Moderate intensity titanium alloy and preparing method thereof
A titanium alloy and high-strength technology, which is applied in the field of high-strength titanium alloys, can solve the problems of low impact toughness and achieve the effects of improving impact toughness, reducing costs, and improving strength and plasticity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] (1) Use 0-1 grade sponge titanium substrate raw materials, add intermediate alloys aluminum vanadium, aluminum molybdenum, iron, aluminum, mix evenly, and press into a titanium alloy electrode of Φ120mm. The pressed electrode blocks are connected by vacuum welding, and then second vacuum self-consumption melting is used to make a Φ190mm titanium alloy ingot. The chemical composition of the ingot is shown in Table 1.
[0029] (2) The titanium alloy ingot is forged and opened, and then formed and forged. The thermal processing process has a deformation amount of 75% in the single-phase region (≥960°C), and a deformation amount of 80% in the two-phase region (880-890°C). %. Made into Φ25mm rod, the phase transition point of the rod is 928°C.
[0030] (3) Carry out heat treatment to the prepared rod, heat treatment system: heating and holding at 890° C. for 2 hours, then air cooling.
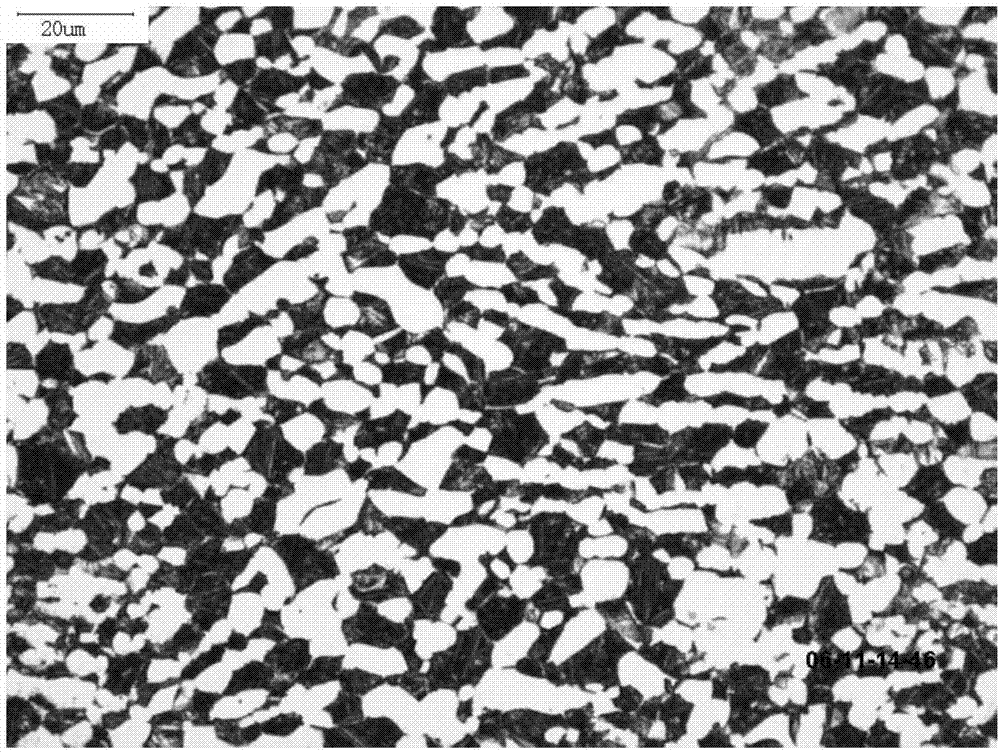
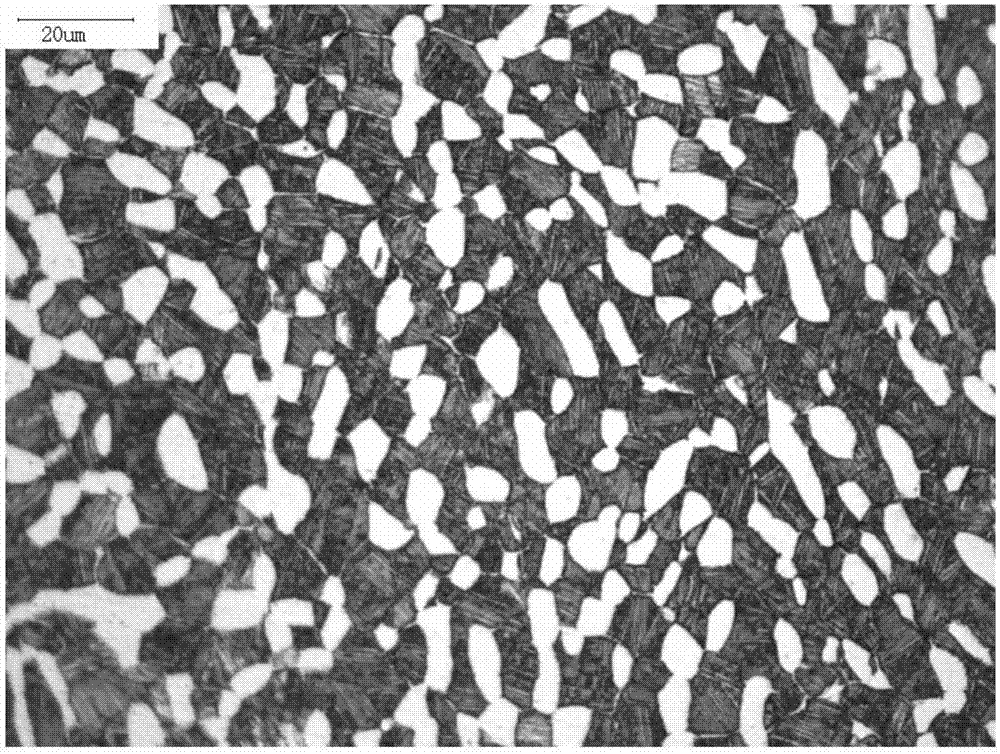
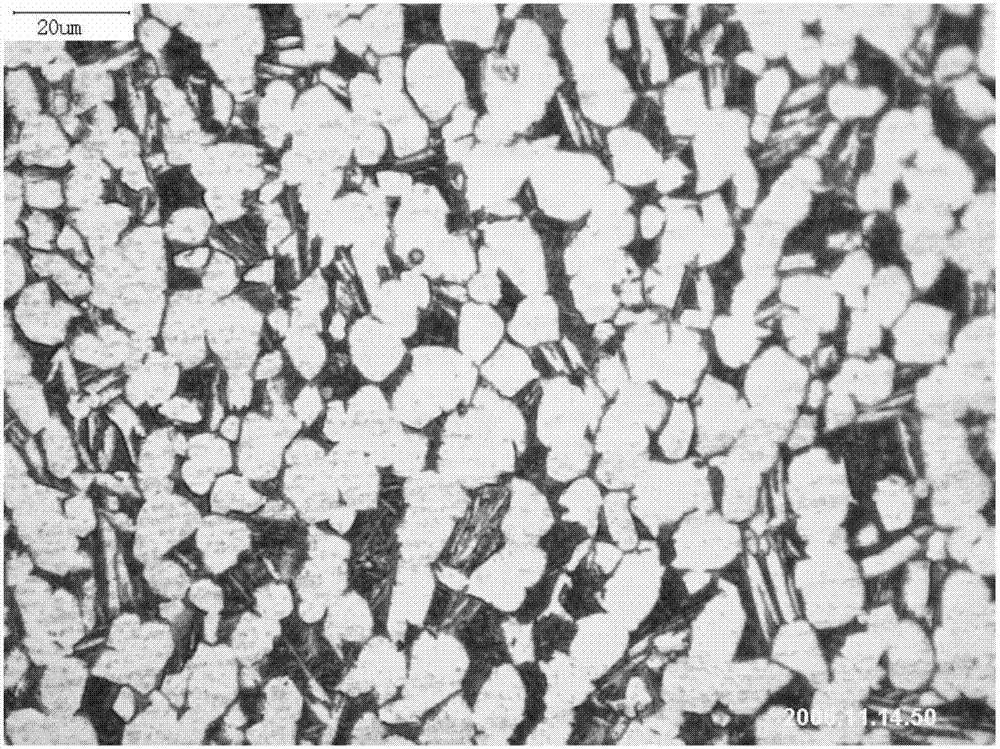
[0031] The mechanical properties of the product are shown in Table 2, and its microstr...
Embodiment 2
[0033] (1) Use 0-1 grade sponge titanium substrate raw materials, add intermediate alloys aluminum vanadium, aluminum molybdenum, iron, aluminum, mix evenly, and press into a titanium alloy electrode of Φ120mm. The pressed electrode blocks are connected by vacuum welding, and then second vacuum self-consumption melting is used to make a Φ190mm titanium alloy ingot. The chemical composition of the ingot is shown in Table 1.
