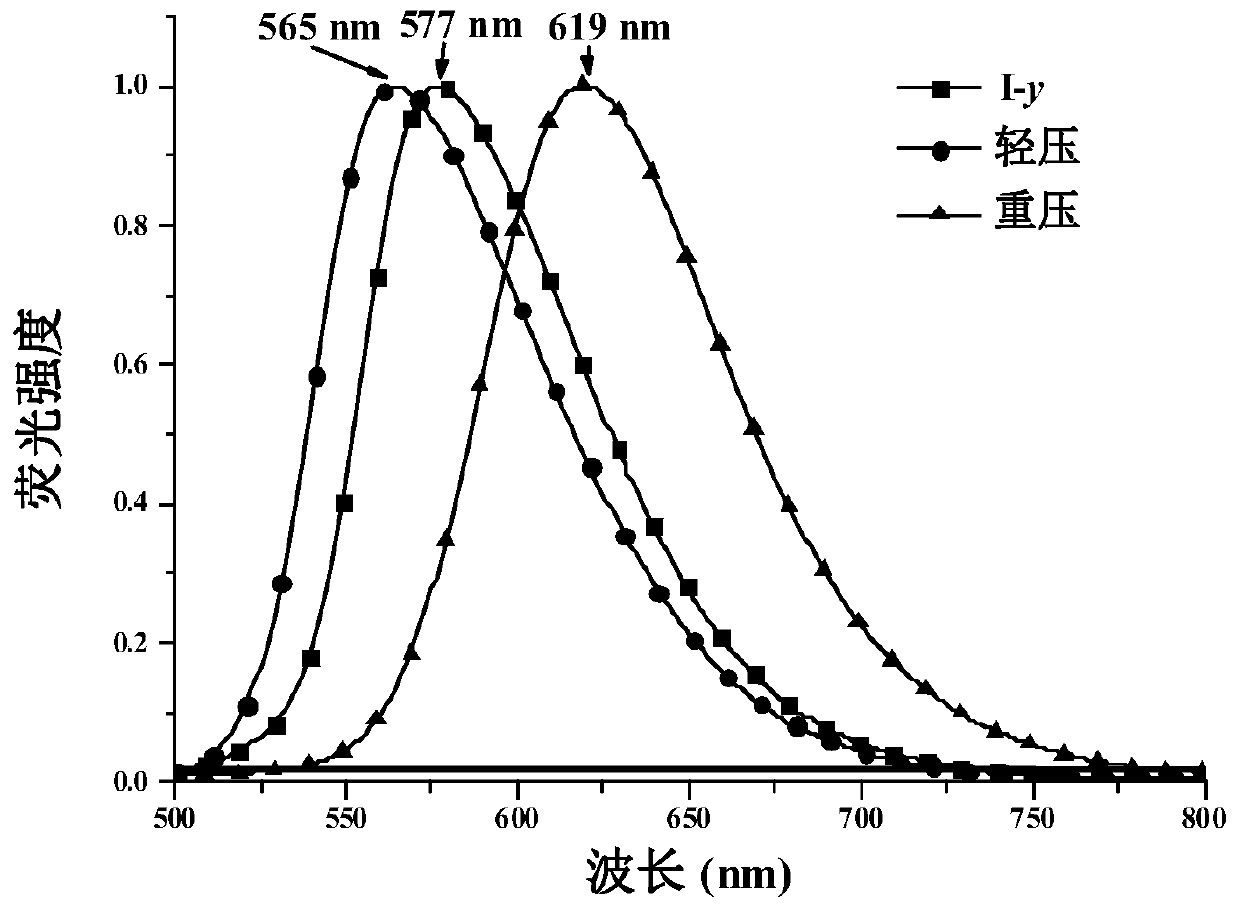
1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives and their preparation methods and uses
A technology of dihydropyridine and its derivatives, which is applied in organic chemical methods, chemical instruments and methods, fluid pressure measurement using optical methods, etc., can solve problems such as low luminous efficiency and limit the application of fluorescent materials, and achieve good scientific research value and The effect of industrial application potential
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
[0051]1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives, which have the following structural formula (I):
[0052]
[0053] The 1,4-dihydropyridine derivative of formula (I) is obtained through different recrystallization methods to obtain three different crystalline compounds I-y, I-o and I-r, and the structural formulas of the three crystalline compounds are the same.
[0054] The preparation method of 1,4-dihydropyridine derivative comprises the following steps:
[0055] (1) Preparation of initial samples of 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives
[0056] (11) Using 2,6-dimethyl-4-pyrone 1 as the starting material, it undergoes an addition-elimination reaction with Michaelis acid to generate intermediate 2;
[0057] (12) Intermediate 2 and 4-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde undergo a condensation reaction to generate intermediate 3;
[0058] (13) Nucleophilic substitution reaction between intermediate 3 and ethylamine to synthesize the initial sample of 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives;
[0059] The ...
specific Embodiment 2
[0082] Roughly the same as specific embodiment 1, the difference only lies in:
[0083] Step (2) includes the following steps:
[0084] (21) n-hexane and acetone are mixed according to the volume ratio of 5:1 to form a mixed solvent;
[0085] (22) Dissolve the initial sample of 1,4-dihydropyridine derivative in the mixed solvent formed in step (21) to form a solution, then heat the solution to 60°C, maintain this temperature for 5 minutes, and cool to room temperature to obtain emission Yellow fluorescent crystalline compound I-y, wherein:
[0086] The molar ratio of the initial sample of 1,4-dihydropyridine derivative to the mixed solvent is 1:3000.
specific Embodiment 3
[0088] Roughly the same as specific embodiment 1, the difference only lies in:
[0089] Step (2) includes the following steps:
[0090] (21) n-hexane and acetone are mixed according to a volume ratio of 3:1 to form a mixed solvent;
[0091] (22) Dissolve the initial sample of 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives in the mixed solvent formed in step (21) to form a solution, then heat the solution to 60°C, maintain this temperature for 3 minutes, and cool to room temperature to obtain emission Yellow fluorescent crystalline compound I-y, wherein:
[0092] The molar ratio of the initial sample of 1,4-dihydropyridine derivative to the mixed solvent is 1:1500.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com