Low-energy-consumption radiator
A radiator and low energy consumption technology, applied in the direction of heat exchanger shell, indirect heat exchanger, heat exchanger type, etc., can solve the problem that the heat dissipation efficiency of the heating radiator cannot cover the heating demand, and achieve excellent heat dissipation effect and enhanced Diversion effect, the effect of reducing energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
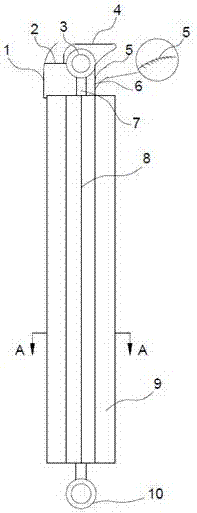
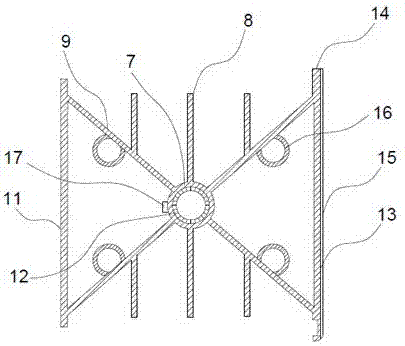
[0019] like Figure 1~2 As shown, a low-energy radiator includes a cooling element 9, a copper tube 7 vertically passing through the inside of the cooling element 9, the cooling element 9 is formed by crossing cooling plates, the center of the copper tube 7 coincides with the intersection point of the cooling plate, and the copper The tube 7 has a built-in core tube 12, the upper and lower ends of the copper tube 7 are connected with the upper horizontal tube interface 3 and the lower horizontal tube interface 10, the two sides of the cooling element 9 are respectively connected to the rear panel 11 and the front panel 13, and the surface of the front panel 13 is provided with a decorative mask 15. The upper and lower ends of the cooling element 9 are provided with side fins 8, and the top of the rear panel is connected with an arc-shaped rear deflector 1, and the rear deflector 1 is connected with the upper horizontal pipe interface 3 through the flat top support plate 2, and ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] like Figure 1~2 As shown, a low-energy radiator includes a cooling element 9, a copper tube 7 vertically passing through the inside of the cooling element 9, and a detection group 17 is provided on the surface of the copper tube 7, and the detection group 17 is composed of a temperature sensor and an alarm. The detection group 17 that is provided can detect the temperature around the heat dissipation element 9, the heat dissipation element 9 is formed by the intersection of heat dissipation plates, the inner side of the heat dissipation plate in the heat dissipation element 9 is connected with a symmetrical heat dissipation pipe 16, and the thickness of the heat dissipation pipe 16 is preferably the heat dissipation in the heat dissipation element 9. 1.1 times the thickness of the plate, the center of the copper tube 7 coincides with the intersection point of the cooling plate, the copper tube 7 has a built-in core tube 12, the upper and lower ends of the copper tube 7 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com