Achromobacter xylosoxidans glutamine synthetase gene and application thereof
A colorless bacteria, glutamine technology, applied in the application, genetic engineering, enzymes and other directions, can solve the problem of reducing the resistance of transgenic crops glufosinate-ammonium
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1 Acquisition of novel glufosinate-ammonium resistance gene glutamine synthetase gene
[0031] 1. Collection of soil samples
[0032] Soil samples were collected from orchards that had been used at least four times a year and had been used continuously for more than ten years.
[0033] 2. Screening of glufosinate-resistant strains
[0034] Weigh 1g of the orchard soil sample frequently used by glufosinate-ammonium, add 1ml of 0.9% (w / v) sodium chloride solution, shake and mix at 5000 rpm, centrifuge gently at 3000 rpm, pour off the supernatant, and then add 0.9% (w / v) 1ml of sodium chloride solution, shake and mix at 5000 rpm, let it stand on ice for 10 minutes, draw 150 μl of the solution, spread it and culture it in LB solid medium containing 20 mM glufosinate-ammonium for 24 hours. Inoculate the grown single colony into a test tube with 1.6ml of LB liquid medium, incubate at 28°C for 48h, then draw 150μl of the culture solution and apply it again to the LB ...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2 Artificial synthesis of novel glufosinate-ammonium resistance gene glutamine synthetase gene
[0044] The gene synthesis method [Nucleic Acids Research, 2004, 32, e98] artificially synthesized obtained in Example 1
[0045] Novel glutamine synthetase gene of the present invention. A total of 34 pairs of primers were designed, and the designed primers were as follows:
[0046] 1. P1: Tm=54, 60mer
[0047] GGA, TCC, ATG, GCA, AGC, CCG, AAA, GAC, GTC, CTG, AAA, CAG, ATC, GCC, GAT, AAC, GAA, GTG, AAA, TTC
[0048] 2. P2: Tm=54, 60mer
[0049] GGT,GCT,CAC,GGC,CAA,CCG,TAT,CGG,TAA,AGC,GGA,AAT,CCA,CGA,ATT,TCA,CTT,CGT,TAT,CGG
[0050] 3. P3: Tm=54, 60mer
[0051] TAC,GGT,TGG,CCG,TGA,GCA,CCA,CGT,TTC,CGT,GCC,CAC,CAC,CGC,TAT,CGA,TGA,AGA,CAA,GCT
[0052] 4. P4: Tm=54, 60mer
[0053] GCC, CGG, GAT, CGA, CGA, ACC, GTC, GAA, AGC, CTG, CCC, GCT, TTC, CAG, CTT, GTC, TTC, ATC, GAT, AGC
[0054] 5. P5: Tm=54, 60mer
[0055] ACG,GTT,CGT,CGA,TCC,CGG,GCT,GGA,AGG,GCA,TCG,AAG...
