Nursing point determination method
A point-of-care, immunoassay technology, applied in measuring devices, instruments, disease diagnosis, etc., can solve problems such as misdiagnosis of liver diseases and elevated enzyme activity levels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0130] Example 1 - Human plasma strongly interferes with the ability of a series of mouse antibodies to bind ALT
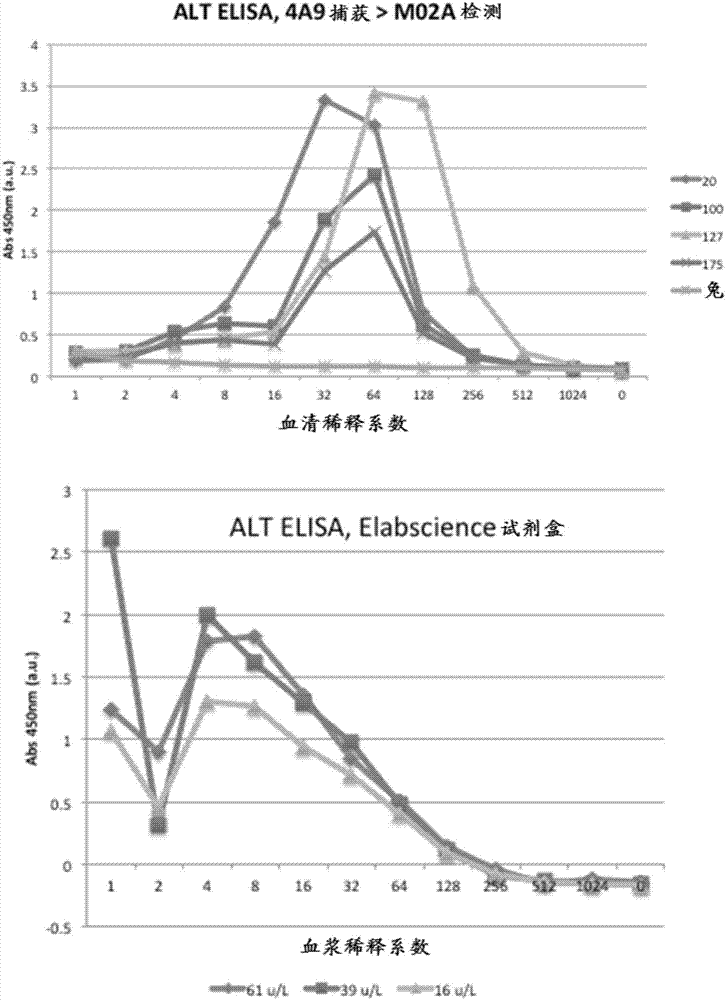
[0131] A commercial ELISA for measuring ALT in human plasma also exhibits very poor correlation with enzymatic ALT levels and, surprisingly, yields results that are highly dependent on sample dilution for serum or plasma (see figure 1 ).
[0132] As shown in Figure 2, preliminary experiments disclosed herein by the inventors provided similar results. Using a series of MAbs generated in mice using ALT1 protein as an immunogen (Figure 2), the results were highly dependent on sample dilution for serum or plasma. However, the inventors reasoned that one or more factors present in human plasma could interfere with the antigenic reactivity of ALT with antibodies, thus preventing the development of a useful assay for ALT mass concentration using this method.
[0133] The surprising and novel observation of strong interference by human plasma at the level of ALT antigen...
Embodiment 2
[0134] Example 2 - Rabbits generate potent antibodies against human ALT1
[0135] The inventors compared the amino acid sequence of ALT1 in humans and mice (see Figure 3A ), and identified proteins with a high level of identity. Thus, only certain parts of the protein surface can be expected to be sufficiently different between humans (antigens) and mice (host animals) to be able to function as exogenous antigens to induce an immune response. Furthermore, a limited number of highly antigenic epitopes can overlap with sites that bind factors present in human plasma, preventing correct recognition of ALT proteins when assayed in human plasma using antibodies directed against such sites.
[0136] The inventors devised a solution to this problem by exploiting the known fact that rabbits have no homologues of the human ALT1 protein or gene, but only have homologues of the ALT2 protein, which appear to provide relevant biochemical function. Thus, it would be expected that substa...
