Isolation and cloning of paddy rice photoperiod sensitive genic male sterility gene pms1 and application thereof
A light-sensitive nuclear sterility, pms1 technology, applied in applications, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve the problems of complex breeding procedures and production links, application limitations, and high costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Example 1: Isolation clones comprise the DNA fragment of the pms1 gene segment
[0051] 1. Using map-based cloning technology to determine the control gene pms1 of rice light-sensitive sterility
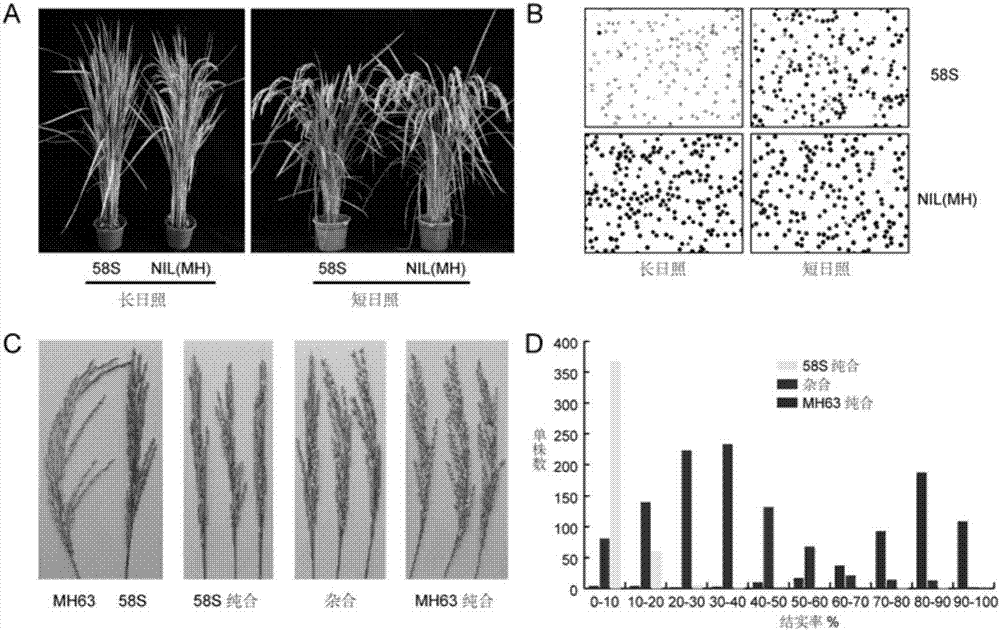
[0052] In the present invention, two parents were used when preparing the positioning population: the photosensitive GMS line Nongken 58S (Li Zebing et al., "Photosensitive GMS Rice Fertility Transformation Mechanism and Application Research", published by Hubei Science and Technology Press, Wuhan, Hubei , 1995 edition) and Minghui 63 (a rice variety selected by the Sanming Academy of Agricultural Sciences for public use). Minghui 63 is a typical indica variety. Nongken 58S was used as the recurrent female parent to cross with Minghui 63, and Nongken 58S / Minghui 63BC were obtained after multiple backcrosses 5 f 2 A random population of 6848 strains was used for fine mapping of the photosensitive genic male sterile gene pms1. These individual plants were planted in the expe...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Embodiment 2: Obtaining of full-length cDNA of pms1 gene
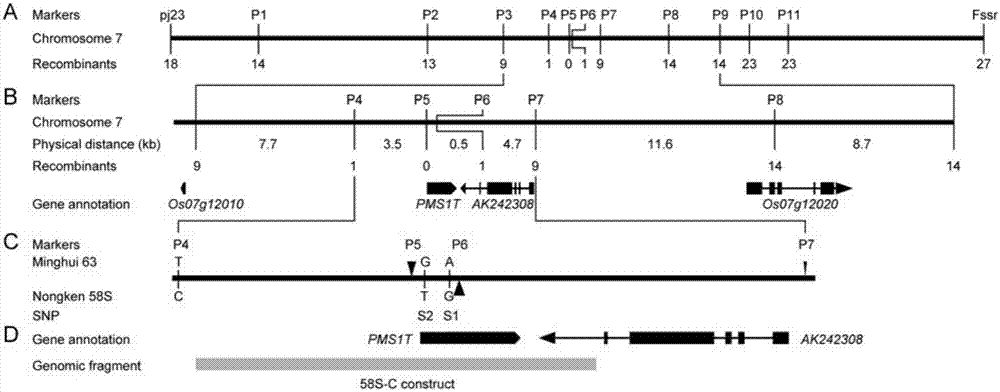
[0069] Example 1 The rice light-sensitive sterility gene pms1 was located between the molecular markers P4 and P6, the physical distance in the Minghui 63 genome was 4.0kb, and genetic transformation experiments also confirmed that the candidate pms1 gene was indeed contained in this interval . Check the gene annotation results in this interval on the Rice Genome Annotation Project website (http: / / rice.plantbiology.msu.edu / ), and find that this interval does not contain complete predicted genes, and the nearest left and right sides Both genes are retrotransposon proteins ( figure 1 ), indicating that the pms1 gene probably has a completely new transcript with unknown function.
