Microcarriers, matrices and scaffolds for culturing mammalian cells and methods of manufacture
A technology of copolymers and polymers, applied in general culture methods, chemical instruments and methods, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of limited application of water-soluble cationic copolymers, minimize costs, and enhance adhesion , the effect of maximizing output
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
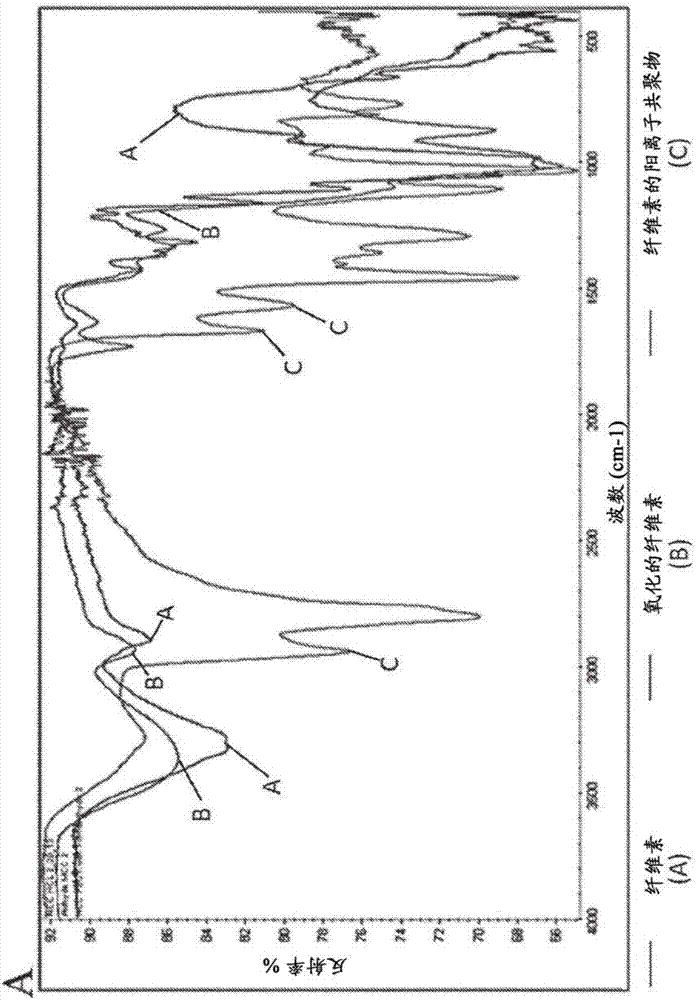
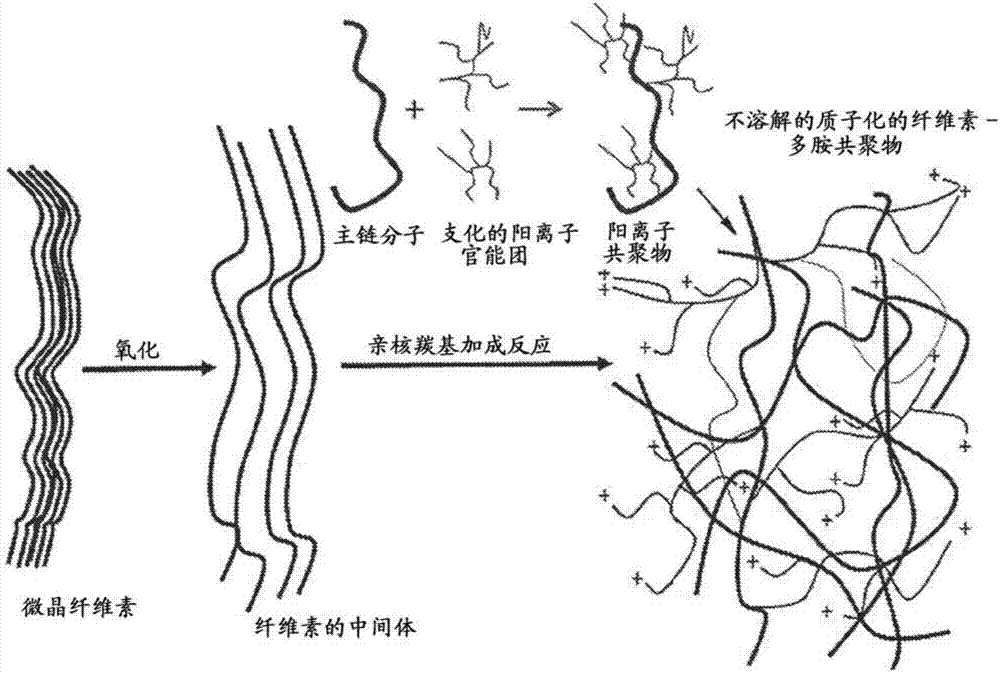
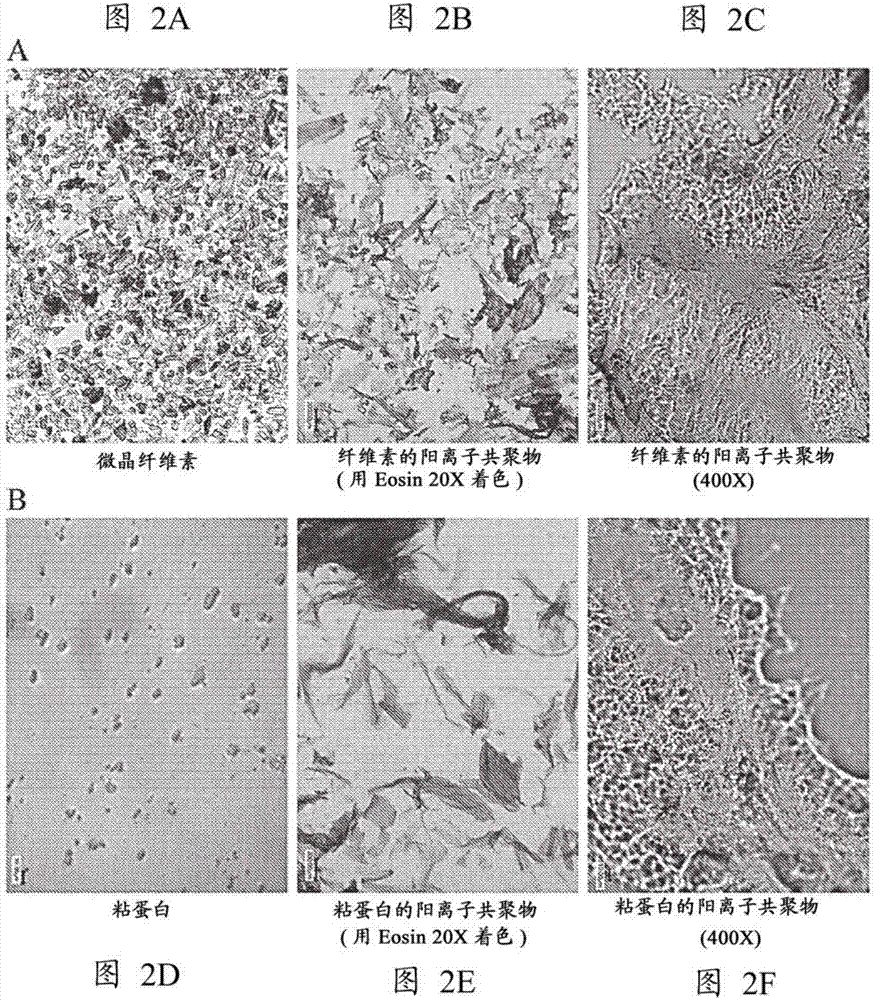
[0114] Soluble 2,3-dialdehyde cellulose (DAC) or selectively oxidized mucin (SOM) can be prepared by sodium periodate oxidation of cellulose. 10 g of cellulose (size: <100 nm, 20 μm, 50 μm, or fibers) or 5 g of mucin (type II or III) can be resuspended by 200 mL of deionized water. Then, 20 g of sodium periodate was added, and then the pH was adjusted to 3.0 with 6X HCl. Next, the composition was degassed and purged with nitrogen, and then allowed to react at pH 3 for 4 hours at 60° C. with stirring in the dark. The reaction was stopped by adding 10 mL of ethylene glycol. The product was dialyzed against deionized water for 3 days. Soluble DAC or SOM was collected as a supernatant by centrifugation at 40,000 xg for 30 minutes to remove insoluble DAC or SOM as a pellet. Then, the collected supernatant is lyophilized (optional).
Embodiment 2
[0116] In another example, (low-oxidized) insoluble 2,3-dialdehyde cellulose (DAC) or selectively oxidized mucin (SOM) can be prepared by sodium periodate oxidation of cellulose. 