Environment-friendly seawater pond culture method for portunus trituberculatus and stichopus japonicus
An environment-friendly technology of portunus trituberculatus and sea cucumber, which is applied in the field of environment-friendly seawater pond cultivation of portunus trituberculatus and japonicus, can solve the problems of high temperature reduction, production of japonicus, and many harmful organisms in sea cucumber cultivation, so as to expand the breeding area and improve the quality of ponds. Utilization rate, effect of improving breeding efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
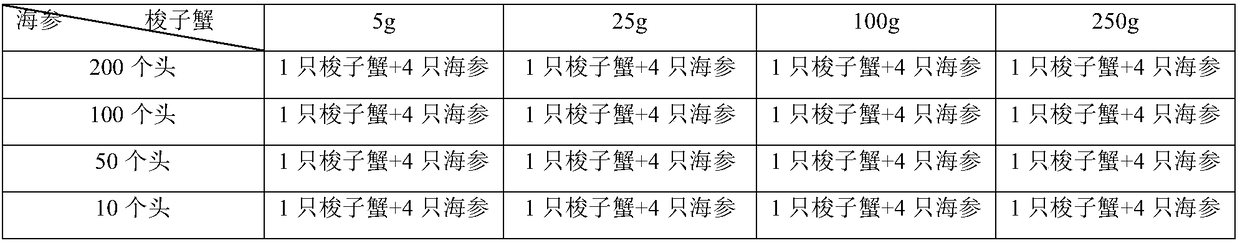
[0016] Polyculture experiment of portunus trituberculatus japonicus: select 4 specifications of sea cucumbers, 200 heads, 100 heads, 50 heads, and 10 heads; -Mixed breeding of different specifications of "Japonicus japonicus" (Table 1), 6 groups were established for each combination: 3 groups were fed, 3 groups were not fed, and each group was put into a white finishing box (580*420*310mm); 168h. The results showed that: during the breeding period, sea cucumbers grew normally without dormancy; Portunus trituberculatus did not ingest or harm sea cucumbers under feeding or starvation conditions; the misconception that "Portunus trituberculatus is the enemy of sea cucumbers" was eliminated.
[0017] Table 1 "portunus-stichopus" polyculture experiment combination
[0018]
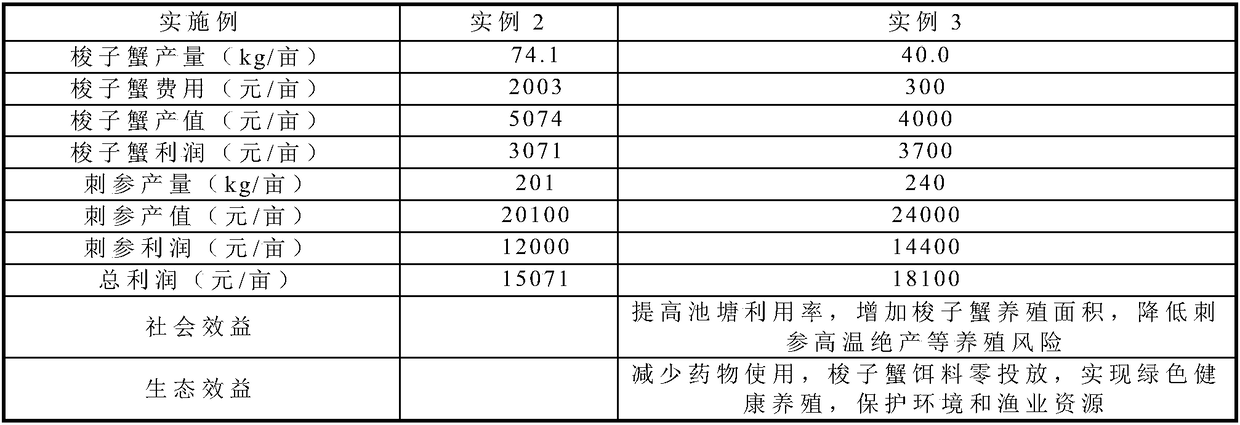
Embodiment 2
[0020] Farming according to conventional farming methods
[0021] (1) Breeding of Portunus trituberculatus
[0022] In this example, the second-stage young crabs of the new species of portunus trituberculatus "Huangxuan No. 1" with complete appendages, smooth body surface, and strong health and vitality were selected; at the beginning of May, seedlings were put in at a density of 2,000 tails per mu according to the area of the breeding pond. Species; feed Artemia adults in the early stage, and after stage VI juvenile crabs, feed blue clams, and the feeding amount is 8-15% of body weight; management is the same as conventional methods. After the mating is over, the male crabs are on the market, and the female crabs continue to feed. The bait is mainly fresh and live miscellaneous fish. In early November, the female crabs are caught and put on the market.
[0023] (2) Sea cucumber farming
[0024] At the beginning of March, tidy up the pond and lay the attachment base of se...
Embodiment 3
[0026] Utilize technical scheme of the present invention to carry out cultivation
[0027] A kind of Portunus trituberculatus-stichopus environmentally friendly culture method, it comprises the following steps:
[0028] (1) Cultivation of Portunus trituberculatus juvenile crabs: select Portunus trituberculatus "Huangxuan No. 1" stage II juvenile crabs cultivated in factory: complete appendages, smooth body surface, strong health and vitality; then cultivate to stage VI in outdoor cement pools Juvenile crabs: Strict disinfection of seawater and bait.
[0029] (2) Portunus trituberculatus-Apostichopus polyculture: At the beginning of March, tidy up the pond and lay the attachment base of Apostichopus japonicus; in early April, according to the area of the pond, put 15 heads / catties of Apostichopus japonicus seedlings at a rate of 240 catties per mu, and feed them normally ; At the beginning of May, according to the biomass of sea cucumber predators in the pond, according to 20...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com