Magnesium cement with high water resistance and preparation method thereof
A magnesium cement, water-based technology, applied in the field of high water-resistant magnesium cement and its preparation, can solve the problems of low water resistance of cement, achieve the effects of improving water resistance, compact structure, and reducing supersaturation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
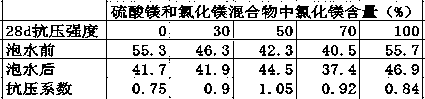
[0023] A high water-resistance magnesium cement is characterized in that it is made of the following raw materials: light-burned magnesia powder, magnesium sulfate and magnesium chloride mixture, water, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, the light-burned magnesia powder, magnesium sulfate and The mass ratio of magnesium chloride mixture to water is 14.5:1:22, wherein the mass ratio of magnesium chloride to the mixture is 0, the content of active magnesium oxide in the light-burned magnesium oxide powder is 60%, potassium dihydrogen phosphate The content is 0.5% of the mass of light-burned magnesia powder.
[0024] The preparation method of described high water resistance cement comprises the following steps:
[0025] S1: raw material weighing;
[0026] S2: weighing each raw material according to the quality of the raw material;
[0027] S3: dissolving the magnesium sulfate and magnesium chloride mixture in water;
[0028] S4: Incorporation of potassium dihydrogen phosphate;
...
Embodiment 2
[0035] A high water-resistant magnesium cement is characterized in that it is made of the following raw materials: light-burned magnesia powder, a mixture of magnesium sulfate and magnesium chloride, water, the light-burned magnesia powder, a mixture of magnesium sulfate and magnesium chloride, water, The substance ratio of potassium dihydrogen phosphate is: 14.5:1:22, wherein magnesium chloride accounts for 30% of the substance ratio of the mixture, the content of active magnesium oxide in the light-burned magnesium oxide powder is 60%, dihydrogen phosphate The content of potassium is 0.5% of the mass of light-burned magnesia powder.
[0036] The preparation method of described high water resistance cement comprises the following steps:
[0037] S1: raw material weighing;
[0038] S2: weighing each raw material according to the quality of the raw material;
[0039] S3: dissolving the magnesium sulfate and magnesium chloride mixture in water;
[0040] S4: Incorporation of p...
Embodiment 3
[0047] A high water-resistance magnesium cement is characterized in that it is made of the following raw materials: light-burned magnesia powder, magnesium sulfate and magnesium chloride mixture, water, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, the light-burned magnesia powder, magnesium sulfate and The mass ratio of the magnesium chloride mixture to water is 14.5:1:22, wherein magnesium chloride accounts for 50% of the mass of the mixture, the content of active magnesium oxide in the light-burned magnesium oxide powder is 60%, dihydrogen phosphate The content of potassium is 0.5% of the mass of light-burned magnesia powder.
[0048] The preparation method of described high water resistance cement comprises the following steps:
[0049] S1: raw material weighing;
[0050] S2: weighing each raw material according to the quality of the raw material;
[0051] S3: dissolving the magnesium sulfate and magnesium chloride mixture in water;
[0052] S4: Incorporation of potassium dihydrogen ph...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com