Method for fault discrimination, checking and fault influence range analysis of power grid
A power grid fault and influence range technology, applied in the direction of measuring electricity, measuring electrical variables, data processing applications, etc., can solve the problems of sacrificing accuracy and reliability, so as to improve accuracy and reliability, avoid misjudgment, avoid The effect of missed judgment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
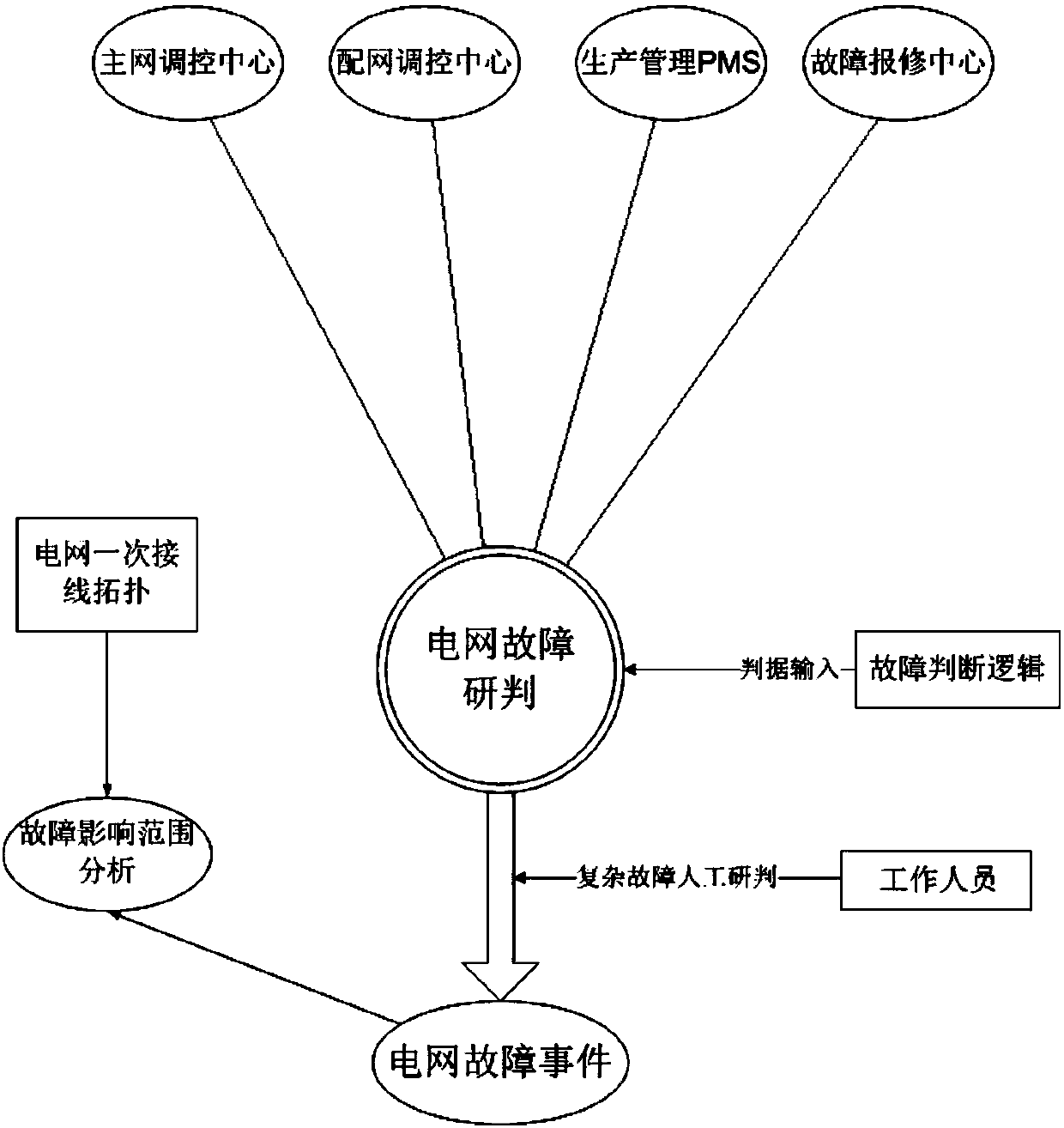
[0033] This application proposes a fault judgment method that includes big data mining to obtain useful information, fault judgment logic design, fault information formation, fault impact range analysis and display, main network / distribution network data fusion, etc. The specific implementation steps are as follows.
