A kind of clean plant cellulose extractant and its preparation method and application
A plant cellulose and extractant technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microorganism-based methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as large oxygen consumption, high water consumption for chemical degumming, and environmental pollution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
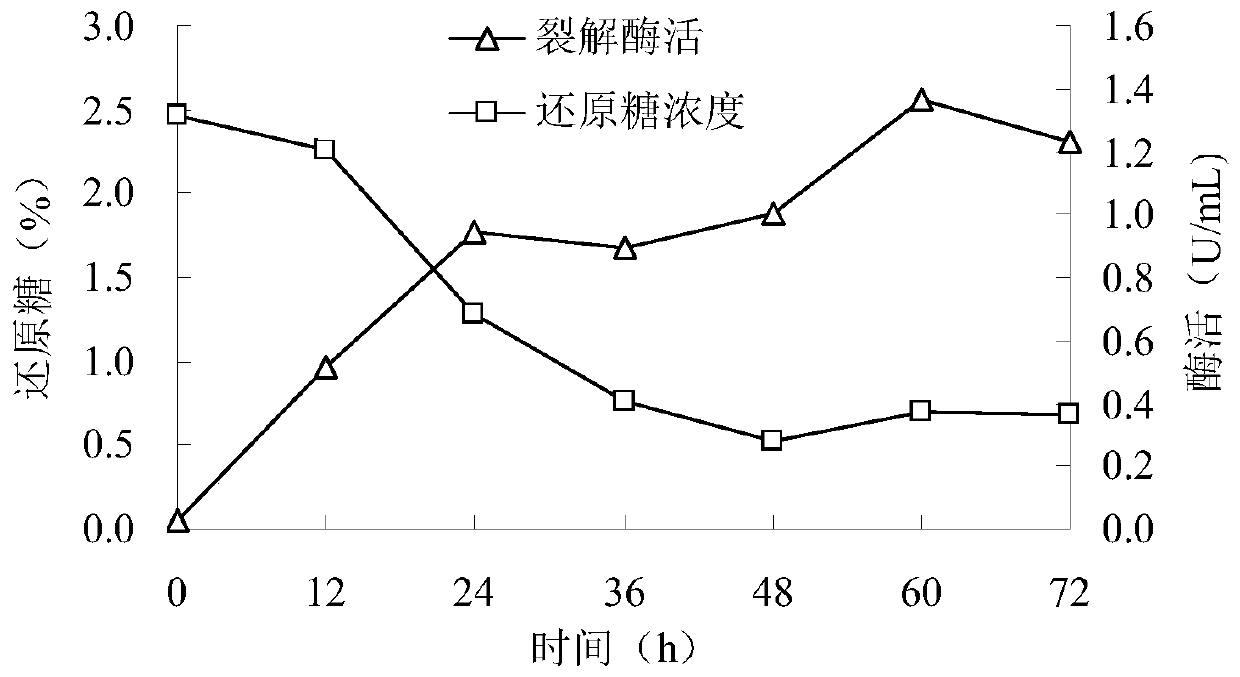
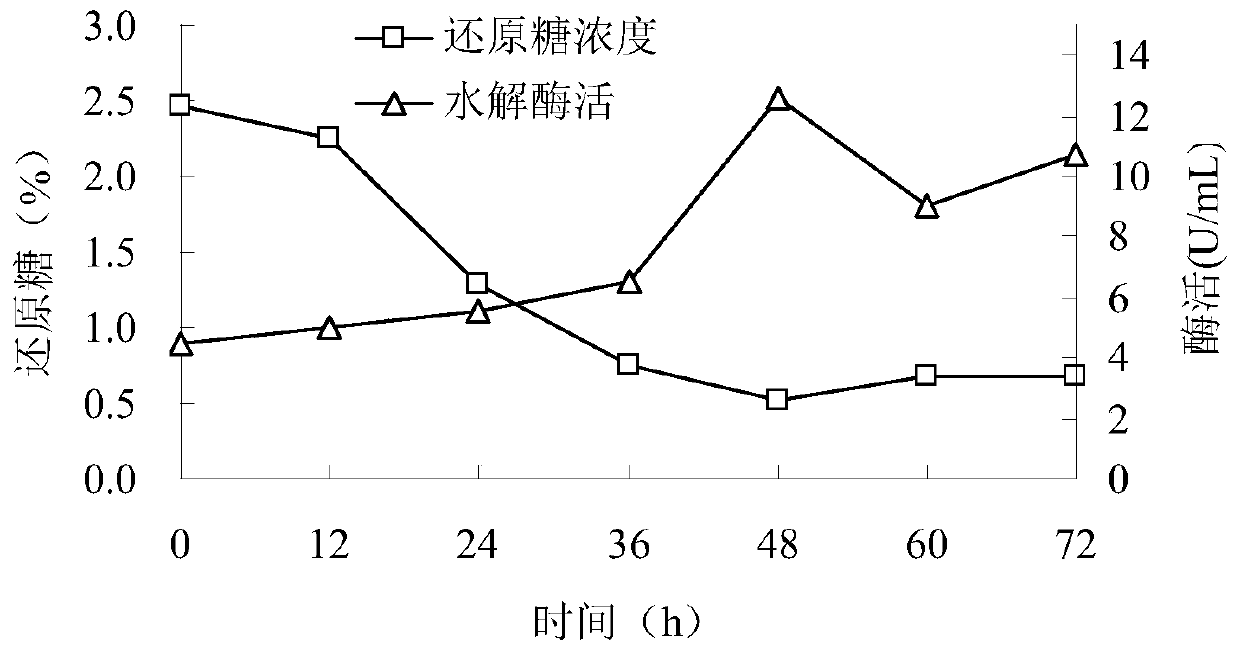
[0075] Inoculate the Bacillus subtilis CGMCC 1.836 seed liquid into the fermenter according to the preparation method of B liquid described above, ferment at 36°C for 72 hours, and detect alkaline pectin lyase and alkaline polygalacturonic acid every 12 hours Enzyme activity and reducing sugar content, see the results figure 1 and figure 2 .
