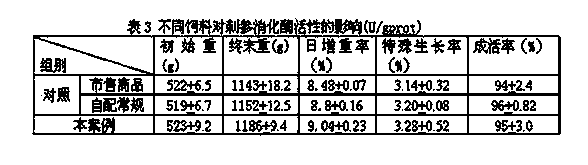
Patents
Literature
42 results about "Polistes japonicus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polistes japonicus is a eusocial paper wasp found in Japan. It was first described by Henri Louis Frédéric de Saussure in 1858. It is closely related to Polistes formosanus. This species lives in small colonies with few workers and a foundress queen. Nests of these wasps are sometimes used as a traditional medicine in Korea, China, and Japan.
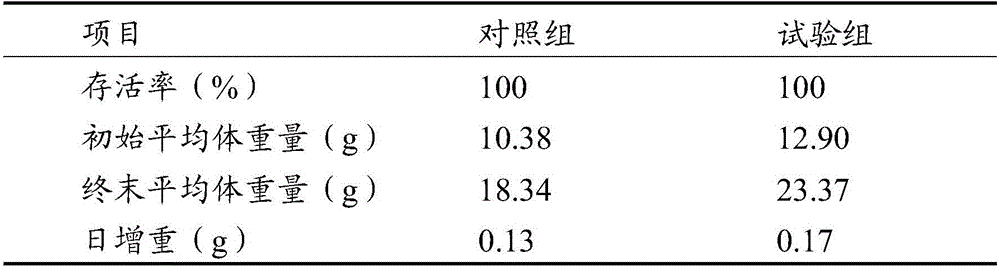
Stichopus japonicus seedling large-scale ecological culture method utilizing outdoor net cages
ActiveCN103026992AReduce cultivation costLow costClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaRhodotorulaEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a stichopus japonicus seedling large-scale ecological culture method utilizing outdoor net cages. The method comprises the following steps that 1, the parent cucumber egg taking is adopted for incubation in a seedling raising workshop, and the breeding collection is carried out when seedlings grow to the early ear larva stage; 2, net cages are arranged in an offshore haven bay or a sea cucumber pond, and 200-to-300-mesh bolting-silk nettings are selected in the net cages; 3, collected early ear larvae are uniformly fed into the net cages; 4, the manual supplementary feeding of rhodotorula benthica is adopted; 5, when the early ear larvae grow to the big ear larva stage, substrata are hung in the net cages, and in addition, the manual supplementary feeding of rhodotorula benthica stops; and 6, the cucumber is raised to the young cucumber stage, the bolting-silk nettings are replaced into 60-80-mesh polyethylene nettings, and the cucumber is continuously raised. The method has the advantages that the offshore or pond net cage culture is carried out from the stichopus japonicus larva culture, so the goals of reducing the cost, improving the survival rate, improving the economic benefit and the like are reached.
Owner:大连棒棰岛海参发展有限公司
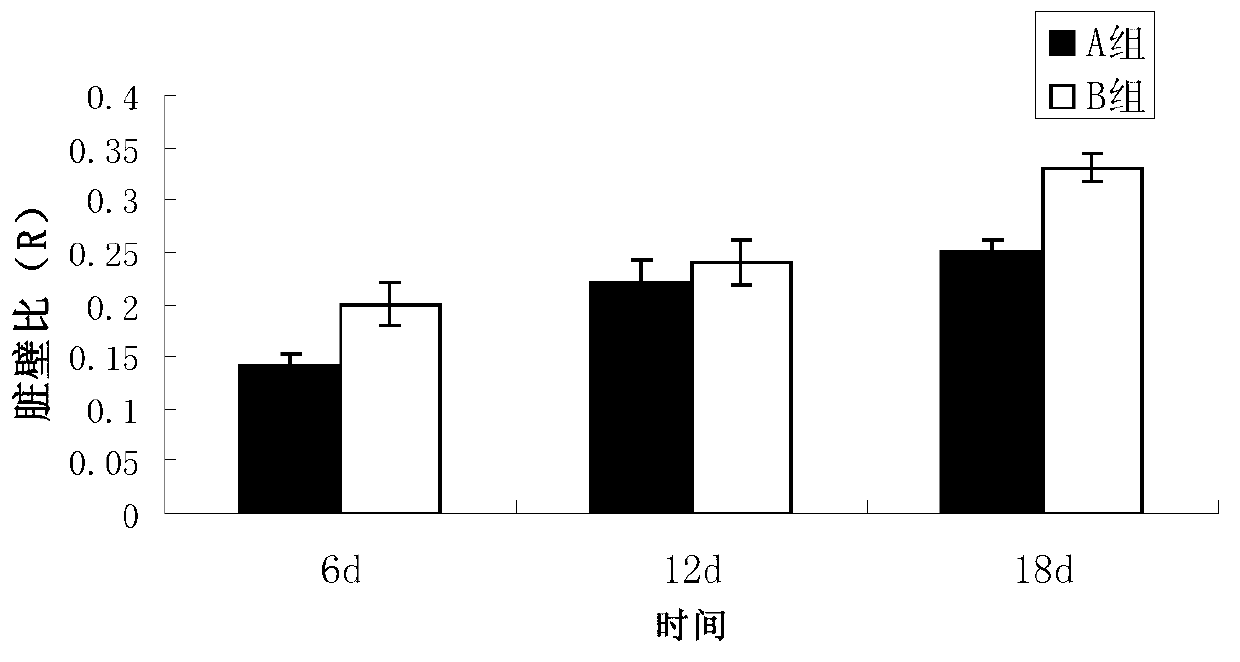
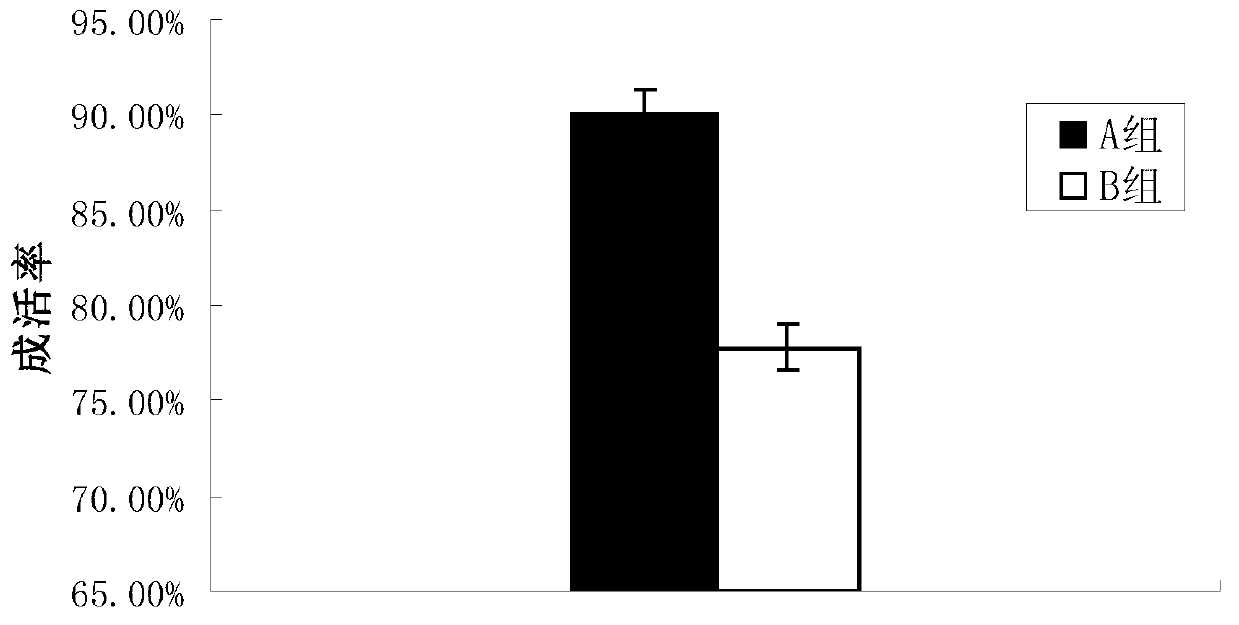
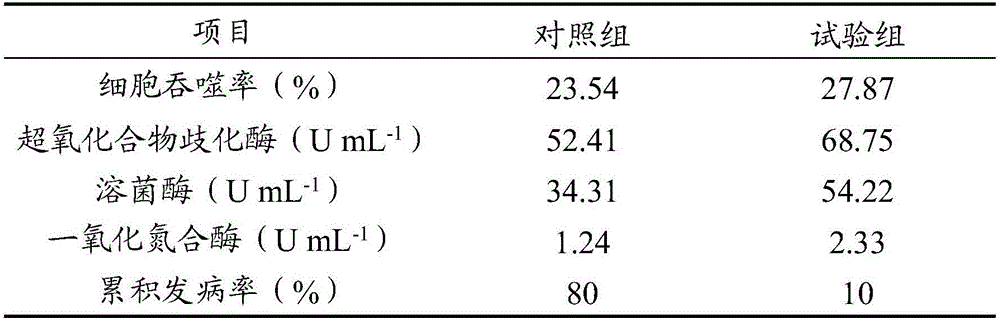
Chinese herbal medicine compound bait for improving growing power, immunity and disease resistance of stichopus japonicus
InactiveCN102972660ARich in nutritional valueEasy feedingAnimal feeding stuffChemical oxygen demandVegetable Proteins
The invention relates to a Chinese herbal medicine compound bait, as well as a preparation method and application of the Chinese herbal medicine compound bait. The Chinese herbal medicine compound bait comprises the following Chinese herbal medicine components by weight percent: 20-30% of radix pseudostellariae, 5-10% of cordyceps sinensis, 10-15% of lycium chinense, 10-15% of clove, 10-15% of honeysuckle, 10-15% of radix bupleuri, 5-10% of liquorice, 5-10% of radix astragali, 1-5% of poria cocos and 1-5% of borneol; and the Chinese herbal medicine compound bait comprises the following basic bait components by weight percent: 30-35% of sea mud, 10-15% of kelp meal, 4-6% of shell powder, 10-15% of sargassum thunbergii powder, 0.5-1% of spiral seaweed, 3-5% of fish meal, 3-5% of vegetable protein, 1-3% of shrimp meal, 2-3% of scallop skirt, 0.6-0.8% of yeast tablets, 2-2.2% of composite mineral salt and 1.8-2% of multivitamin. The Chinese herbal medicine components are mixed into the basic bait components according to the ratio of 2-5%, and the mixture has the particle size of 250-300 meshes. The Chinese herbal medicine compound bait provided by the invention is capable of obviously increasing the weight gain rate and survival rate of stichopus japonicus, reducing the splanchnic ratio, and improving the immunity of the stichopus japonicus; and the Chinese herbal medicine compound bait is free from toxic and side effects, can be used for remarkably improving the 'skin ulceration syndrome' resistance of the stichopus japonicus and has the advantages of reducing the food coefficient as well as NH3-N content and chemical oxygen demand (COD) content in aquaculture water, and the like, thus having good guiding significance for increasing the yield of stichopus japonicus aquaculture and the prevention and treatment of diseases.