[0034] (2) The titanium alloy ingot is forged and opened, and then formed forging. The thermal processing process has a deformation amount of 60% in the single-phase region (≥960°C), and a deformation amount of 65% in the two-phase region (880-890°C). %. Made into a Φ25mm rod, the phase transition point of the rod is 937°C.
[0035] (3) Carry out heat treatment to the prepared rod, heat treatment system: heating and holding at 900° C. for 2 hours, then air cooling.
[0036] The mechanical properties of the product are shown in Table 2, and its microstru...
Embodiment 3
[0038] (1) Use 0-1 grade sponge titanium substrate raw materials, add intermediate alloys aluminum vanadium, aluminum molybdenum, iron, aluminum, mix evenly, and press into a titanium alloy electrode of Φ120mm. The pressed electrode blocks are connected by vacuum welding, and then second vacuum self-consumption melting is used to make a Φ190mm titanium alloy ingot. The chemical composition of the ingot is shown in Table 1.
[0039] (2) The titanium alloy ingot is forged and opened, and then formed and forged. The thermal processing process has a deformation of 85% in the single-phase region (≥960°C), and a deformation of 90% in the two-phase region (880-890°C). %. Made into Φ25mm rod, its phase transition point is 945°C.
[0040] (3) Carry out heat treatment to the prepared rod, heat treatment system: heat and keep at 910° C. for 2 hours, and air cool.
[0041] The mechanical properties of the product are shown in Table 2, and its microstructure is shown in image 3 .
[00...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com