[0076] From figure 1 and 2 Visible, Bacillus subtilis (Bacillus subtilis) CGMCC 1.836 can produce alkaline pectin lyase and alkaline polygalacturonase. After 12 hours of fermentation, both enzymes were produced. With the prolongation of the fermentation period, the secretion of these two enzymes increased gradually. After 48 hours of fermentation, the enzyme activity of alkaline polygalacturonase first reached the maximum, which was 12.6U / mL. After 60 hours of fermentation, the enzyme activity of alkaline pectin lyase also reached the highest level, which was 1.4U / mL. After continuing to ferment for 72 hours, the activities of th...
Embodiment 1
[0077] The influence of embodiment 1 stabilizer on the stability of alkaline pectin lyase in B liquid
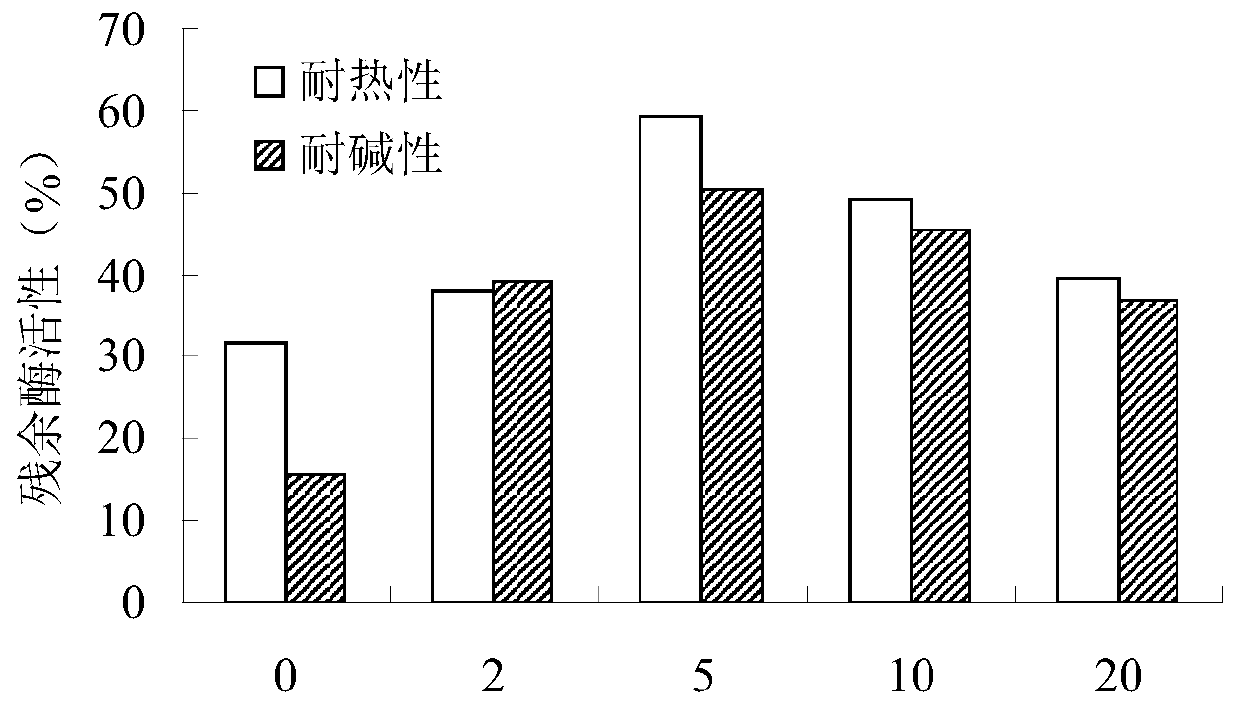
[0078] Carry out heat resistance and alkali resistance tests according to the above-mentioned methods. Determination of the residual enzyme activity rate after adding different concentrations of enzyme stabilizers, the results are shown in image 3 .
[0079] From image 3 It can be seen that the optimum concentration of adding enzyme stabilizer is 5mmol / L, at this concentration, the residual enzyme activity rate in the heat resistance test is increased by 27.6%, and the residual enzyme activity rate in the alkali resistance test is increased by 34.6%.
[0080] Four, clean cellulose extraction (degumming) process and detection method, the steps are as follows:
[0081] a. Hemp fiber degumming: open the hemp fiber, remove impurities, send it into the cooking pot, add the cooking liquid with a dilution ratio of 1:10 to 1:15, and cook it under normal pressure at 50 to 80°C f...
Embodiment 2
[0118] Example 2 Application of cellulose extractant in hemp degumming project
[0119] 1. Preparation of cooking liquid: preparation in cellulose extractant—the volume ratio of liquid A to liquid B is 5:1; then dilute with water at a ratio of 1:10 to prepare cooking liquid.
[0120] 2. Process: 5 kg of hemp fiber raw material for opening and removing impurities; liquor ratio of 1:10; adding cooking liquid and then cooking under normal pressure for 50 minutes; reaction temperature is 80°C; The test results of hemp fiber components are shown in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com