Owner:刘宏生
Preparation method of stichopus japonicus microorganism degumming kelp fermented feed
The invention discloses a preparation method of a stichopus japonicus microorganism degumming kelp fermented feed. The preparation method comprises the steps: adding microecologics capable of degrading sodium alginate in kelp in a basal feed with the kelp as a main raw material and fermenting, wherein the basal feed comprises the following components in percent by weight: 45-55 percent of kelp meal, 5-15 percent of fish meal, 25-35 percent of sea mud, 5-10 percent of shell powder and 1-5 percent of decavitamin and mineral substances, and the amount of the microecologics is 1-5 percent of the weight of the basal feed. According to the feed disclosed by the invention, the digestibility and utilization rate of stichopus japonicus to the kelp can be remarkably increased, the nutrition and energy level required by the growth of the stichopus japonicus are met, the problem of deficiency of sargassum thunbergii resources of an excellent bait for the stichopus japonicus is effectively solved; and the feed has a raw material value-added function, and is low in cost. Under a better ecological condition, the feed is capable of reducing the damage of the residual bait to a culturing water body, promoting the immunity of the stichopus japonicus to a certain extent, and preventing antibiotics from being used.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method of cultivating fry of Apostichopus japonicus by floating cages in ponds
InactiveCN103518658AImprove survival rateIncrease productionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWater qualityFishery
A method of cultivating fry of Apostichopus japonicus by floating cages in ponds includes: 1, producing and placing cages, and producing floating cages; 2, stocking fry of Apostichopus japonicus reasonably; 3, controlling water quality reasonably; 4, managing cultivation of the fry of Apostichopus japonicus reasonably; 5, adjusting cage level reasonably. The method has the advantages that survival rate, yield and fry quality of the fry of Apostichopus japonicus are increased, the method has good effect and is convenient to popularize, the floating cages can sink to proper levels in hot periods of summer and cold periods of winter so that water temperature and water quality are maintained, and growing period of cage-cultivated fry can also be prolonged.
Owner:JINZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Ocytocic for inducing stichopus japonicus to lay eggs in vivo
InactiveCN101987196AIncrease productionReduce cultivation costPeptide/protein ingredientsSexual disorderIn vivoSeawater
The invention discloses an ocytocic for inducing stichopus japonicus to lay eggs in vivo, which is prepared by the following steps of: dissolving NGLWY amide in ultrapure water to obtain 1mu mol / L mother liquid, pouring the mother liquid into 0.5mol / L seawater solution of KCl to obtain the ocytocic of which the NGLWY amide concentration is 1nmoll / L. The NGLWY amide and KCl, which are rationally blended and interacted, directly act on the gonad of the stichopus japonicus to induce the oocytes of the stichopus japonicus to be mature and remove follicle, so that all individuals are basically ovulate at one time of parturition, and the parturition ratio is as high as over 90 percent. The used amount of the ocytocic can guarantee that the parent stichopus japonicus does not produce undesired stuff, that the ovulation rate is greatly improved, that average egg laying amount is increased to 4 million which accounts for over 70 percent of the total brood amount, so that the use efficiency of the parent stichopus japonicus is greatly improved, the problem that the parent stichopus japonicus produces the undesired stuff caused by a large amount of KCl injected simply is solved, and the problem of small egg laying amount caused by simply using the NGLWY amid is solved.