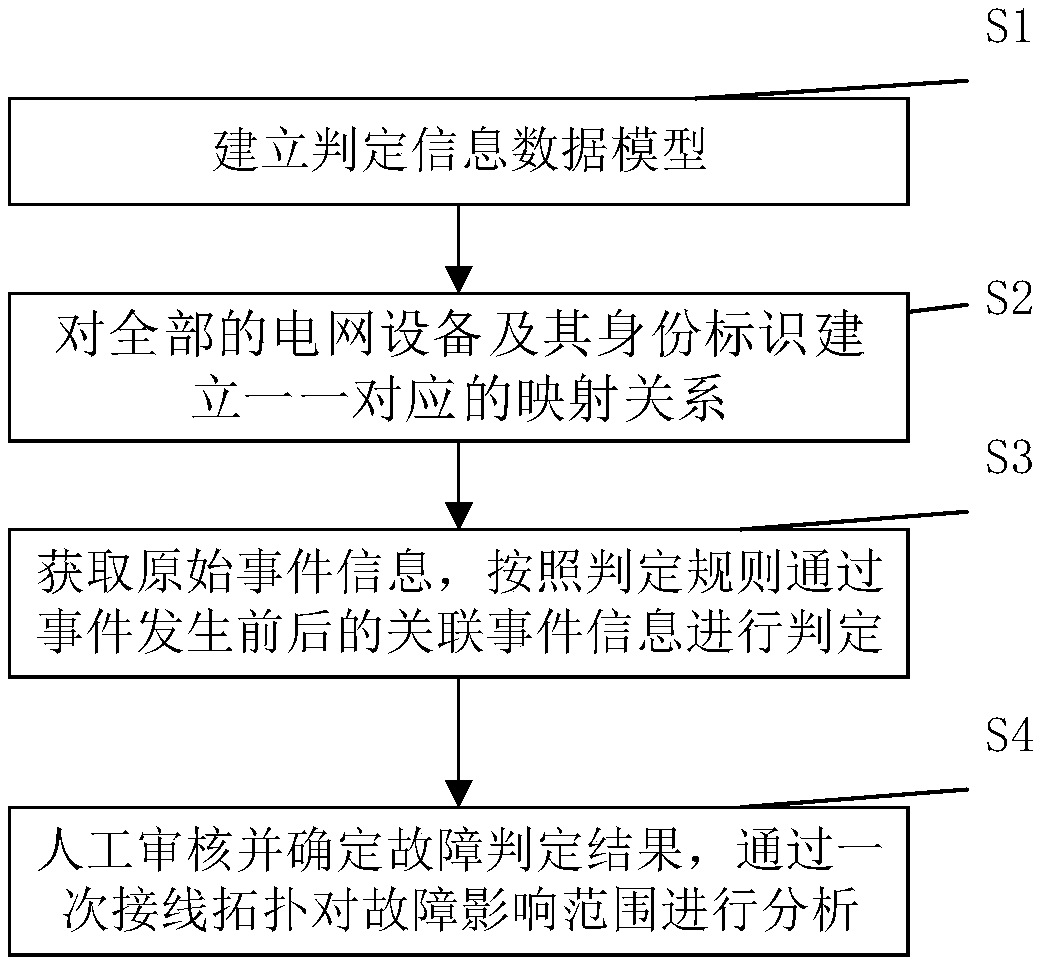
[0034] like figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, a method for grid fault judgment, verification and fault impact range analysis includes the following steps:
[0035] S1. Establish a judgment information data model collected from different fault data sources;
[0036] S2. Obtain updated primary grid topology, wiring diagrams and equipment ledgers of different voltage levels, and establish a one-to-one mapping relationship for all grid equipment and their identifications through a fuzzy matching algorithm;
[0037] S3. Obtain the original event information from different fault data sources, and perform different preliminary screening on it according to different data ...
