Preparation method of stichopus japonicus fermented feed capable of replacing alga
A technology for fermenting feed and sea cucumber, applied in the direction of animal feed, animal feed, application, etc., can solve many problems, achieve the effect of slowing down the process of eutrophication, reducing the excretion of feces, and improving the efficiency of digestion and absorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
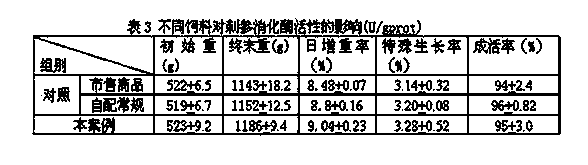
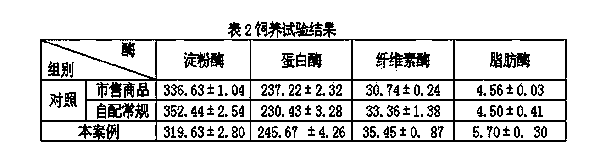
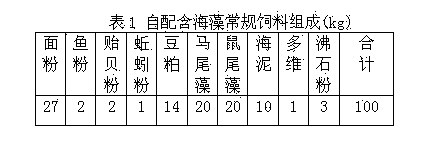
[0019] Describe above-mentioned invention process (by 100kg feed preparation) below in conjunction with embodiment.
[0020] 1. Selection and activation of fermentation strains
[0021] According to the nutritional composition of the fermentation base material and the tropism and complementarity of different strains, the fermentation strains consist of Rhizopus, Trichoderma, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Bacillus subtilis, and lactic acid bacteria, which were purchased from China General Microorganism Culture Collection Center (Beijing) , after amplification, the density of each strain was 1×10 9 ~2×10 11 CFU / g.
[0022] Preparation of fermented bacteria liquid: Boil 1000g of clean fresh water, cool down to 30°C, put into a clean container, add 40g of brown sugar, 10g of salt, 40g of flour, and then add Rhizopus, Trichoderma, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Bacillus subtilis, and lactic acid bacteria. 0.1 g was mixed evenly, left to ferment for 2 hours, and the bacterial liquid f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com