Method for extracting zirconium and hafnium from hydrochloric acid medium
An extraction and hydrochloric acid technology, applied in the field of purification, can solve the problems of large solvent loss, environmental pollution, poor operating workshop environment, etc., and achieve the effects of clean separation process, simple process flow and large extraction capacity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] A method for separating zirconium and hafnium, the specific steps are as follows:
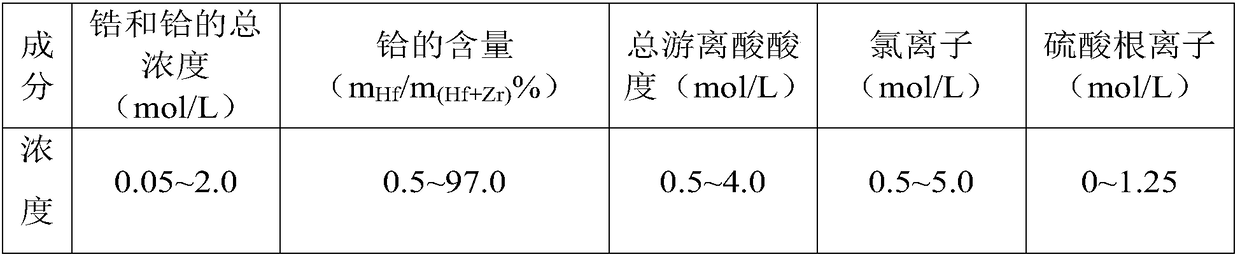
[0054] (1) Preparation of acidic feed solution: the water phase is composed of an initial total concentration of zirconium and hafnium ions of 1.5mol / L, wherein the concentration of hafnium ions is about 0.018mol / L, and the acidity of the water phase is 1.7mol / L, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 The concentration is 0.8mol / L.
[0055] (2) extractant adopts the mixed organic phase that the DIBK of 90% (v / v) and the Cyanex923 of 10% (v / v) form, earlier the hydrochloric acid of extractant and equal volume 3.5mol / L is carried out pre-extraction once, then The extraction agent after the pre-extraction is used as the organic phase, the acid feed liquid is used as the water phase, and the control ratio (organic phase: water phase) is 2: 1, and the feed liquid is carried out to single-stage extraction at room temperature, and the mixing time of the two phases is 10 Minutes, after phase separation, the zirconiu...
Embodiment 2
[0078] The organic phase is composed of 90% (v / v) of DIBK, 2% (v / v) of Cyanex921 and 8% (v / v) of sulfonated kerosene (as a diluent), and pre-mixed with an equal volume of 3.4mol / L Hydrochloric acid pre-extracted once, the aqueous phase composition is the initial total concentration of zirconium and hafnium ions 1.5mol / L, wherein the concentration of hafnium ions is 0.018mol / L, and the acidity of the aqueous phase is 1.7mol / L, (NH4 ) 2 SO 4 The addition amount is 0.8mol / L, the control ratio is 2:1, single-stage extraction is carried out at room temperature, the two-phase mixing time is 5 minutes, and the raffinate and the loaded organic phase containing hafnium are obtained after phase separation. Re-precipitate with ammonia water to obtain zirconium hydroxide precipitate; carry out back-extraction with 1.0mol / L potassium carbonate on the loaded organic phase, the ratio of washing and back-extraction is 1:2, and the mixing time of the two phases is 5 minutes to obtain zirconium...
Embodiment 3
[0081] The organic phase is composed of 90% (v / v) of DIBK, 8% (v / v) of Cyanex923 and 2% (v / v) of isooctane (as a diluent), and pre-filled with an equal volume of 4.0mol / L Hydrochloric acid pre-extracted once, the aqueous phase composition is the initial total concentration of zirconium and hafnium ions 1.0mol / L, wherein the concentration of hafnium ions is 0.012mol / L, and the acidity of the aqueous phase is 2.0mol / L, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 The addition amount is 0.8mol / L, the control ratio is 2:1, single-stage extraction is carried out at room temperature, the two-phase mixing time is 5 minutes, and the raffinate and the loaded organic phase containing hafnium are obtained after phase separation. Re-precipitation with ammonia water to obtain precipitation of zirconium hydroxide with less hafnium; back-extract the loaded organic phase with 1.0mol / L sodium carbonate, the ratio of washing and back-extraction is 1:2, and the mixing time of the two phases is 5 minutes. A zirconium-contai...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Bronsted acidity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flash point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flash point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com