Embodiment 2
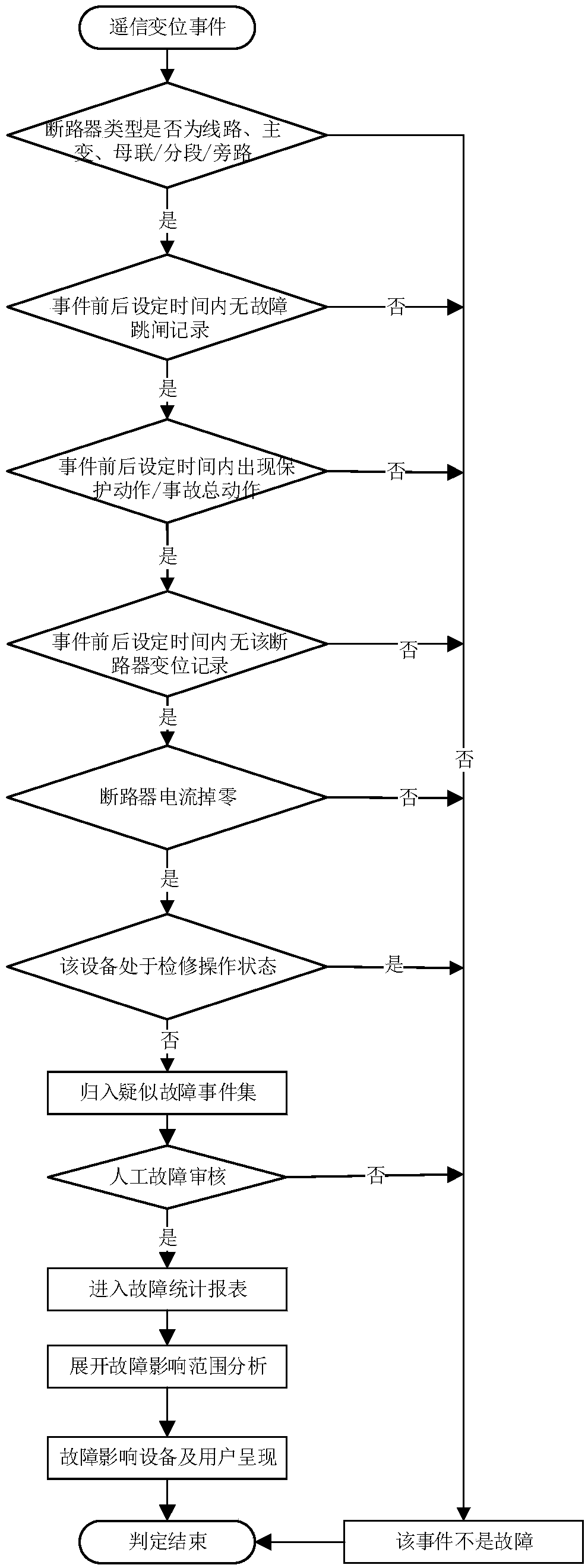
[0048] image 3 Shown is the fault judgment process for the remote signal displacement event in the switch displacement, as follows:
[0049] 1. Determine whether the circuit breaker type is one of line, main transformer, bus coupler / section / bypass, if so, proceed to the next step of judgment, otherwise judge it as a non-fault event, and end the judgment;
[0050] 2. Judging whether there is a fault trip record within the set time before and after the occurrence of the event, if not, proceed to the next step of judgment, otherwise it is judged as a non-fault event, and the judgment ends;
[0051] 3. Judging whether there is a protection action or an accident general action within the set time before and after the event, if so, proceed to the next step of judgment, otherwise it is judged as a non-fault event, and the judgment is ended;
[0052] 4. Judging whether there is a record of the circuit breaker’s displacement within the set time before and after the event, if not, pro...
Embodiment 3
[0058] If there is a protective action within about 5 seconds before and after the opening of the switch, the opening is identified as an accidental opening, which is very likely to be a real fault tripping. The judgment rule of this method for the accidental opening information is The following situations are not considered as real fault tripping events:
[0059] 1. A successful reclosing signal appears after the accident opening occurs;
[0060] 2. After the accident opening occurs, the switching current does not drop to zero;
[0061] 3. The switch current is always zero during the period of accident opening;
[0062] 4. When the accident opening occurs, the switch circuit is in the maintenance state;
[0063] 5. Frequent opening and closing actions occur in a short period of time before and after the accident opening.
[0064] If the above conditions are not met, if there is a remote control operation on the accident trip during the time period when it occurs, no clear ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com