New mechanism of anti-alcoholic hepatic injury by wolfberry red element and application of hepatoprotective products
A technology of alcoholic liver injury and lycium ruberin, which is applied in the fields of medicine, special medical food, and health food, can solve the problems of insignificant detoxification and liver protection, long course of disease, and many side effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
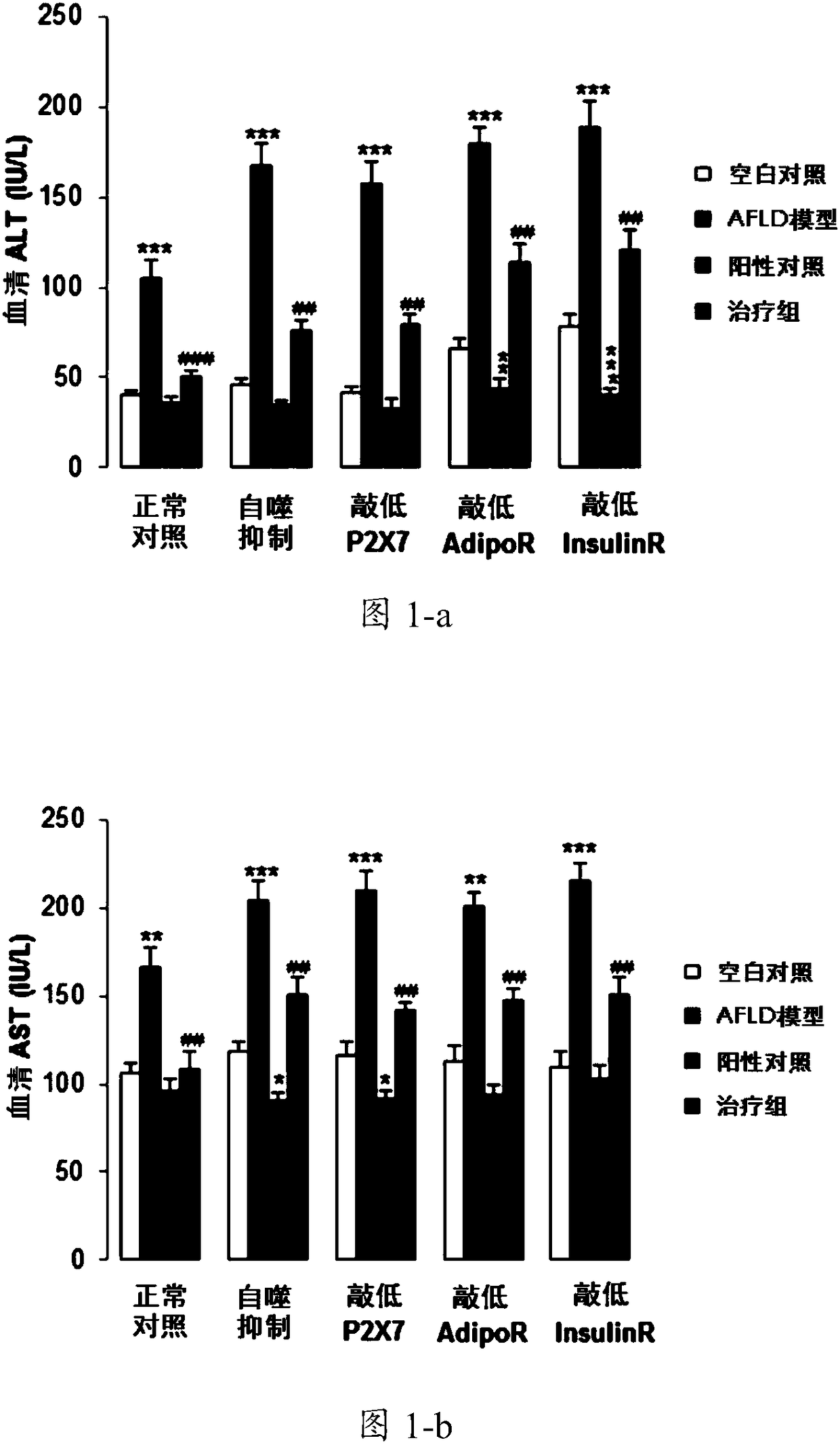
[0068] Example 1 The protective effect of Lycium barbarum on rat AFLD model
[0069] 60 rats were randomly selected and divided into 4 groups. They were blank control group, AFLD model group, positive control group and treatment group.
[0070] For the AFLD model group and the treatment group, the model of alcoholic liver injury in rats was established by intragastric administration of alcohol. The concentration of 1.25% alcohol was stimulated on the first day, the concentration was increased to 1.67% on the second day, and the concentration was increased on the third and fourth days. to 2.5%, then give 5% alcohol by gavage until 4 weeks. The blank control group and the positive control group used dextrin or maltose instead of alcohol to ensure that the two groups of rats consumed the same amount of calories.
