Method for detecting residual erythromycin in bacterial residue
A detection method, the technology of erythromycin, is applied in the detection field of erythromycin residual potency in bacterial residue, which can solve the problems of accurate detection of erythromycin residue in bacterial residue, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing influence and improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
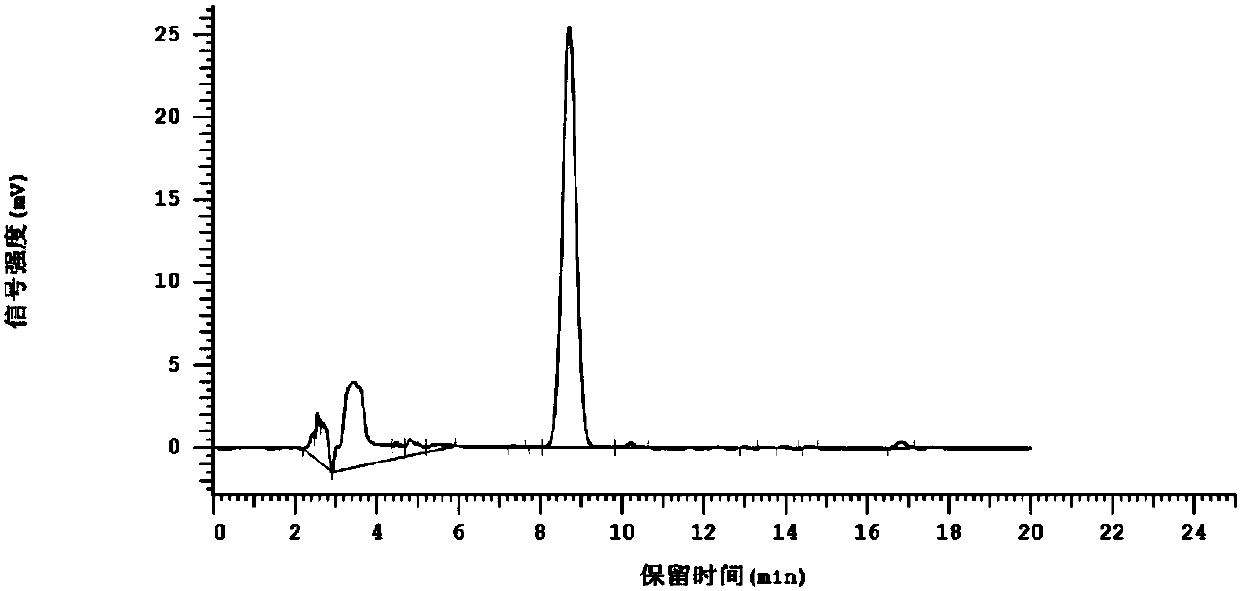
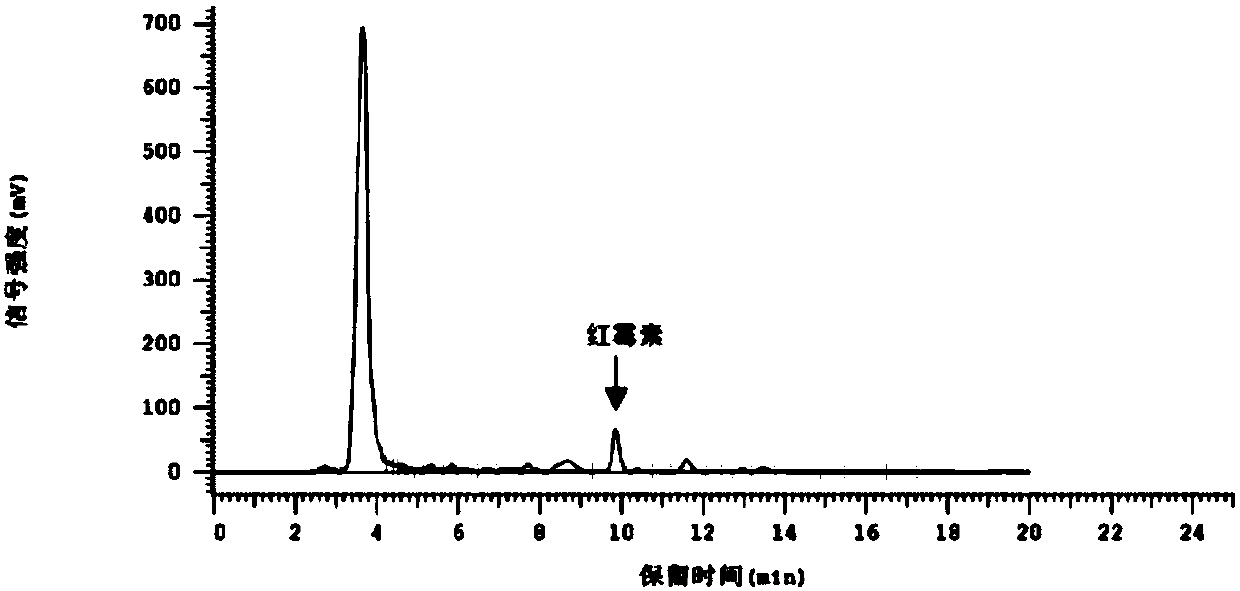
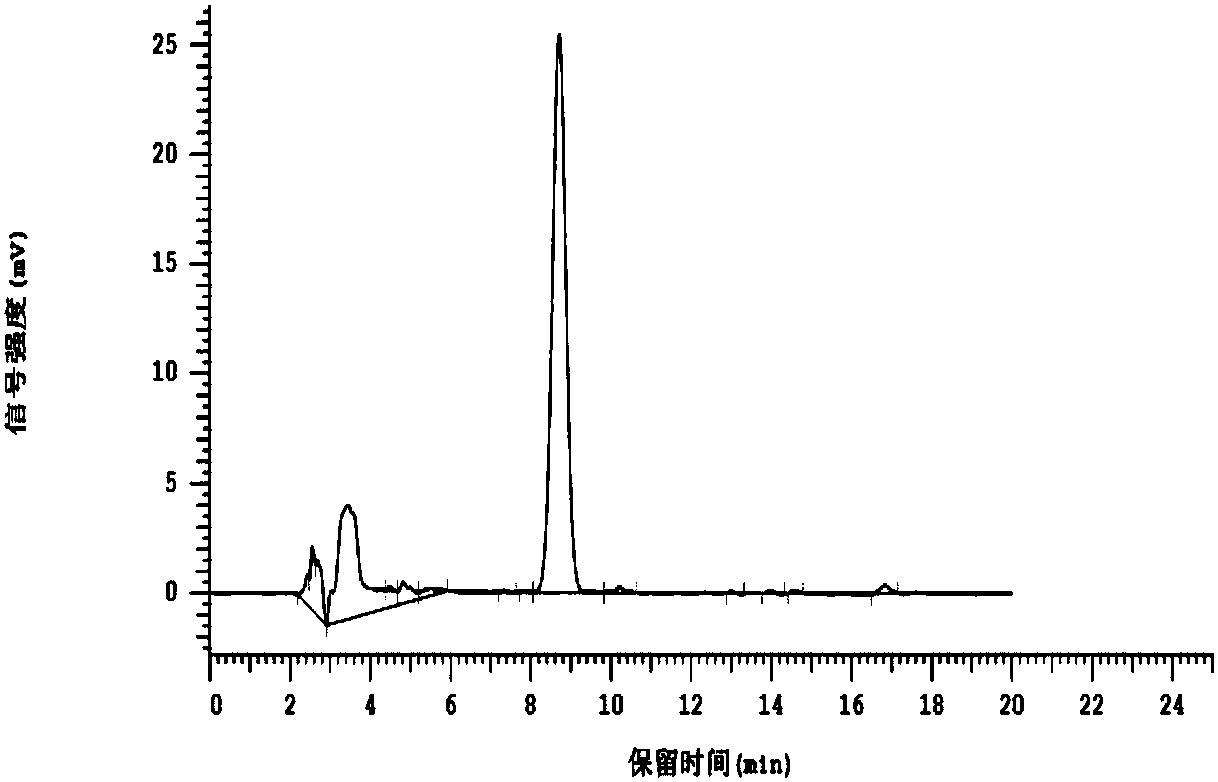
[0027] Specific embodiment one: the detection method of erythromycin residue in a kind of bacterial residue of the present embodiment, it is carried out according to the following steps:
[0028] 1. Sample preparation for the test product:
[0029] 1) Weigh the bacterium residue containing erythromycin, add extractant acetonitrile-Tris-CaCl 2 solution, vortexed for 45-60s, then assisted extraction in ultrasound for 20-30min, then centrifuged at 3500-4000rpm for 5-10min, took the supernatant, and collected the precipitate;
[0030] 2) Add extractant acetonitrile-Tris-CaCl to the precipitate collected in step 1) 2 solution, vortexed for 45-60s, then assisted extraction in ultrasound for 20-30min, then centrifuged at 3500-4000rpm for 5-10min, and took the supernatant;
[0031] 3) Combine the supernatants of step 1) and step 2), and put them in a water bath at 35°C for rotary evaporation to one-fifth of the volume of the supernatant to obtain an inorganic phase;
[0032] 4) Add...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0041] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the pH of the dipotassium hydrogen phosphate solution is 8-10. Others are the same as the specific embodiment one.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0042] Embodiment 3: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in that: the residual amount of erythromycin in the fungus residue is 500-1000 mg / kg. Others are the same as the specific embodiment one.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com