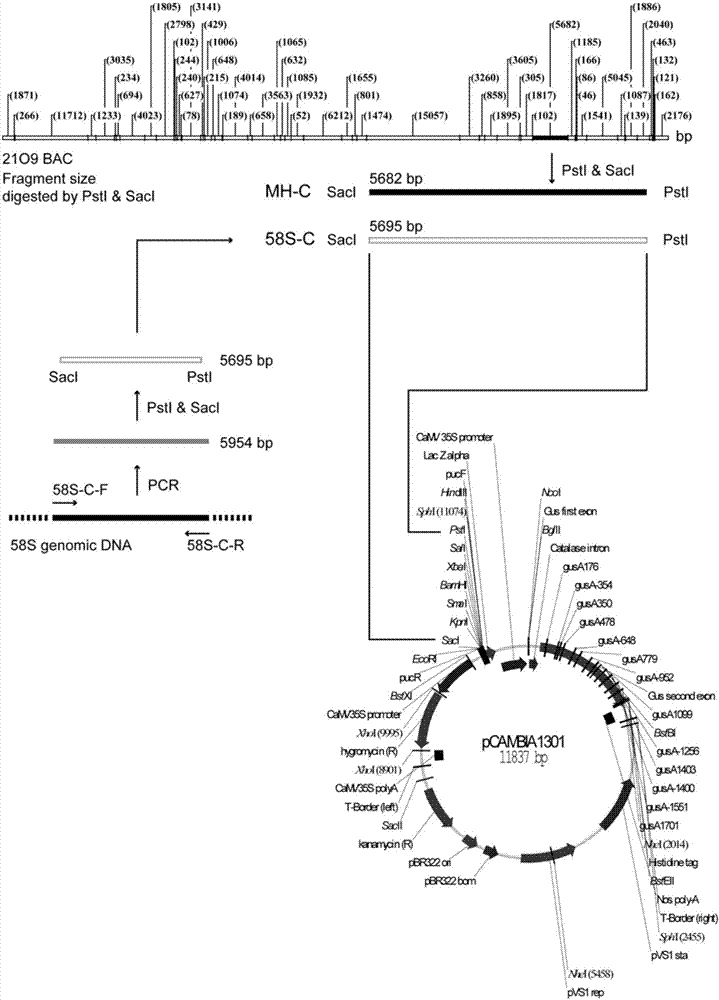
[0070] In order to comprehensively annotate the genes existing in this interval, a series of primers covering this interval were designed, and the reverse transcription products of young panicle RNA of Nongken 58S and NIL (MH) young pa...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Embodiment 3: the design of light sensitive male sterility gene pms1 molecular marker
[0076] Comparative analysis of the sequences between molecular markers P4 and P7 revealed that there were four sequence differences between Nongken 58S and Minghui 63. Except for the co-segregated molecular marker P5 located in the promoter region of PMS1T, the other three were located on the transcript of PMS1T . There is an AT repeat sequence in the promoter region of PMS1T, the number of repeats in Nongken 58S is 14, and the number of repeats in Minghui 63 is 40. Based on this difference, a co-segregated SSR molecular marker P5 can be designed, which has also been used and has been Named Rssr (Liu N et al. Identification of an 85-kb DNA fragment containing pms1, a locus for photoperiod-sensitive genic male sterility in rice. Mol Gen Genomics 2001, 266(2): 271-275). The primers used for this marker detection are P5-F and P5-R.
[0077] Comparative analysis of the PMS1T nucleotide...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com