Owner:DALIAN FISHERIES UNIVERSITY
Molecular marker and method for identifying excellent stichopus japonicus selenka variety
InactiveCN102912015AShorten breeding timeImprove farming efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTotal rnaCytochrome oxidase c
The invention discloses a molecular marker and method for quickly identifying the excellent stichopus japonicus selenka variety. The primers of the molecular marker are the primers of the amplified ADP glycosylation factor, amplified arginine kinase, amplified cytochrome oxidase c subunit, amplified heat shock protein 70 and amplified primer actin. The expressing genes of the molecular marker are the gene fragments of the ADP glycosylation factor, arginine kinase, cytochrome oxidase c subunit, heat shock protein 70 and actin. The method comprises the following steps: extracting the total RNA, synthesizig the cDNA, and amplifying and identifying by PCR (polymerase chain reaction). The molecular marker and the method can be used for identifying quickly, easily, specifically and efficiently. If the expression level of at least three of the gene fragments is 2.0, the stichopus japonicus selenka is the excellent variety which can grow up quickly. Therefore, the stichopus japonicus selenka which can grow up quickly can be screened out and cultured as the excellent variety, the culturing time of the stichopus japonicus selenka can be shortened, and the culturing benefit of the stichopus japonicus selenka can be improved.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
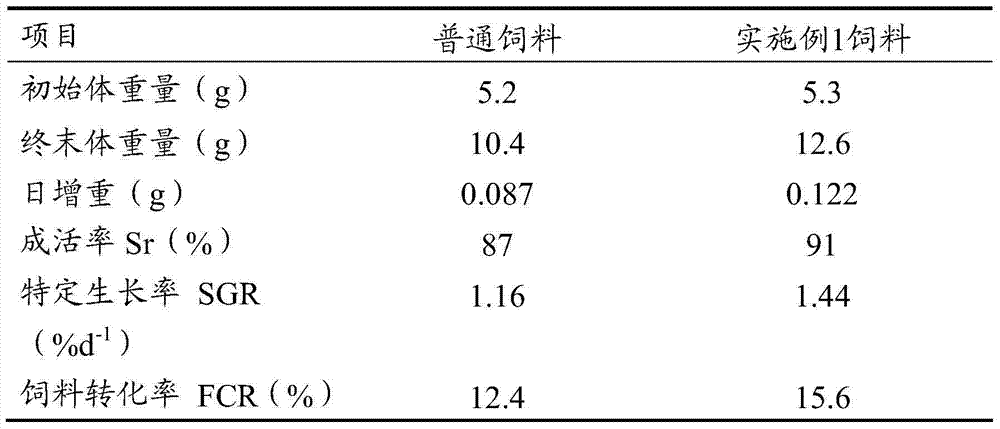
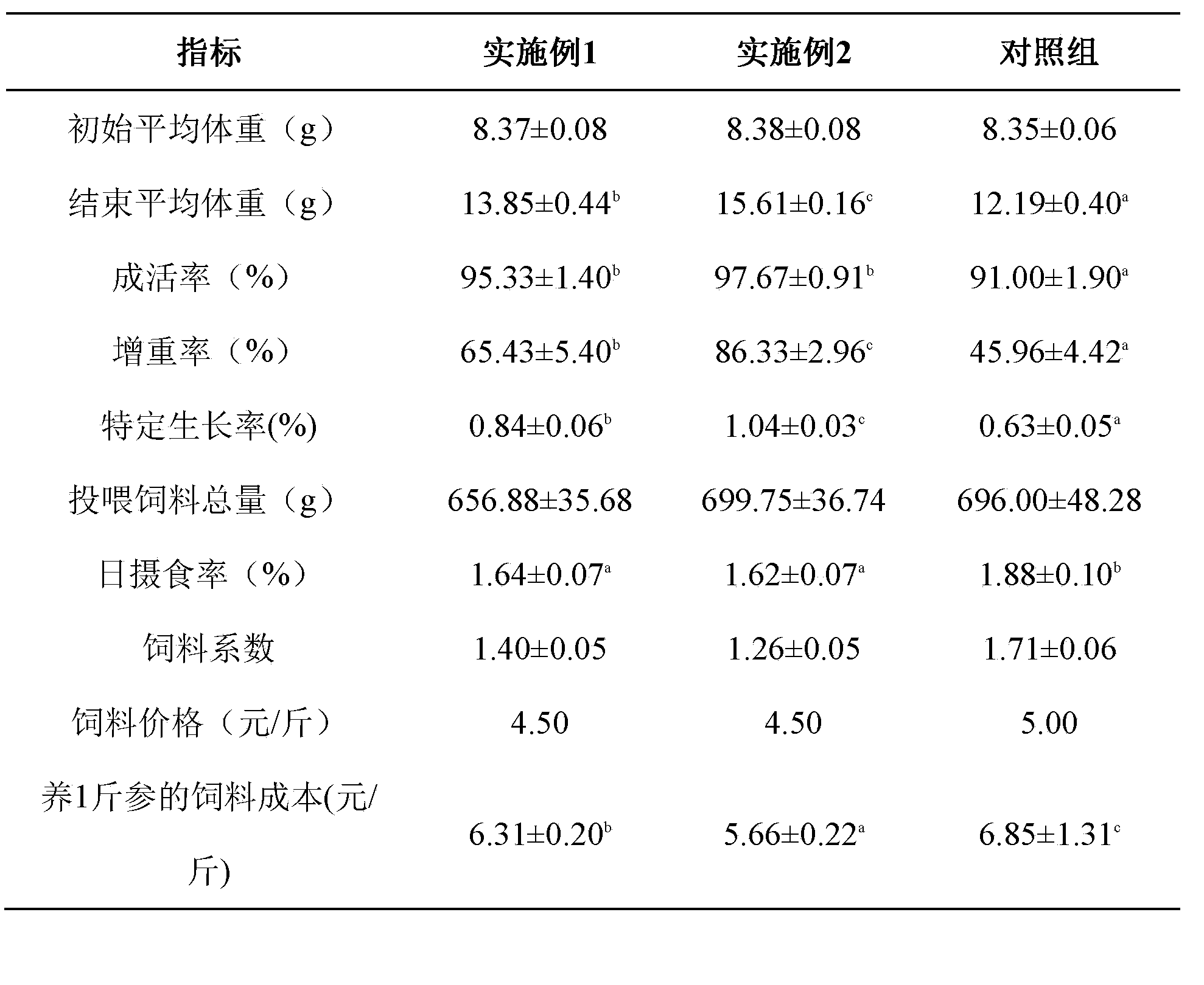
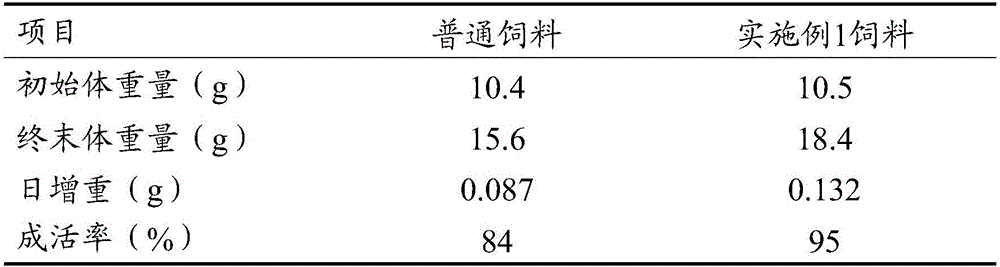
Full-balanced ultrafine pellet feed for stichopus japonicus larva
ActiveCN103392933AExcellent survival rate or weight gain rateLow costAnimal feeding stuffAlgaeVitamin
The invention discloses a full-balanced ultrafine pellet feed for stichopus japonicus larva. The full-balanced ultrafine pellet feed comprises following ingredients, by weight, 30 to 40% of protein, 2 to 15% of starch, 3 to 7% of grease, 1 to 3% of composite vitamin, 1 to 5% of composite mineral, 1 to 3% of bacteria, 35 to 50% of algae and 1 to 6% of Chinese herbal medicine. According to the full-balanced ultrafine pellet feed, feeding characteristics of stichopus japonicus larva under natural conditions are simulated, the requirements of stichopus japonicus larva for key nutrition ingredients are taken into consideration, so that comprehensive and balanced ratio of nutrition ingredients is designed for the growth of stichopus japonicus larva. It is shown by production test of the full-balanced ultrafine pellet feed that, survival rate and weight gain rate of the application of the full-balanced ultrafine pellet feed are both higher than that of the application of existing stichopus japonicus mixed feed of common brands.
Owner:QINGDAO QIHAO NUTRITION TECH
Sea cucumber spring and summer culture method
InactiveCN104170782ASolving the Summer ProblemEnsure healthy and sustainable developmentClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaEcological environmentWater quality
The invention discloses a sea cucumber spring and summer culture method. The sea cucumber spring and summer culture method aims at avoiding the aestivation risk of sea cucumbers and greatly improving the aestivation safety of the sea cucumbers through improvement of four aspects comprising eight steps. The four aspects comprise performing ecological environment regulation on a culture pond; adopting a relay type cultivation mode; constructing the step type pond; cultivating seedlings in batches. According to the sea cucumber spring and summer culture method, the related technology research is performed due to main restricting factors that the water temperature is high, the salinity is low, the water quality is poor, the oxygen deficiency of the bottom is easy to cause, and the like caused by the summer climate according to the area self-characteristics of the stichopus pond cultivation of the yellow river delta, the problem of the aestivation of the stichopus pond cultivation of the yellow river delta is majorly solved, the systematic technical support is provided for the aestivation of the sea cucumbers, and accordingly the healthy sustainable development of the stichopus pond cultivation industry of the yellow river delta is ensured.