10 g of cellulose (size: <100 nm, 20 μm, 50 μm, or fibers) or 5 g of mucin (Type II or Type III) were resuspended with 200 mL of deionized water, and then 10 g of sodium periodate was added. Then, the pH was adjusted to 3.0 with 6X HCl, followed by degassing and purging with nitrogen. The composition was then reacted at pH 3 at 60° C. for 4 hours with stirring in the dark. The reaction can be stopped by adding 10 mL of ethylene glycol. The product was washed 3 times with 4 liters of deionized water for 1 hour each. Insoluble DAC or SOM was collected by centrifugation at 800 xg for 10 minutes. Then, the washed insoluble DAC or SOM solution was resuspended with DI water (deionized water). The washed insoluble DAC solution can then be lyophilized (optional).
Embodiment 3
[0118] Polysaccharide-polyamine copolymers and glycoprotein-polyamine copolymers can be synthesized by reacting DAC or SOM with branched polyethyleneimine (PEI) (MW 750K). The ratio of DAC / SOM to PEI is 50:1 to 1:10. With branched polyethyleneimine 10g (MW 750K, in H 2 50% by weight in O) was added to a 500 mL beaker. The pH of PEI was adjusted to 5.0 with 37% HCl. The pH of 100 ml of DAC or SOM solution containing appropriate amount of DAC or SOM was adjusted to 5.0 by adding 6X HCl. Solutions of PEI and DAC or SOM were incubated on ice for 10 minutes. Solutions containing 10 g of PEI and solutions containing appropriate amounts of DAC or SOM were mixed and incubated on ice at 1000 RPM for 5 minutes. The mixture was kept on ice without agitation until complete product formation. The mixture was incubated at 70°C for 60 minutes. Check the pH of the suspension every 10 min and adjust it to 8.5 with 5M sodium hydroxide solution. The product is forced through a screen to o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com