Methods of treating and preventing gout and lead nephropathy
A toxicity and gout technology, applied in the fields of antidote, bone disease, pharmaceutical formula, etc., can solve the problems of drug hypersensitivity, exacerbation of acute gout attacks, difficulty in taking dosage, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0073] Example 1 - CT°I induces a decrease in serum urate
[0074] CT°I is directly involved in the neutralization of free radicals and reactive oxygen species. The effect of CT°I on serum urate includes at least two possible aspects: 1) through the interaction with xanthine oxidase to directly reduce urate production; 2) through the reduction of renal function induced by CT°I Improvement indirectly reduces serum urate levels.
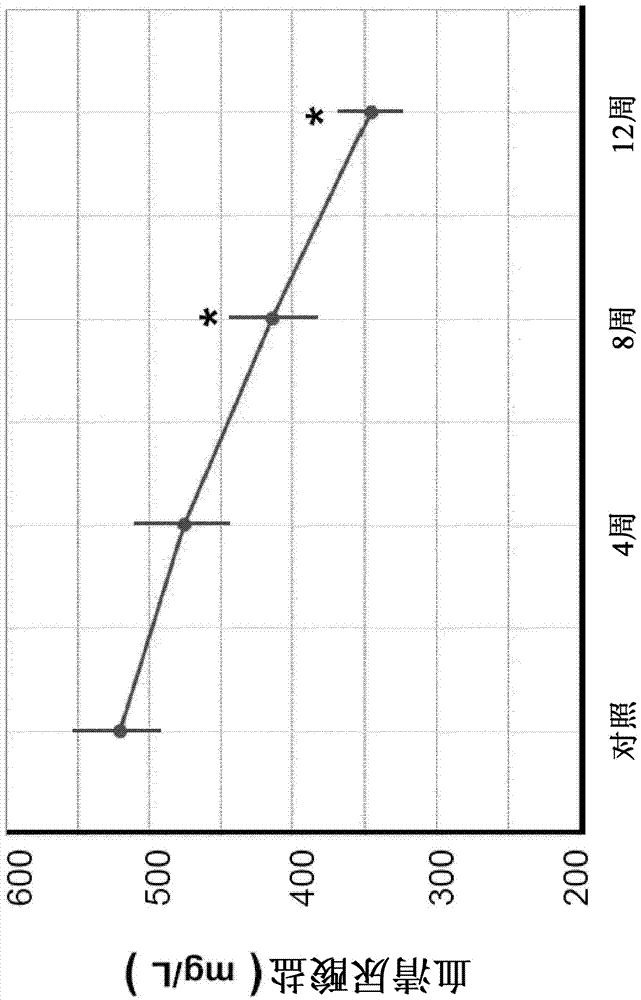
[0075] Such as figure 1 As shown, the average serum urate of the subjects tested was 521.07±40.11 mg / L at their first visit and 346.46±21.17 mg / L after 12 weeks of treatment. This represents a 33.51% decrease in serum urate. The decrease in serum urate after 8 weeks of treatment was significantly different (p<0.05).
example 2
[0076] Example 2 - CT°I Induces Improvement of Renal Function
[0077] All subjects were classified as renally impaired (glomerular filtration rate <80 ml / min). The serum creatinine test measures the level of creatinine in the blood and provides an estimate of the glomerular filtration rate, which indicates the excretory function of the kidneys. If the kidneys are not functioning properly, elevated creatinine levels may build up in the blood.