Owner:SHANDONG HUACHUN FISHERIES CO LTD +1
Environment-friendly seawater pond culture method for portunus trituberculatus and stichopus japonicus
InactiveCN108077140ATake advantage ofCut off the transmission routeWater/sewage treatment by irradiationClimate change adaptationMarine cultureMixed culture
The invention relates to an environment-friendly seawater pond culture method for portunus trituberculatus and stichopus japonicus and belongs to the technical field of marine culture. The method includes: in early March, preparing a pond, and laying a stichopus japonicus adhering base; in early April, adding 240 jin of 15 / jin stichopus japonicus seeds to each mu of the pond according to pond area, and normally feeding; in early May, adding 200-400 Huangxuan No. 1 stage-VI female portunus trituberculatus to each mu of the pond according to the number of the enemies of the stichopus japonicus in the pond, wherein the portunus trituberculatus is not fed during culture; in the first ten days of November, harvesting the portunus trituberculatus and the stichopus japonicus for selling. Experiments of the method prove that the portunus trituberculatus can be added in the whole culture process of the stichopus japonicus to perform mixed culture, the portunus trituberculatus adding is not limited to an estivation period, and the portunus trituberculatus does not prey on or damage the stichopus japonicus even if the portunus trituberculatus is not fed. The method has the advantages that theidea that technicians in the field takes the portunus trituberculatus as the culture enemy of the stichopus japonicus for a long time is changed, culture water is utilized sufficiently, and culture economic benefits are increased.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Preparation method of stichopus japonicas bait
InactiveCN103918927ASimple production processMedium simpleFood processingAnimal feeding stuffMicroorganismSargassum thunbergii
The invention relates to a preparation method of a stichopus japonicas bait, aiming at solving the technical problem that the existing trepang feed is high in cost and unstable in effect. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding water to a mixture of vinasse, kelp residue, mixed microorganism bacterium liquid, kelp powder, sargassum thunbergii powder, gulfweed powder and shell powder and stirring to be uniform, performing solid fermentation for 2-6 days under the condition of the temperature of 20-35 DEG C, grinding, and adding sea mud to obtain the stichopus japonicas bait. The preparation method is used for the field of preparation of the stichopus japonicas bait.
Owner:WEIHAI GOLD FEED
Breeding method of high-temperature-resistant stichopus japonicus strain
ActiveCN106259067AMeet the characteristics of patienceImprove selection efficiencyClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaSexual maturityZoology
The invention discloses a breeding method of a high-temperature-resistant stichopus japonicus strain and belongs to the field of genetic breeding of aquatic products. Stichopus japonicus surviving after natural high temperature elimination in summer in different regions is selected as a parent, families are constructed through breeding after sexual maturity, heat shock at the temperature of 28 DEG C is performed at the auricularia stage of each family, 20% of families are reserved according to the survival rate and the malformation rate, the reserved families are mixed and bred until the average weight of individuals is larger than 50 g, high-temperature stress is performed at 32 DEG C to remove dead and damaged individuals, less than 25% of individuals are reserved and continuously bred until sexual maturity, heat shock selection and breeding of three generations are performed continuously in the same principle, and the new stichopus japonicus strain with the high-temperature-resistant character is obtained. The original parent of stichopus japonicus better conforms to the tolerance characteristic of the actual breeding environment; high-temperature domestication screening of the families in the larva period and high-temperature stress screening in the breeding period are performed, family breeding and group breeding are combined, and the selection efficiency is improved; breeding of three generations is performed continuously, the high-temperature-resistant character is stabilized, and the breeding method has good economic benefit and broad breeding prospect.
Owner:山东省海洋资源与环境研究院
Stereo mixed culture method for sea cucumber and abalone
InactiveCN104686400AReduce infectious diseasesPlay a cleaning roleClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaForeign matterFeces
The present invention relates to the technical field of aquaculture, specifically to a stereo mixed culture method for sea cucumber and abalone. The method comprises the following steps: clearing away foreign matters on an abalone culture container when the water temperature in a southern sea area falls to 19 to 21 DEG C in each fall, and disinfecting the container; putting sea cucumber fingerlings into the disinfected abalone culture container; and feeding feeds and carrying out mixed culture of the sea cucumber and the abalone. According to the invention, through the mixed culture of the cucumber and the abalone, self purification ability of the culture water is strengthened to the greatest extent, and environmental conditions of the aquaculture water are effectively improved; since the sea cucumber substantially feeds on residual feeds and manures produced by the abalone, pollution to water is lightened, propagation and diffusion of pathogens are reduced and infection of the abalone with diseases is reduced; and since the sea cucumber is bred through mixed culture, extra increase of culture cost is not needed, and high culture efficiency is obtained.
Owner:夏雪飞
Stichopus japonicas pond subsection type polyculture method capable of avoiding macroalga inundation
ActiveCN105494181AImprove the ecological environmentImprove water quality conditionsClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaRaft culturePolyculture
The invention discloses a stichopus japonicas pond subsection type polyculture method capable of avoiding macroalga inundation. The method comprises the following steps that young stichopus japonicas is put into a stichopus japonicas pond in a conventional mode every year; when the water temperature of the pond is at least 14 DEG C in spring every year, rabbitfish fry are put into the stichopus japonicas pond; when the water temperature is below 18 DEG C in autumn every year, young strongylocentrotus intermedius is put into the stichopus japonicas pond; the quantity of macroalga in the stichopus japonicas pond needs to be monitored in the culture process, and when the quantity of the macroalga is smaller than the feeding quantity of strongylocentrotus intermedius and rabbitfishes, macroalgae are fed; mature stichopus japonicas is fished and caught in spring and autumn every year; the rabbitfishes are fished and caught in autumn every year; before the water temperature rises to 23 DEG C in spring every year, the strongylocentrotus intermedius is fished and caught, and the strongylocentrotus intermedius of the specification smaller than the commercial specification is transferred to a sea area to continue to be subjected to raft culture.
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV +1
Preparation and application of synbiotics additive used for culturing of stichopus japonicus
InactiveCN106721654APromote growthPromote healthy growthAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsBacillus licheniformisSynbiotics
The invention provides preparation and application of synbiotics additive used for culturing of stichopus japonicus. The additive is composed of bacillus licheniformis, bacillus subtilis and plant lactic acid bacillus; prebiotics is composed of alginate oligosaccharide and inulin; other auxiliary ingredients comprise a thallus protective agent and a mineral substance carrier. The invention further provides a preparation method of the synbiotics additive. Probiotics liquid is taken, the prebiotics and the thallus protective agent are added, and the mixture is mixed with the mineral substance carrier; the prepared mixture is subjected to vacuum freeze-drying, and freeze-dried powder is prepared and is namely the synbiotics additive used for culturing of the stichopus japonicus. The invention further provides application of the prebiotics additive for culturing of stichopus japonicus. Probiotics and synbiotics are efficiently and scientifically compatible, and achieve a synergistic effect and the effect that 1+1>2; by the utilization of the synbiotics additive, the dual probiotic effects of the probiotics and prebiotics can be achieved at the same time, the growth performance and non-specific immunity response of the stichopus japonicus can be obviously improved, and the healthy growth of animals can be better promoted.