Embodiment 3
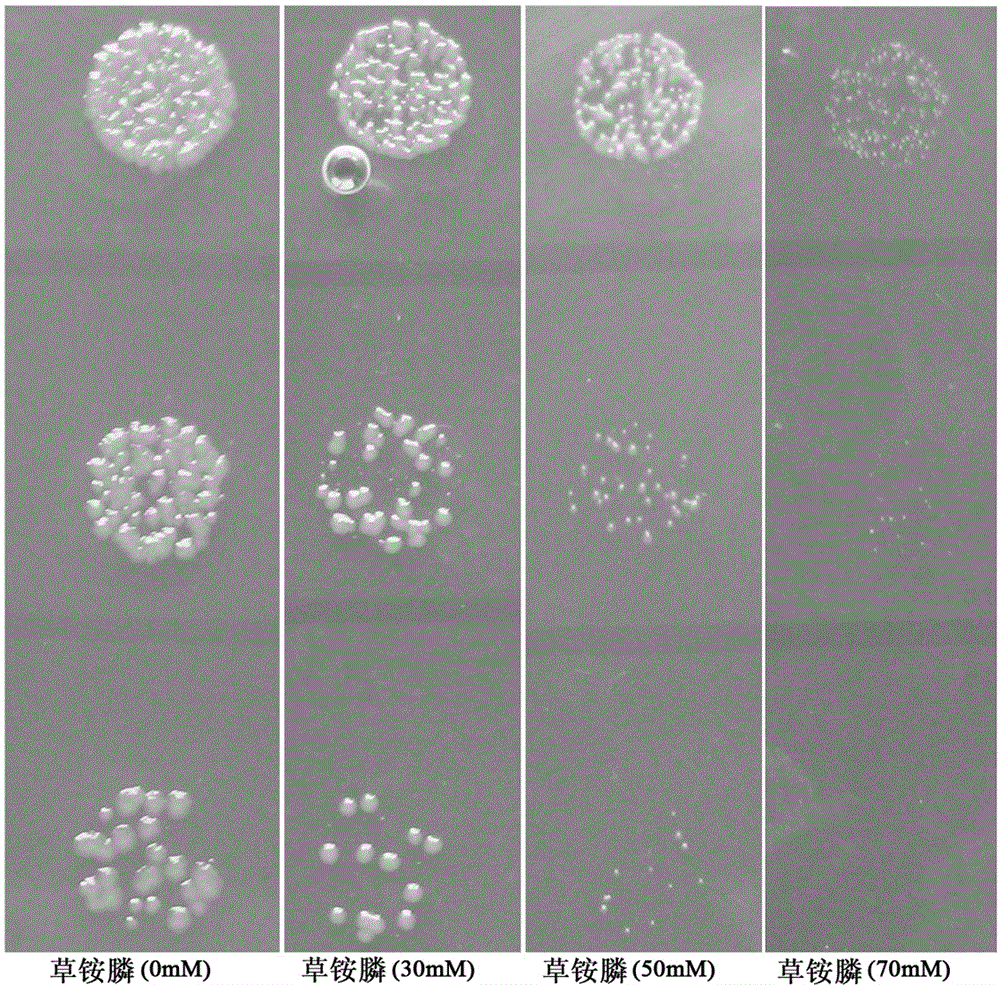
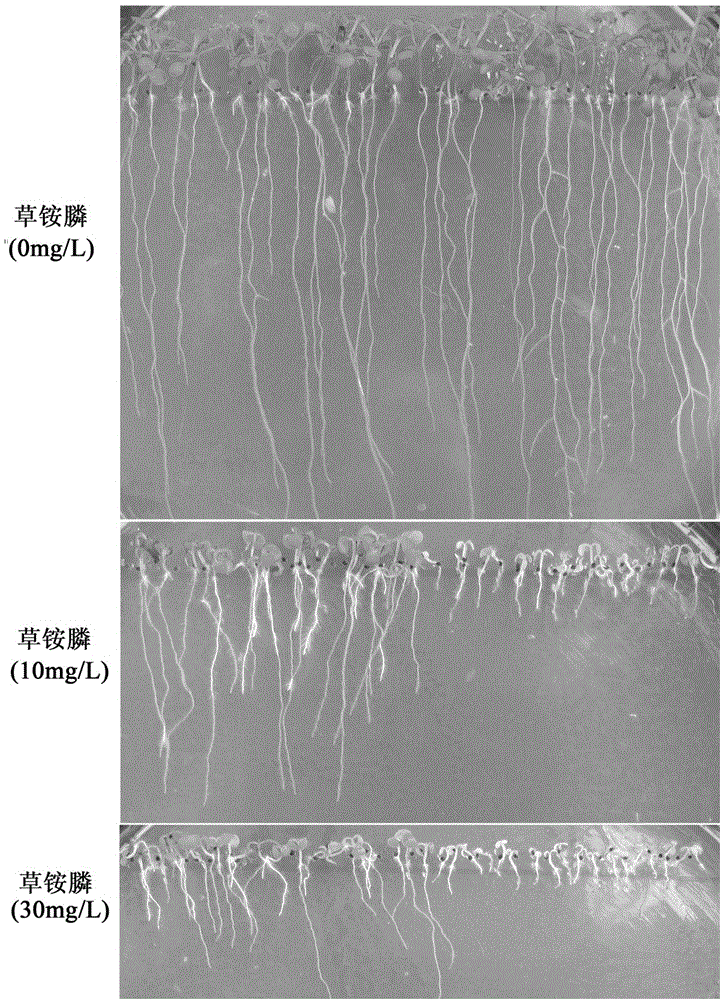
[0116] Example 3 In vitro glufosinate-ammonium resistance test
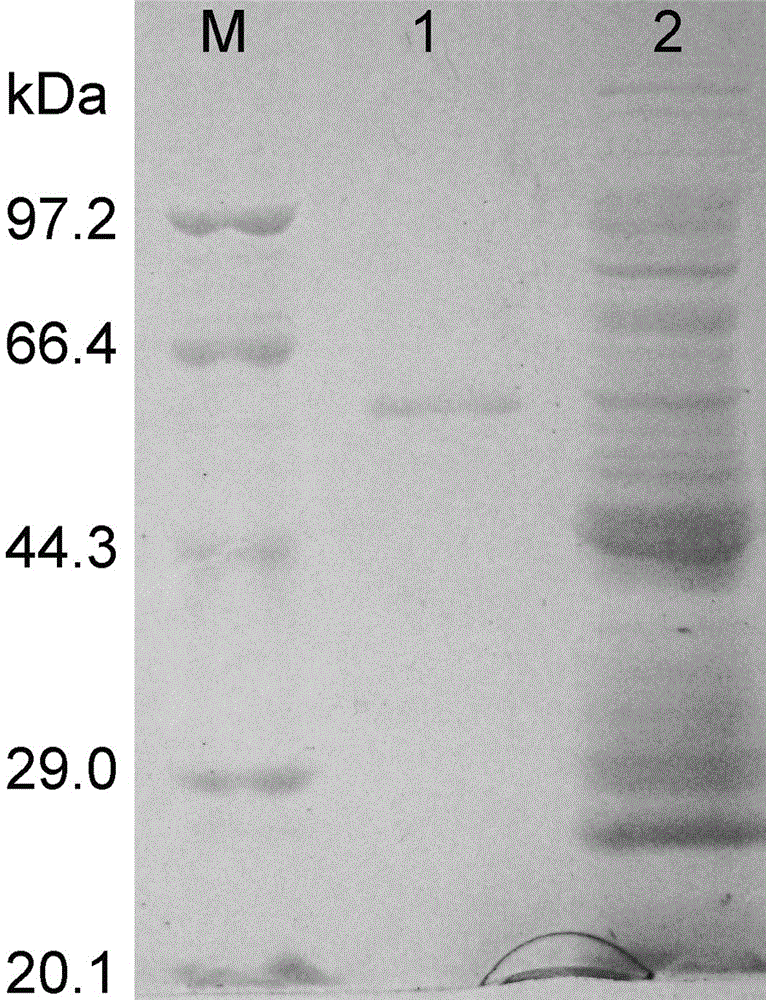
[0117] The glutamine synthetase gene obtained in Example 2 was digested with BamH I and Sac I, and then constructed into the prokaryotic expression vector pG251 to obtain the recombinant plasmid pG251- glnA A.xylosoxidans . The recombinant plasmid pG251- glnA A.xylosoxidans , smeared on M9 plate and cultivated for 48h, picked the transformant with a toothpick and inoculated it in LB liquid medium for cultivation until the concentration reached 5 × 10 3 For cells / μL, take 2μL of cell culture fluid and 1 / 5 and 1 / 25 diluted cell culture fluid to spot on M9 plates containing different concentrations of glufosinate-ammonium (0, 30 mM, 50 mM and 70 mM) Cultivate for 48h. It was subsequently observed that 50 mM glufosinate-ammonium had started to inhibit the growth of glutamine synthetase gene cells of the present invention. But when the concentration of glufosinate-ammonium is 70mM, the glutamine synthetase ge...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com