[0071] After 14 days of alcohol gavage, the positive control group and the treatment group were given 5mg / kg wolfberry red element (dissolved in PBS containing 5% Twe...
Embodiment 2
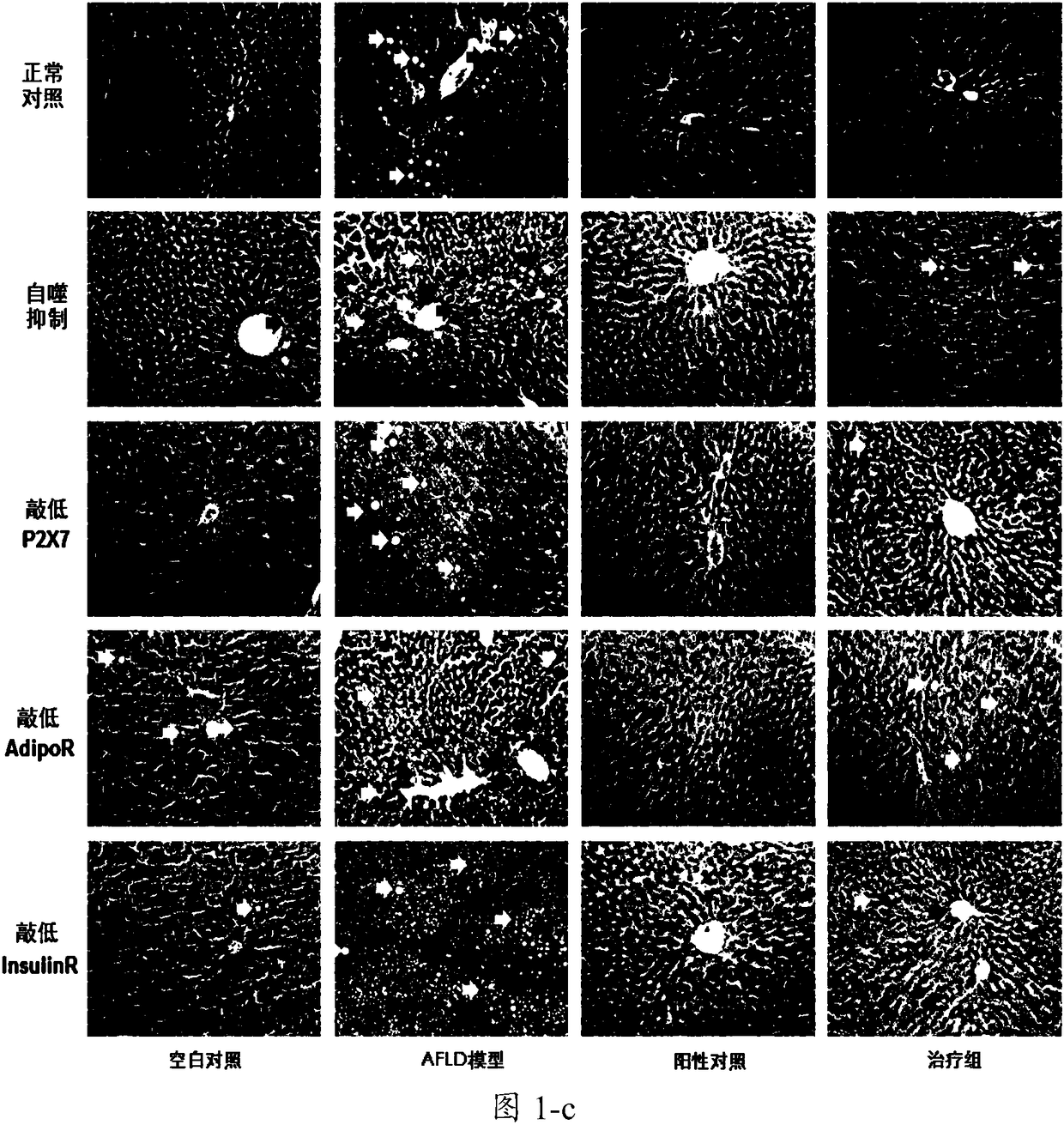
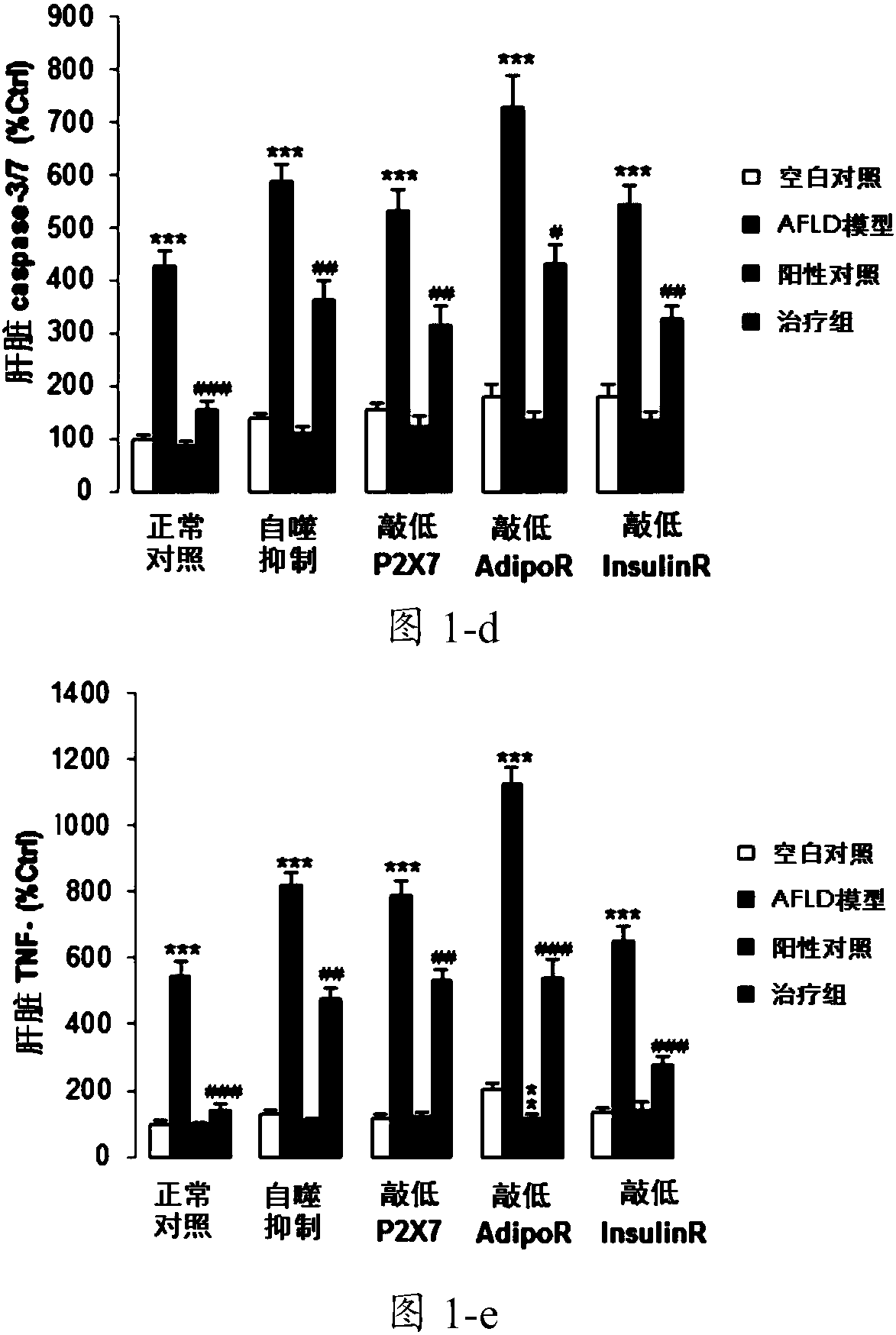
[0079] Example 2 The protective effect of Lycium barbarum on autophagy inhibition or receptor knockdown rats
[0080] 1. Models are grouped as shown in Table 2, with 15 animals in each group.
[0081] Table 2: Grouping processing methods
[0082]
[0083] Knockdown of receptors:
[0084] For mice with liver-specific knockdown of P2X7 receptor, Adiponectin receptor 1 and insulin receptor, 1 × 10 12 Genomic copies of AAV8 were coated with respective shRNAs to knockdown the expression of target genes in the liver. Sixty knockdown rats were constructed for each receptor. For the group of rats whose systemic "autophagy" was inhibited, Chloroquine (CQ, chloroquine) (60mg / kg) was intraperitoneally injected on the first day of AFLD modeling. 60 autophagy inhibited rats were constructed.
[0085] Construction of the AFLD model:
[0086] They were blank control group, AFLD model group, positive control group and treatment group. For the AFLD model group and the treatment group...
Embodiment 3
[0097] Rat normal liver cell line BRL-3A (purchased from ATCC, USA) was used and divided into 6 groups. Respectively, blank control group, alcohol treatment group, alcohol + wolfberry red pigment group, inhibitor control group, inhibitor + alcohol group, alcohol + inhibitor + wolfberry red pigment group.
[0098] Among them, the inhibitor group was divided into four groups, which were given respectively:
[0099] Autophagy inhibitor 3-MA (purchased from Sigma, USA),
[0100] P2X7 receptor-specific siRNA (purchased from Sigma, USA),
[0101] Adiponectin receptor 1-specific siRNA (purchased from Sigma, USA);
[0102] Insulin receptor-specific siRNA (purchased from Sigma, USA).
[0103] When the BRL-3A cells were cultured to a density of 60%, inhibitors were firstly added to the corresponding groups at concentrations of 3-MA (10 mM) and three siRNAs (both 100 nM). After 12 hours, add 250 nM alcohol and / or 1 μM Lycirubin and treat for 24 hours. Then, the cell viability was dete...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com