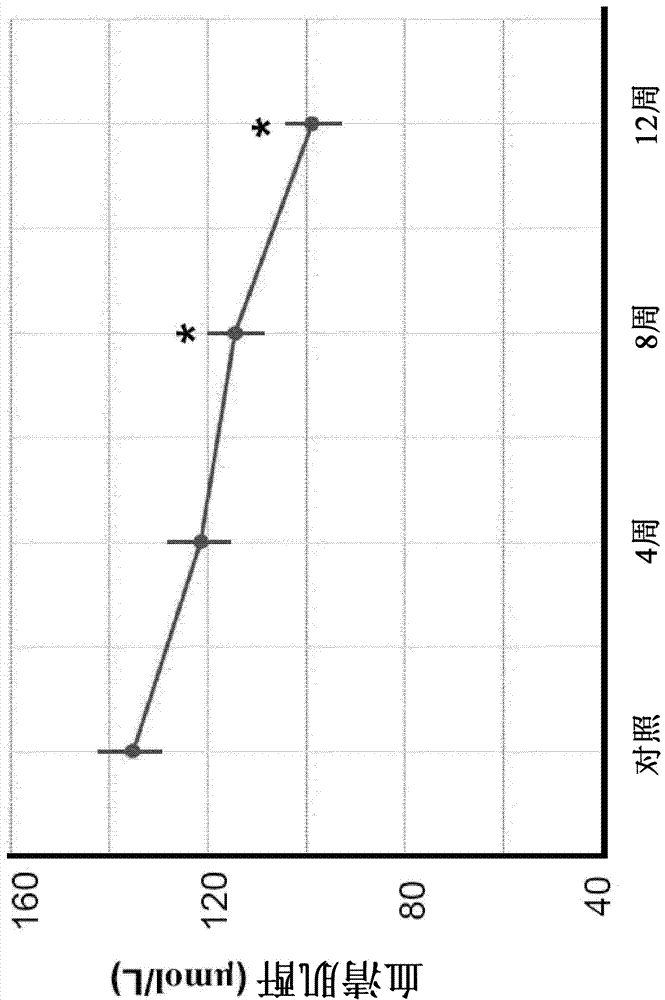
[0078] Such as figure 2 As shown, the mean serum creatinine of the subjects tested was 135.29±6.89 μmol / L at their first visit and 99.00±4.45 μmol / L after 12 weeks of treatment. This represents a 26.82% decrease in serum creatinine. The decrease in serum creatinine after 8 weeks of treatment was significantly different (p<0.05).
example 3
[0079] Example 3 - CT°I induces a decrease in blood lead levels
[0080] Lead is toxic to the kidneys. Accumulated heavy metal ions, including lead, damage the body primarily through their intense oxidative damage to major organs, especially the kidneys and liver. CT°I protects the body from heavy metal ion poisoning mainly through its direct chelation and its enhanced antioxidant effect.
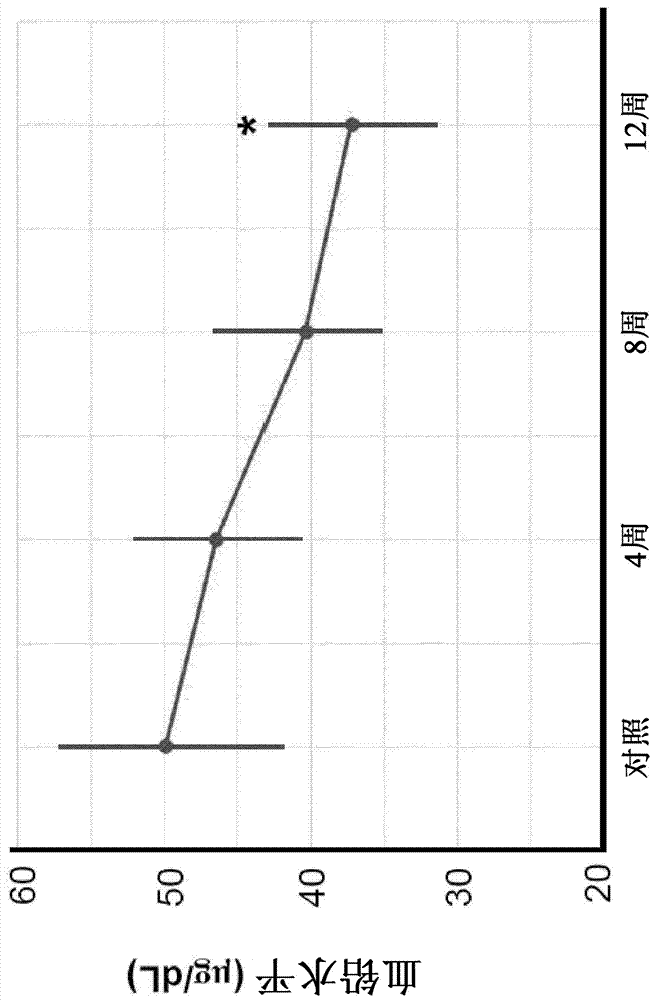
[0081] Such as image 3 As shown, the average blood lead level of the subjects tested was 49.90±8.41 μg / dL at their first visit and 37.26±6.29 μg / dL after 12 weeks of treatment. This represents a 25.33% drop in blood lead levels. The reduction in blood lead levels after 12 weeks of treatment was significantly different (p<0.05).
[0082] other embodiments
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com