Method for promoting growth of sweet sorghum in saline-alkali land with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and organic fertilizer
A technology of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and organic fertilizers, applied in the direction of organic fertilizers, botany equipment and methods, applications, etc., to achieve the effects of promoting plant growth, reducing the poisoning effect of salt ions, and improving plant tolerance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Utilize the method for the growth of sweet sorghum in saline-alkali land by Phylopodium moses, described Phylopodium moses is Funneliformis mosseae, this bacterial classification is common bacterial classification, provided by China Agricultural University, described The method includes the following steps:
[0035] Step 1, preparation of moses stipe fungus agent
[0036] The initial inoculant is a soil sample containing Funneliformis mosseae spores, hyphae and infected root segments;
[0037] Air-dry the farmland soil and organic fertilizer separately, pass through a 2mm fine screen, sterilize by high-pressure steam at 121°C for 1 hour, take out after high-pressure steam sterilization and cool to room temperature, and then put the farmland soil and organic fertilizer cooled to room temperature according to volume Ratio 2:1 mixing and stirring to form a matrix evenly;
[0038] Adopt mixed application method to inoculate described initial inoculant in matrix, inoculum ...
Embodiment 2
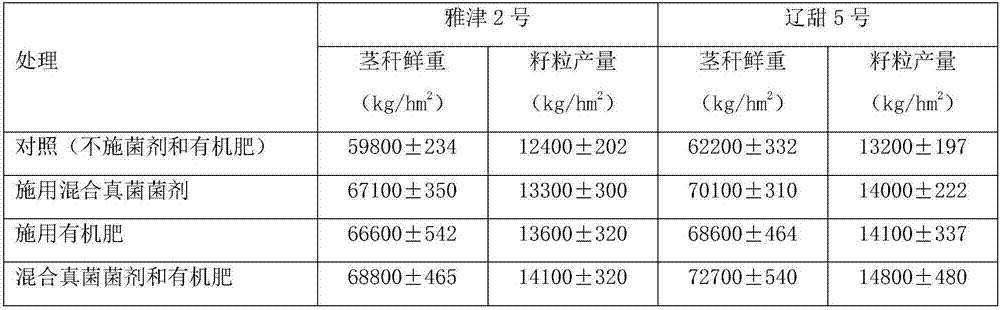
[0048] Utilize the method of rhizoma physalis to promote the growth of sweet sorghum in saline-alkali soil, except that arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus bacterial classification and sweet sorghum kind are different from embodiment 1, all the other are the same;
[0049] The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus is Rhizophagus intraradices, provided by China Agricultural University; the sweet sorghum variety is Liaotian 5, which is purchased from the market; the biological yield of sweet sorghum is measured after maturity As in Table 2:
[0050] deal with
[0051] It can be seen from Table 2 that the average fresh weight of the stalks in the control treatment was 62200kg / hm 2 , the average biomass of stalks treated with the application of rhizocystis fungi, organic fertilizers, and simultaneous application of fungal agents and organic fertilizers was 68500kg / hm 2 、68600kg / hm 2 、72100kg / hm 2 , respectively increased by 10.1%, 10.3%, and 15.9% compared with the control treatme...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Utilize Phylopodium scotlandii to promote the method that sweet sorghum grows in saline-alkali soil, except that the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus bacterial classification is different from embodiment 1 and has adopted two sweet sorghum varieties, all the other are the same;
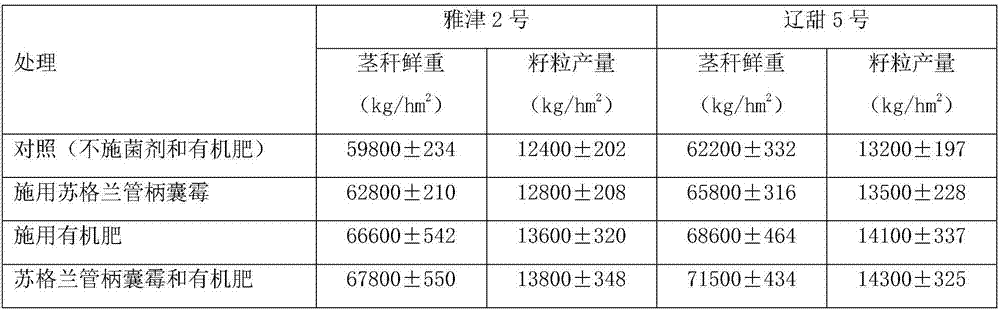
[0054] The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus was Funneliformis caledonium, provided by the Nanjing Soil Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences; the sweet sorghum varieties were Yajin 2 and Liaotian 5, both of which were purchased from the market; The measurement results of the yield are shown in Table 3:
[0055] Table 3 Effects of Scotch stalk fungi and organic fertilizers on sweet sorghum (Yajin 2 and Liaotian 5) stalk fresh weight and grain yield
[0056]
[0057] It can be seen from Table 3 that for Yajin No. 2 sweet sorghum, the average fresh weight of the stalks treated with Phylopodium scotidica, organic fertilizer, and bacterial agent and organic fertilizer were respectively ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com