Owner:DALIAN SEM BIOLOGICAL ENG TECH
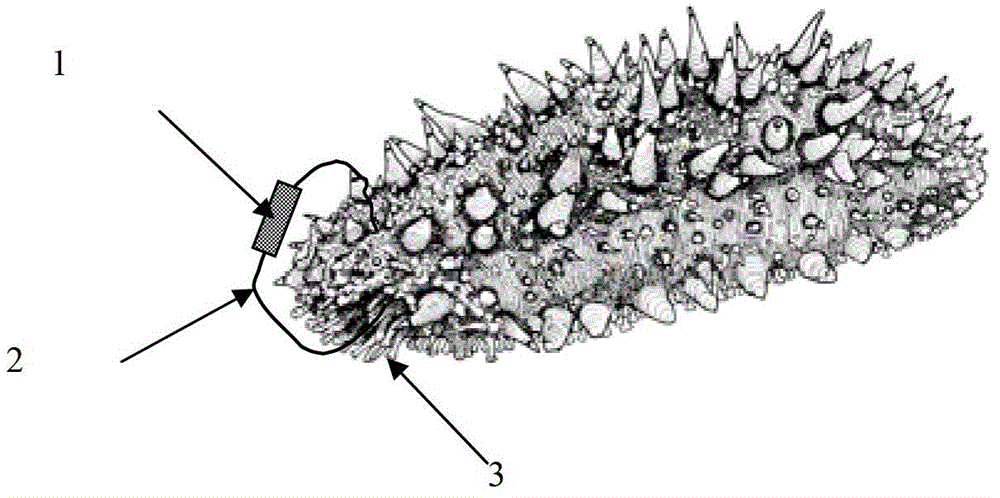
In-vitro long-acting labeling method applicable to stichopus japonicus
ActiveCN103141418ASolve the difficult problem of long-term in vitro labelingNormal feeding activityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaComputer scienceAquaculture
The invention relates to the technical field of aquaculture, in particular to an in-vitro long-acting labeling method applicable to stichopus japonicas. The method comprises the following steps: penetrating a labeling line from the mouth of the stichopus japonicas; after penetrating a lime ring, penetrating out of the body from the position above the head of the stichopus japonicas; fixing a tag capable of identifying the stichopus japonicas on the penetrated labeling line; and stably closing the labeling line to realize the in-vitro long-acting labeling of the stichopus japonicas. By adoption of the labeling method, the stichopus japonicas individual can maintain the in-vitro tag for more than 3 months, the normal activity of the stichopus japonicas individual is influenced hardly, and various field labeling release tests and other work which needs to accurately identify the stichopus japonicas individual after the stichopus japonicas individual is labeled can be further developed.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
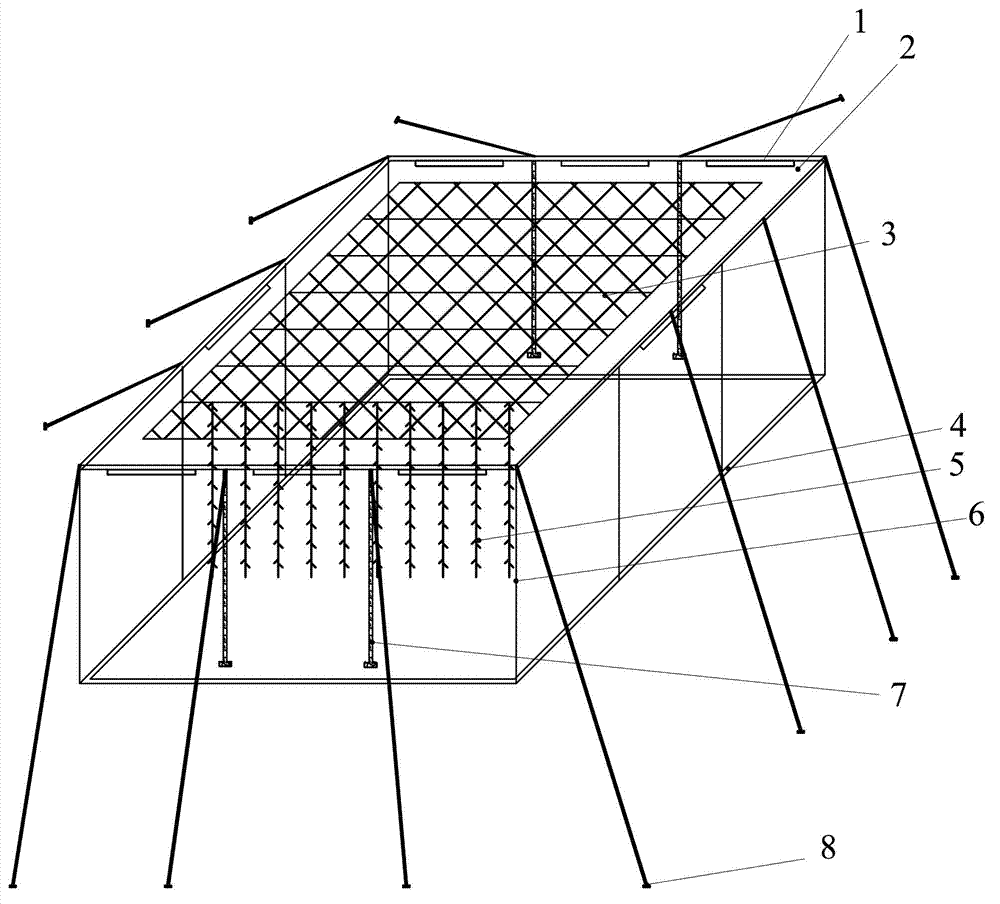
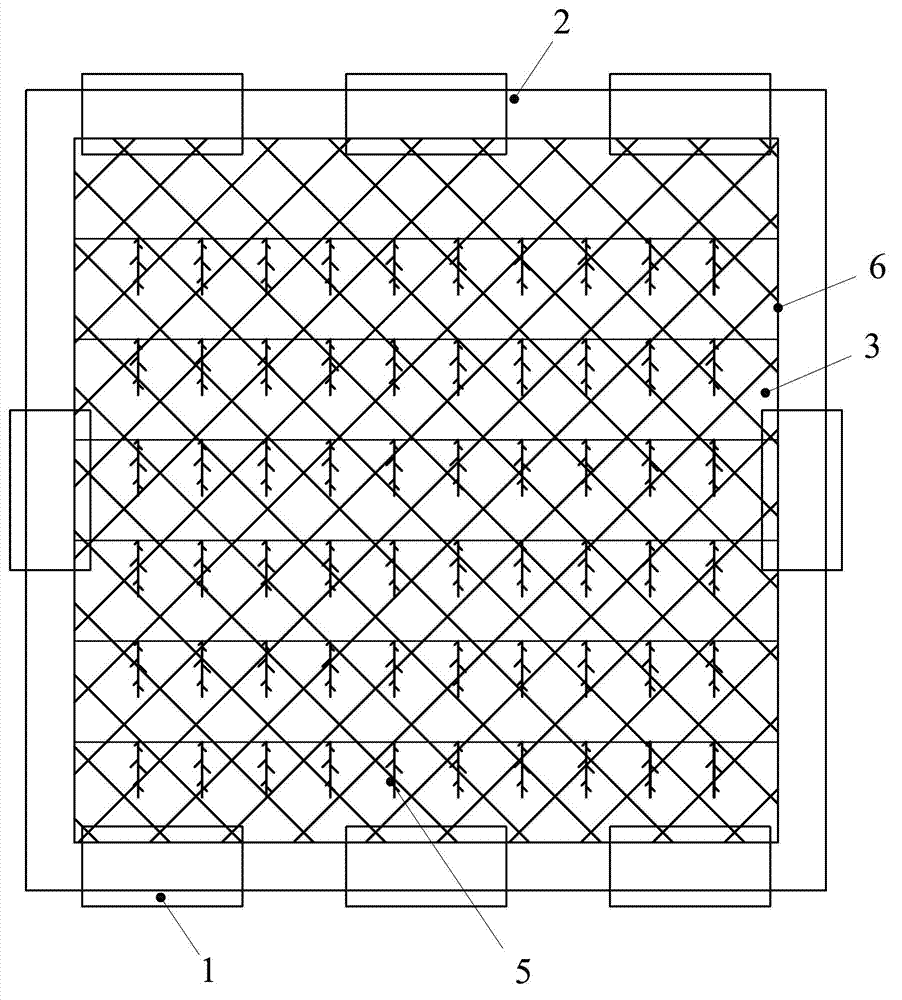
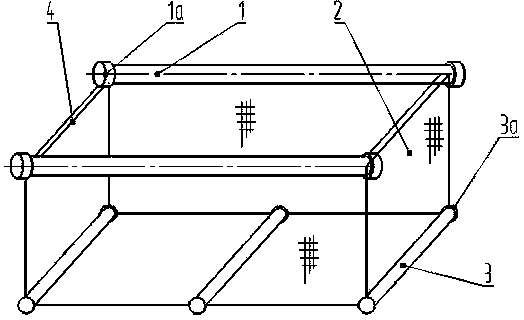
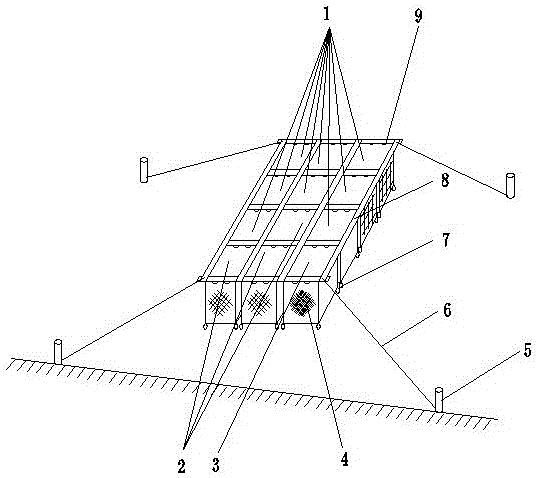
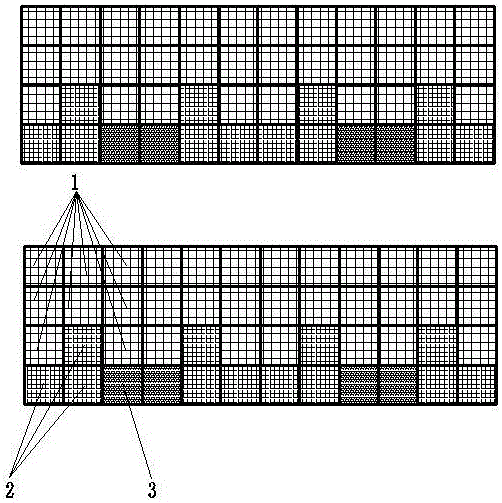
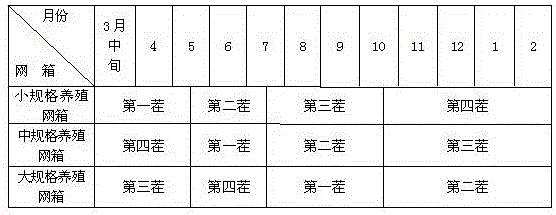
Shallow sea cage apostichopus japonicus recirculating aquacultural facility and aquacultural method
ActiveCN105660494ASafe sheltered habitatIncrease attachment spaceClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaShallow seaEngineering
The invention provides a shallow sea cage apostichopus japonicus recirculating aquacultural facility and an aquacultural method. The shallow sea cage apostichopus japonicus recirculating aquacultural facility comprises a plurality of cages. The shallow sea cage apostichopus japonicus recirculating aquacultural facility is characterized in that the plurality of cages comprise small, medium and large aquacultural cages which are respectively used for aquaculture of small, medium and large juvenile apostichopus japonicus, the small, medium and large aquacultural cages are connected in proportional allocation that quantity of the small aquacultural cages is lower than quantity of the medium aquacultural cages and the quantity of the medium aquacultural cages is lower than quantity of the large aquacultural cages to form aquacultural units, and the aquacultural units are connected and then are fixed under the sea through piling. In March, April and May every year, the small, medium and large juvenile apostichopus japonicus are put into the cages to be cultivated according to specific density, and cultivation in each stage can provide enough juvenile apostichopus japonicus for the next stage; and then the small juvenile apostichopus japonicus are continuously supplemented and put into the cages, and the process is repeated, so that ecological efficient continuous product is realized. Aqucultural facility utilization rate is greatly improved, production cost is greatly reduced, growth rate of the juvenile apostichopus japonicus is improved, survival rate of the juvenile apostichopus japonicus is greatly improved, operation management is convenient, and comprehensive benefits are obviously improved.
