Mixing method for making glass bottles
A glass bottle and material mixing technology, which is applied in glass production, chemical instruments and methods, mixers with rotating stirring devices, etc., can solve the problems of slow melting process, long production cycle, and low glass strength, and achieve melting Rapid production, reduced labor, and high glass strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
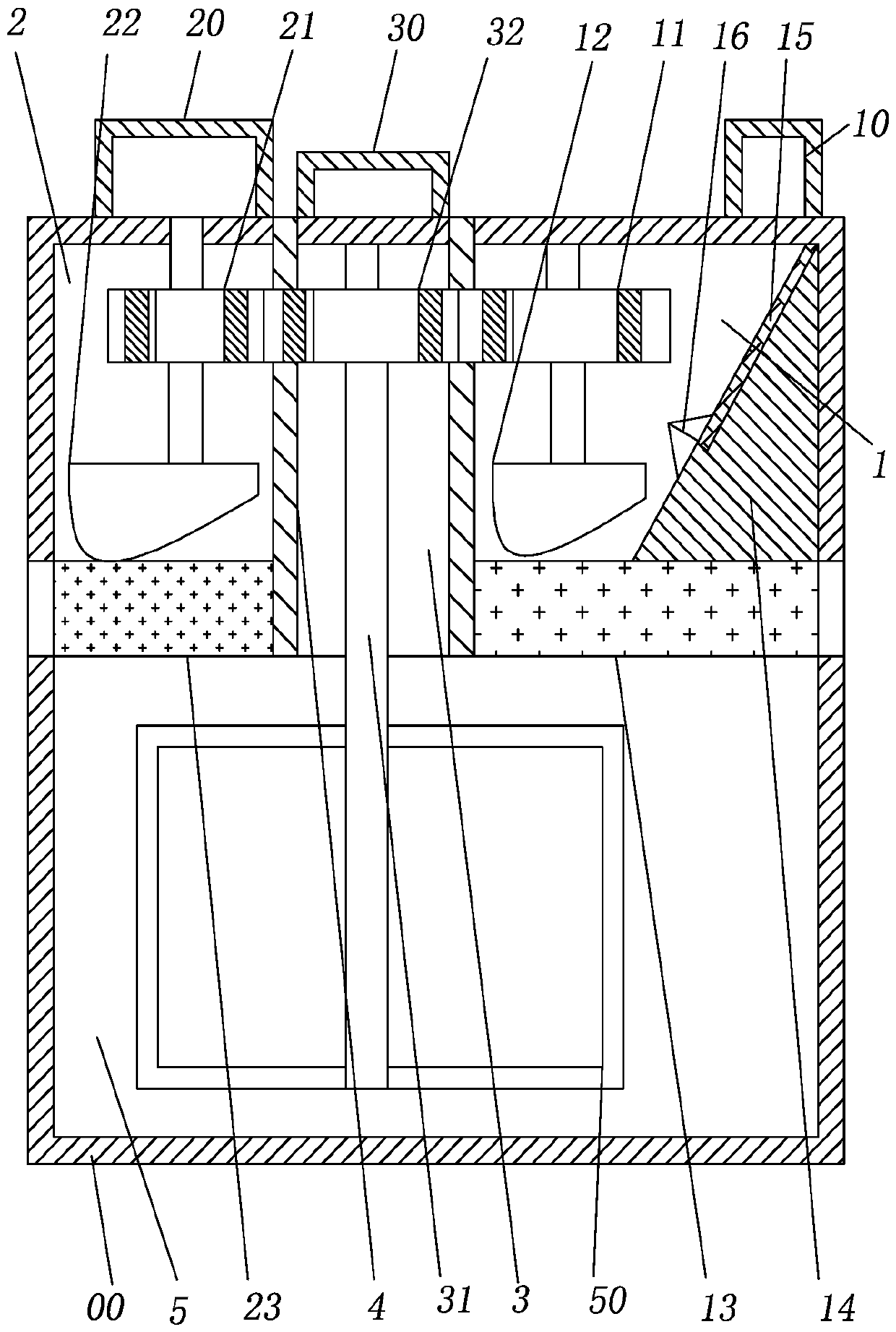
[0032] The embodiment is basically as attached figure 1 Shown: the mixing method for making glass bottles, the mixing device is used for mixing. The mixing device includes a motor and a box 00. The box 00 is equipped with a coarse crushing chamber 1, a fine crushing chamber 2, a feeding chamber 3 and The mixing chamber 5; the coarse crushing chamber 1, the fine crushing chamber 2 and the feeding chamber 3 are separated by two partitions 4, and the two partitions 4 are provided with through holes.
[0033]The coarse crushing cavity 1 is connected with a coarse material port 10 for inputting broken glass, and the coarse crushing cavity 1 is provided with a third gear 11, a coarse crushing wheel 12 and a coarse screen for screening the crushed glass. 13. The third gear 11 and the primary crushing wheel 12 are coaxially connected. The bottom of the primary crushing wheel 12 is provided with a protrusion for crushing glass. The coarse screen 13 is located below the primary crushing...
Embodiment 2
[0047] The difference between this embodiment and Example 1 is: in step B, the mass fraction of broken glass is 20, and the aperture of the coarse screen is 10 mm; in step C, the mass fraction of quartz sand is 55, and the aperture of the fine screen is 0.6 mm; in step D, the mass fraction of soda ash is 25; in step E, the rotational speed of the stirring blade is 60 rpm.
Embodiment 3
[0049] The difference between this embodiment and Example 1 is: in step B, the mass fraction of broken glass is 30, and the aperture of the coarse screen is 20 mm; in step C, the mass fraction of quartz sand is 50, and the aperture of the fine screen is 0.8 mm; in step D, the mass fraction of soda ash is 20; in step E, the rotational speed of the stirring blade is 80 rpm.
[0050] It is worth noting that the feeding port 30 can also add raw materials other than soda ash that do not need to be pulverized, such as salt, etc., and the fine material port 20 can also add raw materials other than quartz sand that require smaller particle size, such as limestone, feldspar, etc. , the specific raw materials can be determined according to the specific process.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com