Method grafting Chinese rose onto wild rose
A technique for rose and Chinese rose, applied in the field of plant grafting, can solve the problems of inability to increase the grafting survival rate, insufficient flowering, and increase the growth rate, etc., and achieve the effects of shortening the grafting process, improving the survival rate, and saving land area.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
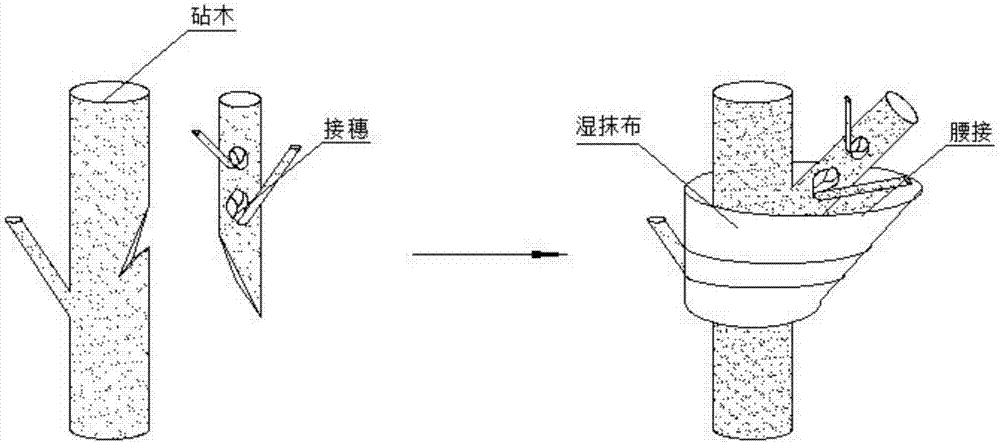
[0029] Artificially select wild roses with fast growing trunks and fork roots and taproots, and cut the 1.2m height part as the rootstock, and remove the sprouts and sprouts around the rootstock; cut off the semi-lignified dormancy after bud removal before germination The fork branch of Chinese rose 4cm is used as the scion, and the wound part of the lower end of the scion is sharpened with 15° as a slope of 1.2cm in length; on the rootstock, the grafting position is cut deep into 1 / 4 of the rootstock diameter at an oblique angle of 25°, and the knife edge reaches the xylem deeply. Form a longer wound, smear tree wound healing ointment at the junction of grafted wounds, insert the scion against the cambium of the rootstock, sprinkle nutrient soil on the junction of the wound, soak it with a concentration of 10% containing indole acetic acid The wet rag of dilute potassium nitrate solution wraps the nutrient soil around the wound of the rootstock, and the scion leaks out; use th...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Artificially select wild roses with fast-growing trunks and fork roots and taproots, and cut the parts at a height of 1m as rootstocks, and remove the sprouts and shoots around the rootstocks; cut off the semi-lignified semi-lignified before germination and the dormant period after bud removal The 3cm fork branch of Chinese rose is used as a scion, and the wound part of the lower end of the scion is sharpened at 20° to be a slope of 0.5cm in length; 1 / 3 of the diameter of the rootstock is cut at a 20° oblique angle at the grafting position on the rootstock, and the knife edge reaches the xylem deeply, forming For a longer wound, smear tree wound healing ointment at the junction of grafted wounds, align the scion with the cambium of the rootstock and insert, sprinkle nutrient soil on the junction of the wound, soak it with a concentration of 12% dilute indole acetic acid The wet rag of potassium nitrate solution wraps the nutrient soil around the wound of the rootstock, a...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Artificially select wild roses with fast-growing trunks and fork roots and taproots, and cut the parts at a height of 0.8m as rootstocks, and remove the buds and shoots around the rootstocks; cut the semi-lignified dormancy after bud removal before germination 2 cm of the Chinese rose fork branch is used as a scion, and the lower wound part of the scion is sharpened at 30° to be a slope of 0.5 cm in length; 1 / 4 of the rootstock diameter is cut deep at a 25° bevel at the grafting position on the rootstock, and the knife edge reaches the xylem deeply. Form a longer wound, smear tree wound healing ointment at the junction of grafted wounds, insert the scion against the cambium of the rootstock, sprinkle nutrient soil on the junction of the wound, soak it with a concentration of 15% containing indole acetic acid The wet rag of dilute potassium nitrate solution wraps the nutrient soil around the wound of the rootstock, and the scion leaks out; use the elastic film to spirally...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com