Owner:MARINE BIOLOGY INST OF SHANDONG PROVINCE
Full-balanced powder forage for adult stichopus japonicus
ActiveCN103392934AIncrease growth rateFast growthAnimal feeding stuffGreenhouse cultivationMultivitamin
The invention discloses a full-balanced powder forage for adult stichopus japonicas. The full-balanced powder forage comprises compounds of protein, starch, grease, composite vitamin, composite mineral, bacteria, algae and Chinese herbal medicine. The ratio of the compounds is designed based on physiological characteristics and nutritional requirements of adult stichopus japonicus; the ratio is scientific and reasonable, and meets growth requirements of stichopus japonicus; the powder forage is developed based on characteristics of greenhouse cultivation of stichopus japonicus; it is confirmed by feeding that absorptivity is high, and digestive efficiency is excellent. The Chinese herbal medicine and the bacteria are added specially, so that the full-balanced powder forage has significant effects on improvement of physical condition of adult stichopus japonicus, and morbidity in cultivation is low. Single-celled algae and macrophytic algae are added into the full-balanced powder forage according to feeding characteristics of stichopus japonicus, so that the full-balanced powder forage is popular with stichopus japonicus, and growth speed of stichopus japonicus fast.
Owner:QINGDAO QIHAO NUTRITION TECH
Preparation method of microbial kelp degummed fermented feed and application thereof in stichopus japonicus culture
InactiveCN106578732AImprove digestibilityIncrease profitAnimal feeding stuffWorking-up animal fodderMicroorganismMultivitamin
The invention discloses a preparation method of a microbial kelp degummed fermented feed and application thereof in stichopus japonicus culture. The method includes the step of adding a microecological preparation capable of degrading algin in kelp into a kelp based basic feed to perform fermentation. The basic feed is composed of the following components by mass percentage: 45-55% of kelp powder, 5-15% of fish meal, 25-35% of sea mud, 5-10% of shell powder, and 1-5% of compound vitamin and minerals. The dosage of the microecological preparation accounts for 1-5% of the mass of the basic feed. The feed provided by the invention can significantly enhance the digestibility and utilization of stichopus japonicus to kelp, meets the needs of stichopus japonicus growth for nutrition and energy level, effectively solves the high quality bait sargassum thunbergii resource shortage problem of stichopus japonicus, has raw material value adding function, and is low in cost. Under good ecological conditions, the feed provided by the invention can reduce the destruction of residual bait to aquaculture water, can promote stichopus japonicus immunity to certain degree, and avoids the use of antibiotics.
Owner:DALIAN SEM BIOLOGICAL ENG TECH
Breeding method of purple apostichopus japonicus
ActiveCN105613383AStrong selection purposeImprove efficiencyPisciculture and aquariaF1 generationPhenotypic trait
The invention provides a breeding method of purple apostichopus japonicus. The breeding method is characterized by collecting purely wild apostichopus japonicus individuals of which the back part and the abdomen part are totally purple, and transplanting the apostichopus japonicus individuals into a breeding pond for carrying out independent separation, temporary rearing and preserving; screening breeding base populations in the middle of May, and carrying out artificial spawning, hatching and breeding; when 30 percent of planktonic larvae develop to be doliolaria, feeding an adhering substrate, changing water and feeding fodder; recording the body color and the growth and development situation of the doliolaria at a fixed period, and screening and weeding out weak individuals; performing an overall breeding process in a purple environment, and strengthening the coloring of young purple apostichopus japonicus by feeding the fodder containing purple natural pigment components in an assisting manner; respectively carrying out selfing on bred F1-generation purple apostichopus japonicus and hybridization on the bred F1-generation purple apostichopus japonicus and preserved base populations, thus forming F2 filial generations, wherein a breeding technology and breeding conditions of the F2 filial generations are the same as those of F1 generations; carrying out three times of high-strength standard breeding, thus obtaining F3-generation new varieties of the purple apostichopus japonicus, wherein the selection and reservation rate is 90 percent or more, and no significant difference of the growing speed and the anti-capability is generated between the F3-generation new varieties of the purple apostichopus japonicus and original apostichopus japonicus.
Owner:MARINE BIOLOGY INST OF SHANDONG PROVINCE
Water changing method for culturing auricularia of stichopus japonicus
InactiveCN110476849AImprove labor productivityReduce manufacturing costPisciculture and aquariaDiseaseFeces
The invention relates to a water changing method for culturing auricularia of stichopus japonicus, and belongs to the technical field of artificial culturing and water changing methods of stichopus japonicus. The method comprises the following steps of 1), water changing in the earlier stage, wherein in the earlier stage, water is only added but not drained, specifically, water which accounts for1 / 3-1 / 2 of the volume of a culture pond 1 is added into the culture pond 1 on the day when the auricularia is put into the pond, and afterwards, water which accounts for 1 / 10 of the volume of the culture pond 1 is added into the culture pond 1 every day until the culture pond 1 is filled up; 2), water changing in the later stage, wherein after the culture pond 1 is filled up, water needs to be changed every day, before water changing, the auricularia needs to sufficiently float upwards at first, after the auricularia sufficiently floats upwards, bottom water with poor water quality is drainedfrom the bottom of the pond, meanwhile, residual feeds, feces, dead and inferior auricularia and other sundries settled at the bottom of the pond are discharged out of the pond, when the discharged water accounts for 1 / 5-1 / 3 of the volume of the culture pond or the upward-floating auricularia has the sign of diffusing, water draining is stopped, the culture pond is filled with new water until theculture pond is filled up, when 5-10% of the auricularia in the culture pond is metamorphosed into doliolarias, a substratum is put, and then water changing in the later stage is finished. The water changing method has the advantages that the water changing effect is good, the water changing efficiency is high, the labor intensity is lowered, the auricularia is prevented from being injured, crossinfection of diseases is prevented, run-off of the auricularia is reduced, and the culturing cost is lowered.
