Method for killing bacteria in microalgae by using electromagnetic pulse
An electromagnetic pulse and microalgae technology, applied in the field of algae cultivation, can solve the problems of inability to process, low efficiency, increase of disinfection by-products, etc., and achieve the effects of convenient use, simple operation and good sterilization effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
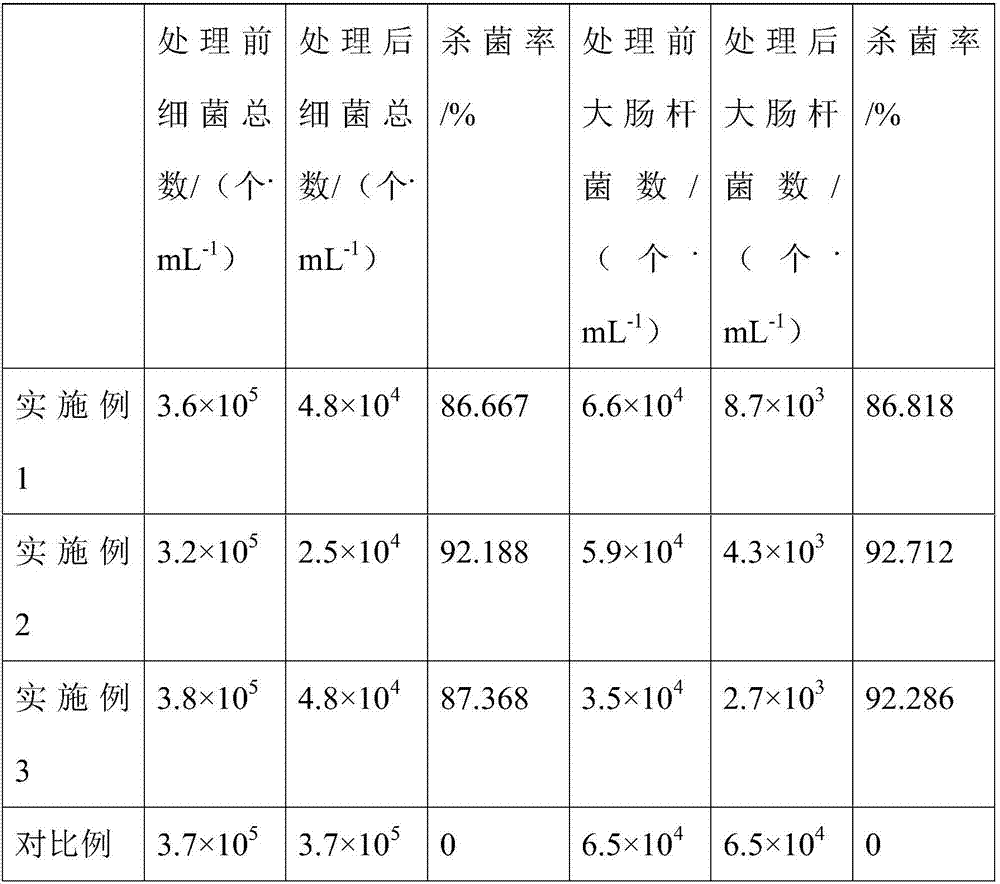
Embodiment 1
[0021] A method for killing bacteria in microalgae by electromagnetic pulse of the present invention, the square wave pulse carried out in the microalgae solution, the beam of the square wave pulse is aimed at the position of the microalgae solution containing bacteria; the beam of the square wave pulse is controlled , so that the focused beam moves on the microalgae solution containing bacteria, the electromagnetic pulse discharges through the liquid phase, and then acts on the bacterial cells through the aqueous solution, thereby killing the bacteria in the microalgae.
[0022] The temperature of the part containing the microalgae containing bacteria was 42° C., and the maintenance time was 50 minutes.
[0023] The square wave pulse on the microalgae solution was controlled by PC.
[0024] Electromagnetic pulse liquid phase discharge is an extremely complex process. It can not only form a strong electric field during discharge, non-equilibrium plasma channels, but also accom...
Embodiment 2
[0027] The difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is: a kind of electromagnetic pulse method of the present invention kills the bacterium in microalgae, the square wave pulse that carries out in microalgae solution, the beam of square wave pulse is aimed at the microalgae that contains bacteria The part of the algae solution; control the beam of the square wave pulse, so that the focused beam moves on the microalgae solution containing bacteria, the electromagnetic pulse discharges through the liquid phase, and then acts on the bacterial cells through the aqueous solution, thereby killing the bacteria in the microalgae.
[0028] The temperature of the part containing the microalgae containing bacteria was 60° C., and the maintenance time was 40 minutes.
[0029] The square wave pulse on the microalgae solution was controlled by PC.
[0030] The pulse frequency of the square wave pulse is 200s -1 , pulse voltage 1kV, pulse width 3μs, the maximum instantaneous output ...
Embodiment 3
[0032] The difference between embodiment 3 and embodiment 1 is: a kind of electromagnetic pulse method of the present invention kills the bacterium in microalgae, the square wave pulse that carries out in microalgae solution, the beam of square wave pulse is aimed at the microalgae that contains bacteria The part of the algae solution; control the beam of the square wave pulse, so that the focused beam moves on the microalgae solution containing bacteria, the electromagnetic pulse discharges through the liquid phase, and then acts on the bacterial cells through the aqueous solution, thereby killing the bacteria in the microalgae.
[0033] The temperature of the part containing the microalgae containing bacteria was 50° C., and the maintenance time was 30 minutes.
[0034] The square wave pulse on the microalgae solution was controlled by PC.
[0035] The pulse frequency of the square wave pulse is 1100s -1 , pulse voltage 5kV, pulse width 4μs, the maximum instantaneous output...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com