Method for efficiently localizing exogenous mammal cytoplasmic protein in cell nucleus and application thereof
A cytoplasmic protein and mammalian technology, applied in the field of life sciences, can solve problems such as inaccurate experimental results, inability to obtain dose-effect relationships, and inconvenience
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] A method for efficiently localizing exogenous mammalian cytoplasmic proteins in the nucleus is as follows:
[0032] (1) The synthesized single-stranded NLS sequence, forward: 5-"GTCGACCCGAAGAAGAAGCGTAAGGTC"-3, shown in SEQ ID NO.1; reverse: 5-"CAGCTGGACCTTACGCTTCTTCTTCGG"-3, shown in SEQ ID NO.2; using annealing To synthesize double-stranded DNA, the reaction system is as follows:
[0033] 10x annealing buffer 2ul (100mM Tris-HCL (pH=7.5), 10mM EDTA, 1M NaCl)
[0034] Oligonucleotide 1 final concentration 100nM
[0035] Oligonucleotide 2 final concentration 100nM
[0036] Make up to 20ul with nuclease-free water
[0037] Reaction conditions: 95°C: 5 minutes, 70°C: 10 minutes, gradually cool to room temperature.
[0038](2) At the same time, pRK5-Sufu-GFP will be digested with SalI enzyme, and the reaction system is as follows:
[0039] pRK5-Sufu-GFP 2ug
[0040] 10xNEB cutsmart buffer 5ul
[0041] SalI enzyme 1ul
[0042] wxya 2 O make up to 50ul
[0043] Reac...
Embodiment 2
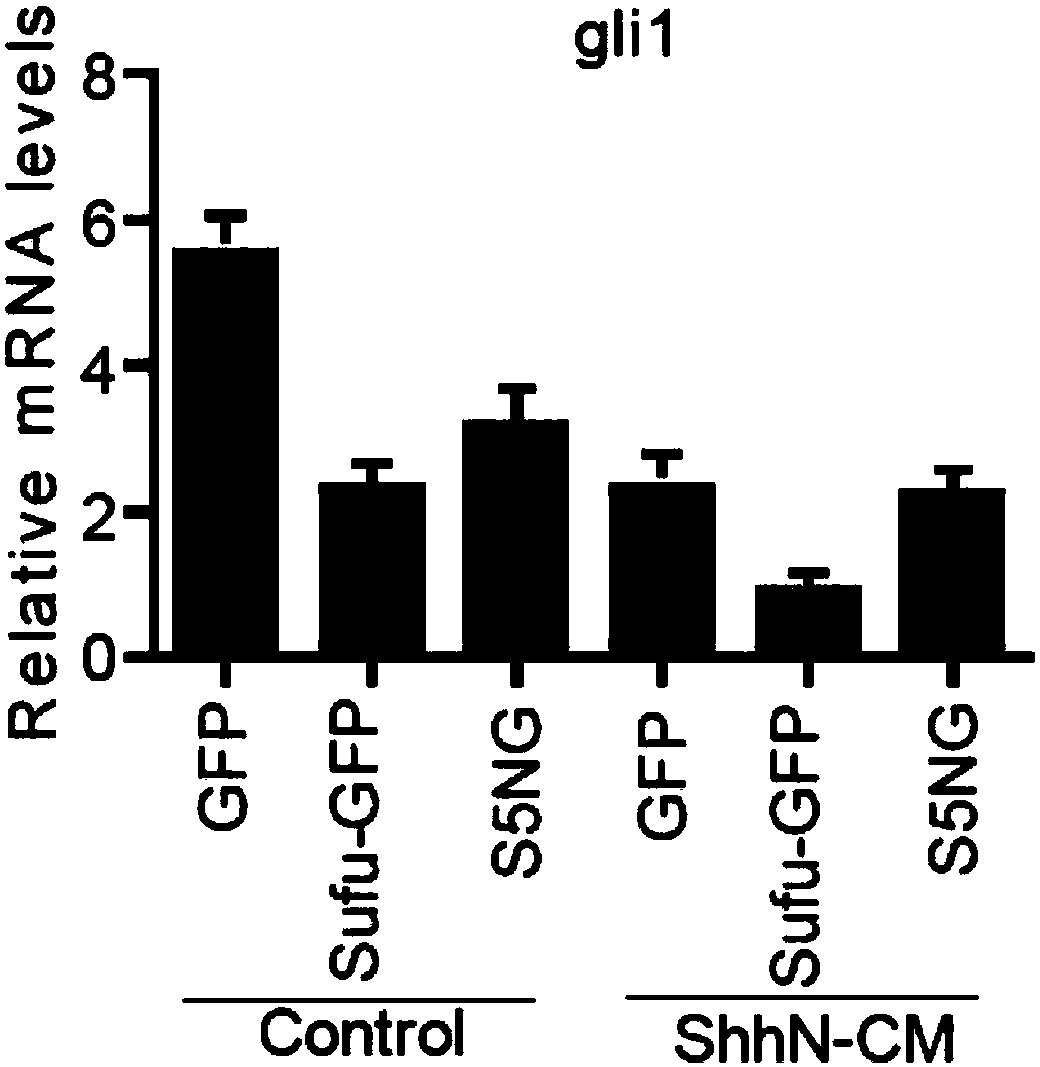
[0062] The control plasmid and the positive plasmid were transfected into Sufu gene knockout MEFs, and the cells were harvested 24 hours later to extract RNA, and a fluorescent quantitative PCR experiment was performed to detect the expression difference of S5NG on the downstream target genes ptch1 and gli1 of the Hedgehog signaling pathway ( Figure 3a with Figure 3b ).