Owner:烟台市海洋经济研究院
Preparation method of stichopus japonicus fermented feed capable of replacing alga
InactiveCN103039727BAlleviate the pressure of overharvestingReasonable useAnimal feeding stuffSnow moldEcological environment
A preparation method of stichopus japonicus fermented feed capable of replacing alga is prepared by taking water caltrop, hydrilla varticillata, water hyacinth, aggregation of grass, alfalfa and common seepweed herb as the alga replacing raw material and additionally adding four, sea mud, multi-vitamin, fish meal, mussel powder, bean pulp, earthworm powder and zeolite powder with the steps of: drying all materials till the water content is less than 12%, and crushing to be 60 meshes, so as to obtain a fermentation substrate; mixing water, brown sugar, table salt and flour, adding rhizopus, trichoderma, saccharomyces cerevisiae, bacillus subtilis and lactic acid bacteria, mixing uniformly, standing and fermenting for 2h, so as to obtain a feed fermenting bacteria solution; and inoculating the fermentation substrate according to the ratio of 0.4% to 0.5% at the environment temperature of 25 DEG C to 30 DEG C, carrying out solid fermentation, and then drying and crushing, thereby obtaining the stichopus japonicus fermented feed. The preparation method has the advantages that the raw material source is stable, the cost is low, the process is simple and east to operate, and a great significance is provided in reducing culture cost of stichopus japonicas, maintaining an ecological environment, reasonably using idle resource and prompting the health sustainable development of stichopus japonicu culture industry.
Owner:JINZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Vibrio parahaemolyticus phage and application thereof in prevention of stichopus japonicus disease
ActiveCN110468110AAvoid infectionReduce abundanceAntibacterial agentsMicroorganism based processesAnaplasma phagocytophilumVibrio parahemolyticus
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to a phage isolate capable of specifically cracking Vibrio parahaemolyticus and application of the phage in the field of sea cucumber disease prevention, so that the economic benefit of sea cucumber breeding enterprises is improved, and food safety is guaranteed from the source. The vibrio parahaemolyticus phage vB_VpaP_VP-ABTNL-1 has a preservation number of CGMCC No.17991. The vibrio parahaemolyticus phage provided by the invention is applied to the prevention of the stichopus japonicus disease and can effectively prevent the infection of the vibrio parahaemolyticus in the breeding process.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
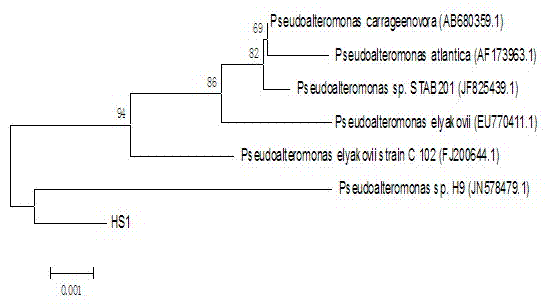
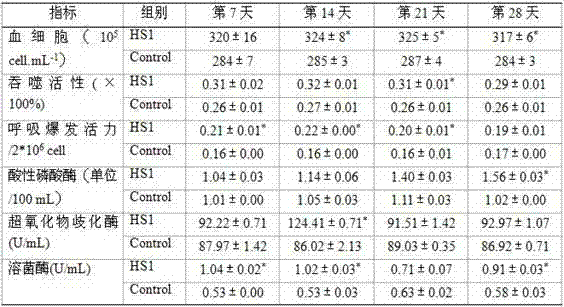
Apostichopus japonicus Pseudomonas elyacovii HS1 strain and its use
ActiveCN103289913ANo killing effectPlay the role of purifying water qualityBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffEcological environmentWater quality
Owner:DALIAN HAIBAO FISHERY
Culture method for mixed culture of Penaeus vannamei and sea cucumber
InactiveCN106165658AHelps growEfficient use ofClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaMixed cultureFeces
The invention provides a culture method for mixed culture of Penaeus vannamei and sea cucumber. The culture method mainly comprises the following steps: disinfecting a Penaeus vannamei pond, and adding nutrients, water and an attaching substrate; putting sea cucumber fingerlings; regulating and controlling the quality of the water; putting young Penaeus vannamei; monitoring the environment, and feeding feeds; and harvesting young Penaeus vannamei and sea cucumber fingerlings. The method has the advantage that mixed culture of a generation of Penaeus vannamei and sea cucumber is realized in a Penaeus vannamei culture pond through controlling the culture environment. The sea cucumber is fed on Penaeus vannamei feces and organic scraps in the Penaeus vannamei culture pond, so feeding cost is reduced; the quality of the water is purified; and the pollution of the water quality is avoided. The method provided by the invention has good operability, realizes an ecological culture mode of mixed culture of the Penaeus vannamei and sea cucumber, has significant culture effects and avoids the unused waste of the Penaeus vannamei pond.
Owner:青岛浩然海洋科技有限公司
Method for ecologically breeding stichopus japonica, siganus oramin and jellyfishes in pond of Yellow River delta area
InactiveCN105900880AImprove water qualityExpand the breeding areaClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaProtozoaJuvenile fish
The invention provides a method for ecologically breeding stichopus japonica, siganus oramin and jellyfishes in a pond of the Yellow River delta area and belongs to an aquaculture method. When water temperature reaches 16-18 DEG C in later April, 900-1100 siganus oramin young fishes are put into each mu of water in the stichopus japonica breeding pond, a net cage is defined by a filtering screen in the middle of the stichopus japonica breeding pond, and 30-50 jellyfish young fishes with the diameter being 1.5-2.2 cm are put into every cubic meter of water; after breeding is conducted to early November, water temperature of the pond is reduced to 14-16 DEG C, siganus oramin is harvested, and in the breeding process, the jellyfishes are harvested twice. By means of the ecological breeding method, stichopus japonica, siganus oramin and jellyfishes are bred in a mixed mode; the characteristic that siganus oramin and jellyfishes eat alga and protozoa in the stichopus japonica breeding pond is used, so alga and disease organisms of the stichopus japonica breeding pond of the Yellow River delta area are effectively inhibited; good quality of the stichopus japonica breeding pond is maintained, yield increase of stichopus japonica is achieved, and the environment problem caused by stichopus japonica breeding is alleviated..
Owner:SHANDONG YOUFA AQUATIC PROD CO LTD
Method used for inducing Apostichopus japonicus gonad development
InactiveCN105454108AEasy to operateImprove production efficiencyClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaAccessory gonadSeawater
The invention provides a method used for inducing Apostichopus japonicus gonad development. The method comprises that Apostichopus japonicus is arranged in seawater for breeding, seawater is heated to induce the Apostichopus japonicus to carry out gonad development, during the heating process, a linear function K=N(T-C) is employed to monitor the biological zero degree and the effective accumulated temperature of the Apostichopus japonicus, when the biological zero degree of the Apostichopus japonicus C=6.14+ / -0.82 DEG C, and the effective accumulated temperature of the Apostichopus japonicus K=800.19+ / -78.62 DEG C *d, the gonad of the Apostichopus japonicus is mature, N is the gonad development number of days, and T is the average water temperature of seawater during the breeding period. According to the invention, through a heating manner, the Apostichopus japonicus gonad development is induced, the biological zero degree and the effective accumulated temperature are monitored to accurately indicate that the gonad of the Apostichopus japonicus is mature, a full year breeding mode can be achieved, operating level and productivity effect of manual large-scale breeding are improved.