Embodiment 3
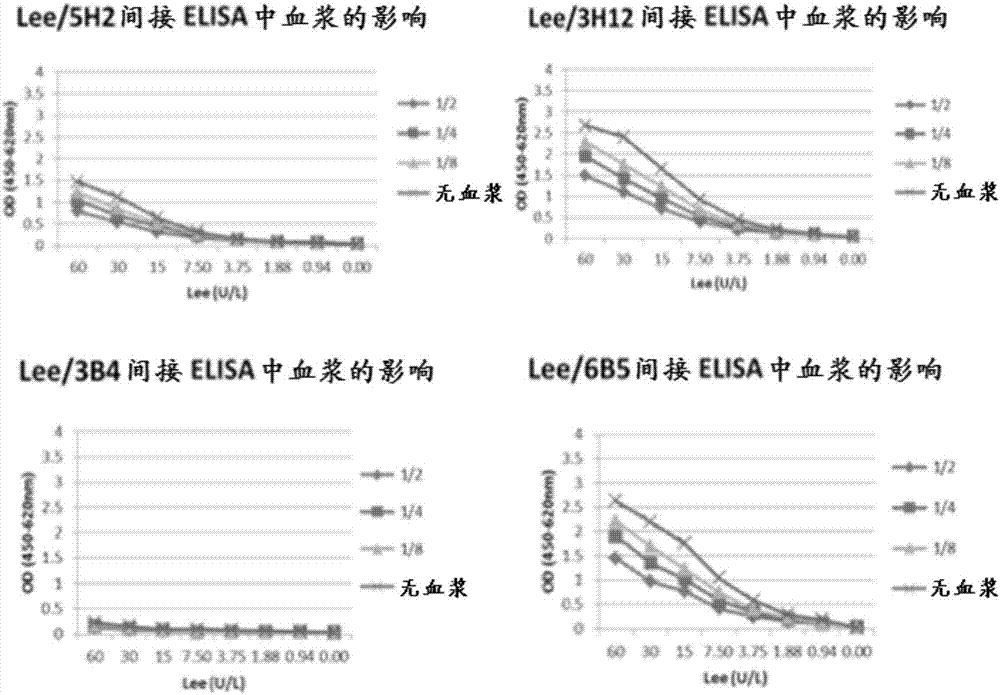
[0138] Example 3 - Lack of Interference from Human Plasma in Results of Rabbit Antibody ELISA
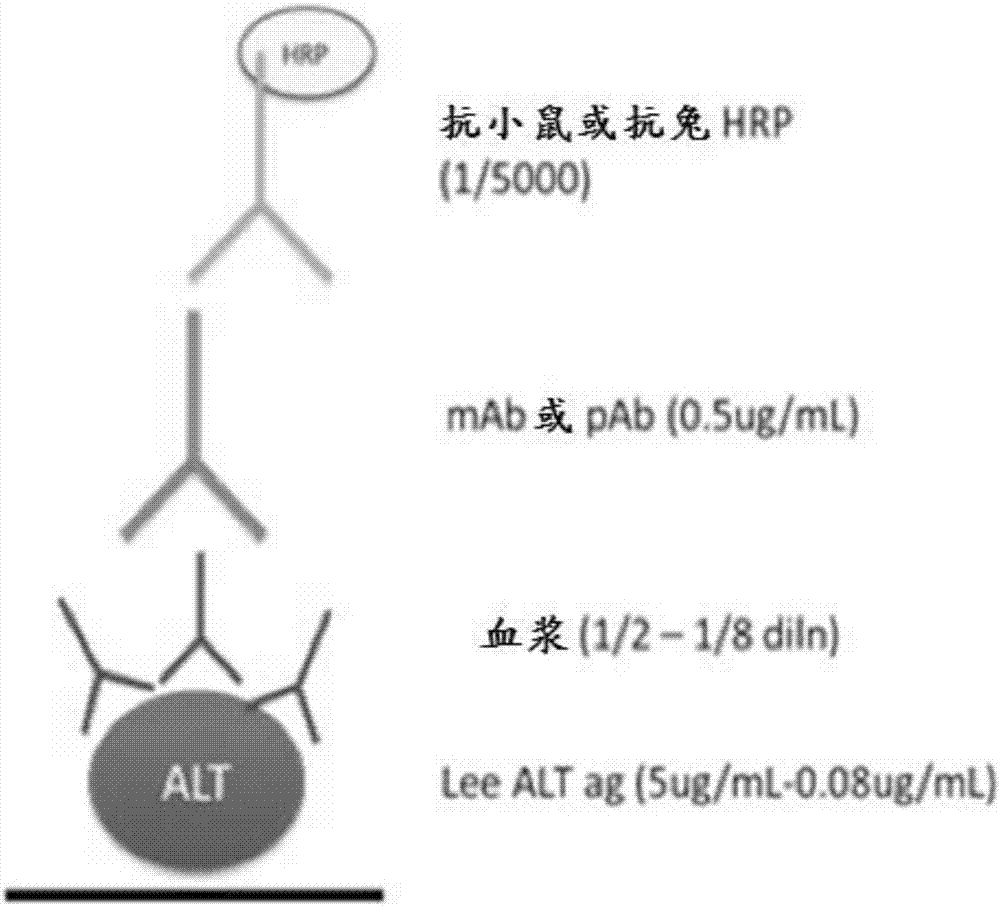
[0139] After purification of specific anti-ALT antibodies from total rabbit IgG by antigen affinity chromatography, rabbit anti-ALT was used to capture ALT in human plasma, and biotin-labeled rabbit anti-ALT and horseradish peroxidase-labeled chains An ELISA was established for the detection of captured ALT by mycovidin.
[0140] like Figure 5 As shown, this ELISA is not adversely affected by the presence of human serum / plasma, making it suitable for analytical determination of ALT mass concentrations in human clinical specimens. Image 6 A strategy for converting the tested ELISA format into a colloidal gold detection method suitable for lateral flow immunochromatography is described.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com