Embodiment 3
[0064] The control plasmid and positive plasmid were transfected into Sufu gene knockout MEFs, and the luciferase reporter gene and sea cucumber gene plasmids of the 8xGli transcription factor binding site were transfected at the same time. After 48 hours, the reporter gene detection system was used to detect the difference. The effect of the plasmid on the transcriptional regulation of Gli1 protein ( Figure 4 ).
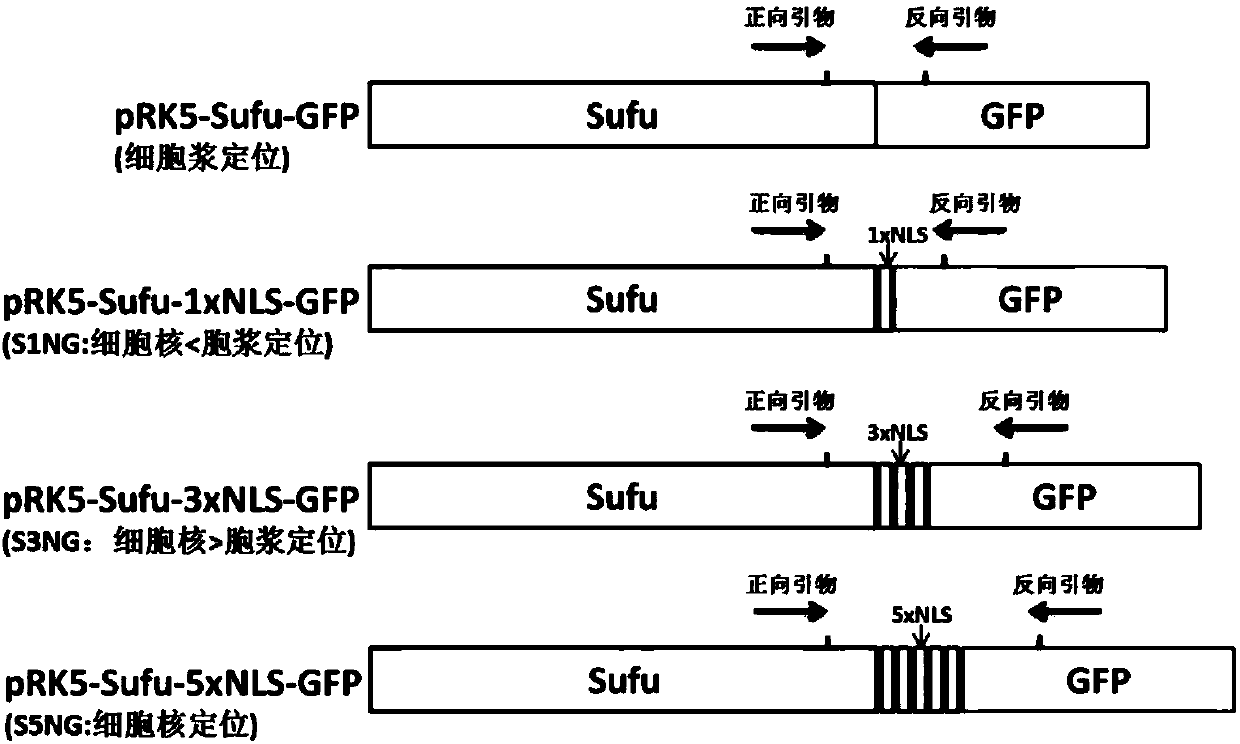
[0065] As an intermediate regulator of the Hedgehog signaling pathway, Sufu regulates the transcriptional activity of the transcription factor Gli1, and the location of Sufu will definitely affect its regulation of the transcriptional activity of the Gli protein. Therefore, the luciferase reporter gene system was used to detect the regulation of Gli1 transcriptional activity by these Sufu-GFP plasmids inserted with different numbers of NLS; at the same time, the method of fluorescent quantitative PCR was used to detect the effect of Sufu-GFP inserted with different...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com