Owner:中国水产科学研究院营口增殖实验站 +1
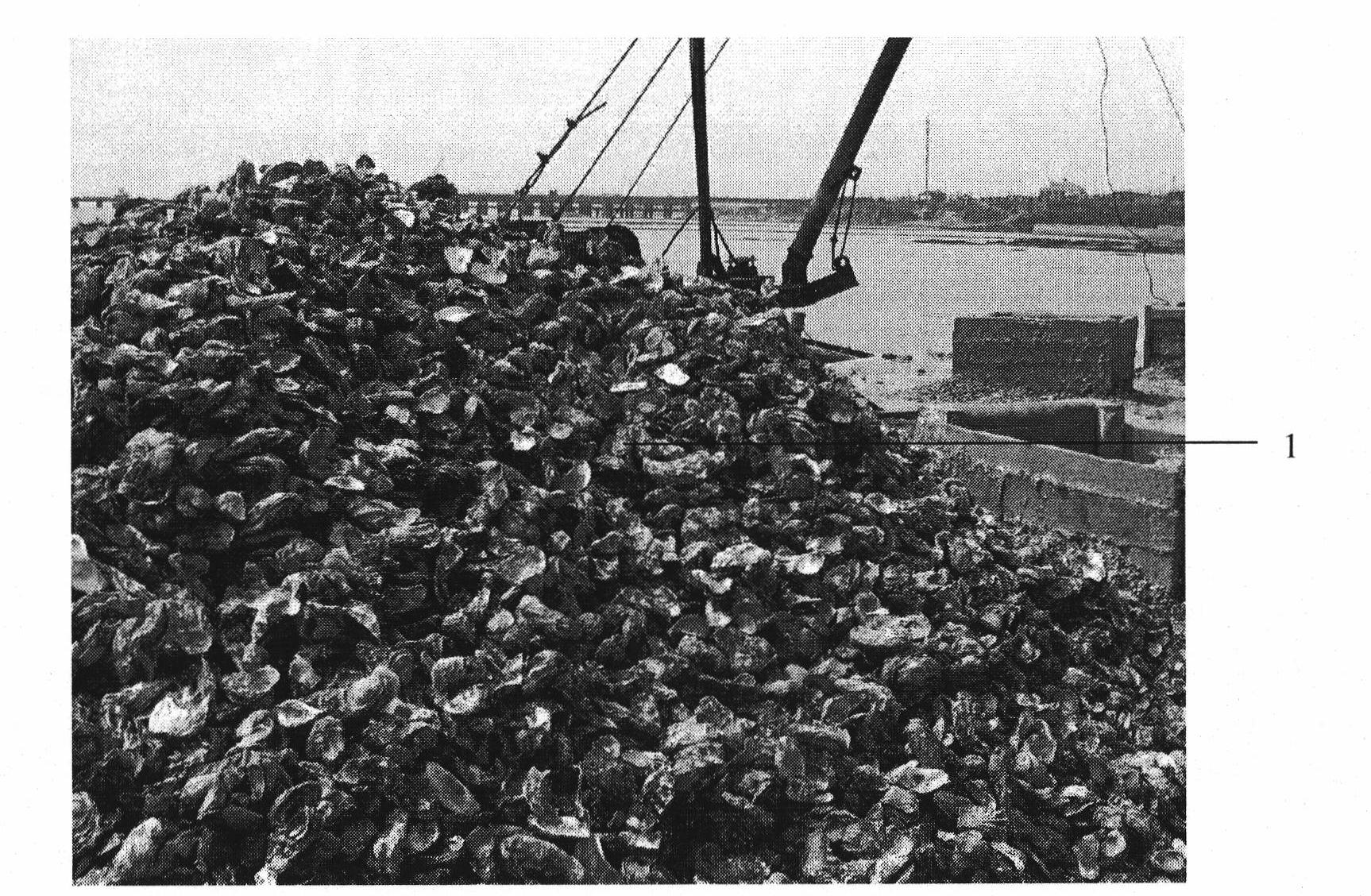
Stichopus japonicus aquaculture sea reef taking oyster shell as material and aquaculture method thereof
ActiveCN101627734BAdequate shelterSuitable for growthClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaMud oysterOyster shells
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
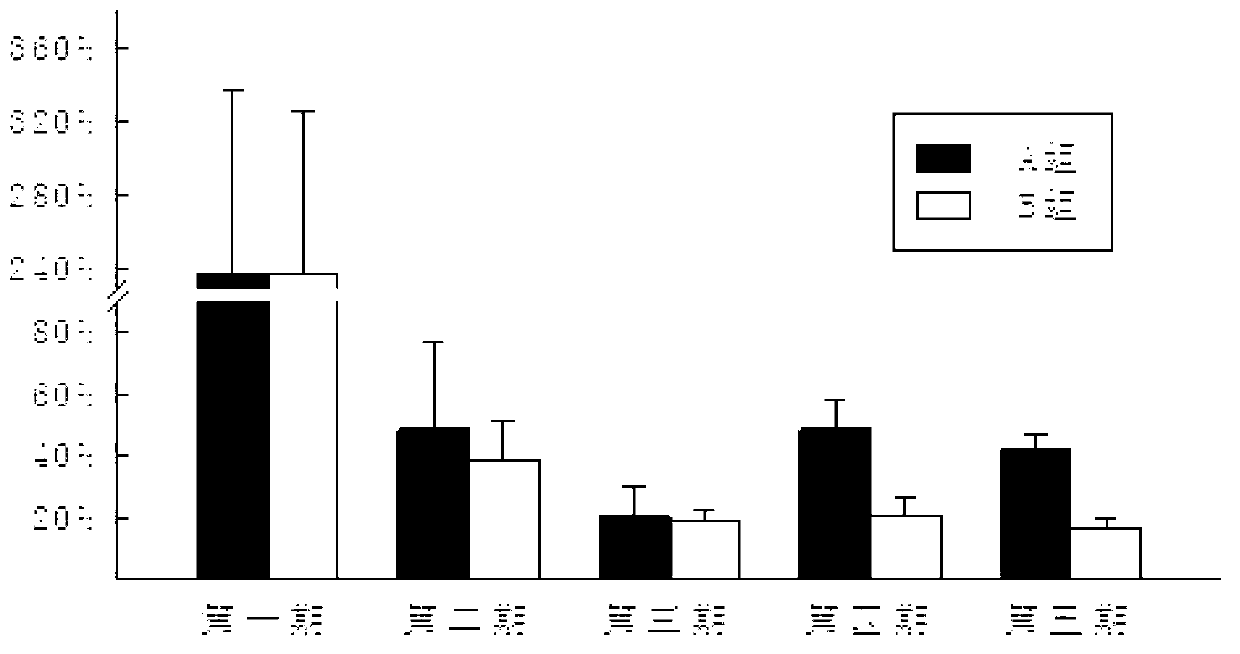
Method for research on influence of temperature on embryonic development and growth of sea cucumber
The invention relates to a method for research on influence of a temperature on embryonic development and growth of sea cucumber. The method comprises the following steps: allowing sea cucumber parents with maturely-developed gonad to release sperms and ova through heating stimulation, then after 4 h, carrying out sampling and observing, and selecting fertilized ova with a fertilization rate larger than 99% and a diameter larger than 160 [mu]m for an experiment; before the experiment begins, incubating the fertilized ova in water at 22.5 DEG C for 6 to 7 h so as to obtain blastocysts in an early period; respectively placing the blastocysts into prepared seawater with temperature gradients, a salinity of 31 and a pH value of 7.8 to 8.2, wherein the temperature gradients are arranged as follows: 5, 10, 12, 15, 19, 21, 25, 28, 31 and 34 DEG C; carrying out indoor natural lighting by day and no lighting at night; allowing the culturing density of each group to be 0.5 ind / ml, and replacing half of water once every two days, wherein air is not inflated, and oceanic red yeast is used as a bait when embryos are developed to larvae; and sampling 15 to 30 larvae every two days, and carrying out observation and measurement. The method provided by the invention is reasonable in design, has ingenious temperature gradient arrangement, and can conveniently and effectively determine the influence of temperature change on embryonic development and growth of the sea cucumber.
Owner:QINGDAO QINGQUAN BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for cultivating Pseudobagrus fulvidraco in rice field
InactiveCN103392930BIncrease productionImprove qualityAnimal feeding stuffSemenPhotosynthetic bacteria
The invention relates to a method for cultivating Pseudobagrus fulvidraco in a rice field, particularly a stichopus japonicus fertilizer which comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 2-4 parts of Bacillus subtilis powder, 1-4 parts of ferment bacteria, 0.5-0.9 part of solid photosynthetic bacteria, 0.8-1.2 parts of bdellovibrio bacteriovorus, 0.2-0.6 part of vitamin additive, 10-16 parts of mineral additive, 0.2-0.4 part of chelator, 60-80 parts of hyacinth, 50-80 parts of edible fungus residue, 100-110 parts of vinasse, 40-60 parts of fishbone dust, 70-80 parts of rice bran, 10-16 parts of brown sugar, 45-55 parts of kongpo monkshood root, 40-50 parts of semen momordicae, 1-15 parts of Stellera chamaejasme and the like. A comparison shows that the composite microbial fertilizer can promote quick growth of stichopus japonicus, increase the EPA content, reduce the fish diseases and the amount of fish dying of illness, and increase the beneficial microbes in the water body, thereby enhancing the final quality and grade.
Owner:SUZHOU YANGCHENGHU MODERN AGRI INDPARK SPECIAL AQUACULTURE
Chinese herbal medicine feed additive for promoting growth of seedling of Apostichopus japonicus
InactiveCN101433268BChange color quicklyFast stretchClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffSide effectSurvival ratio
Owner:DALIAN FISHERIES UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com